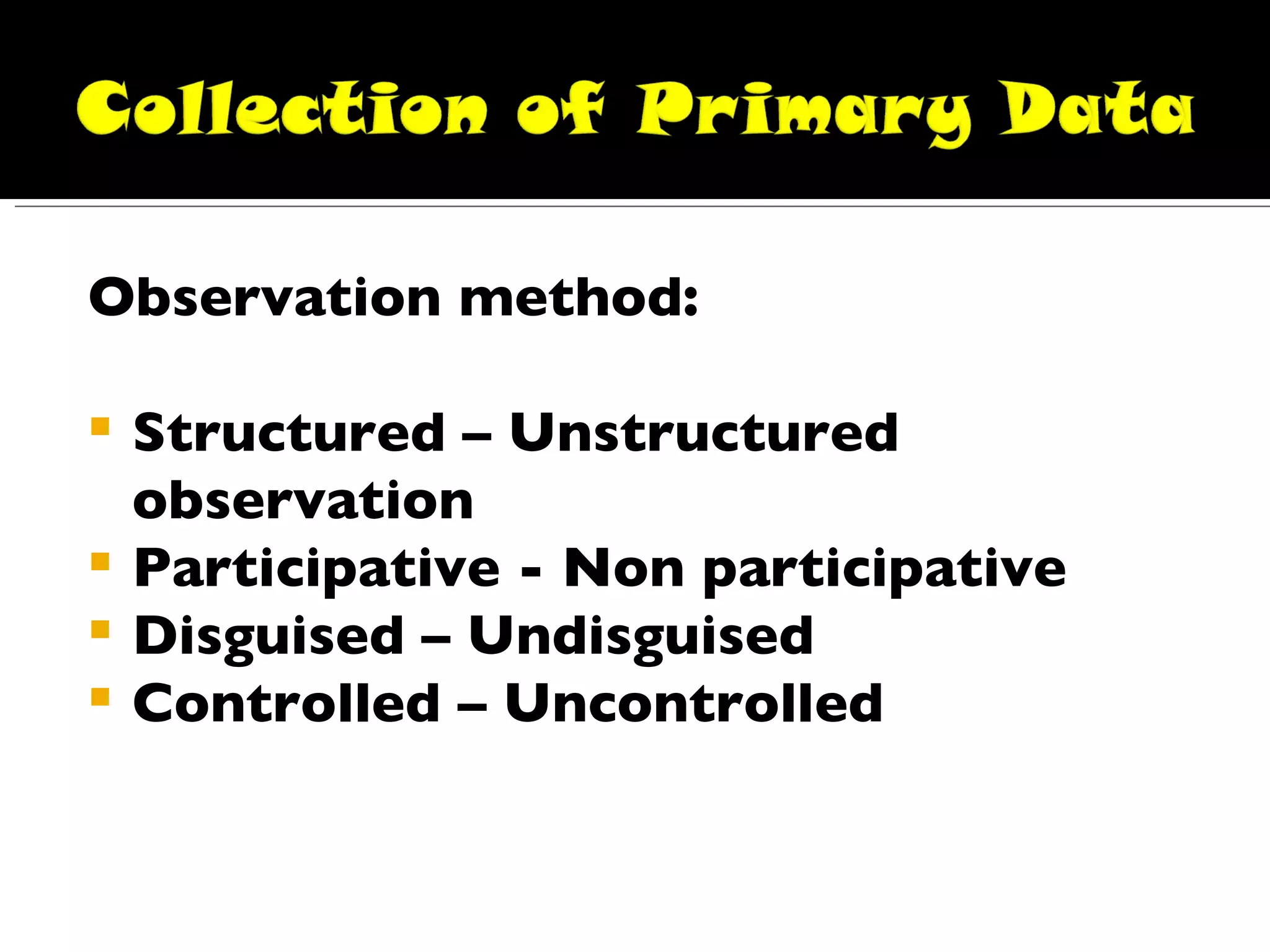
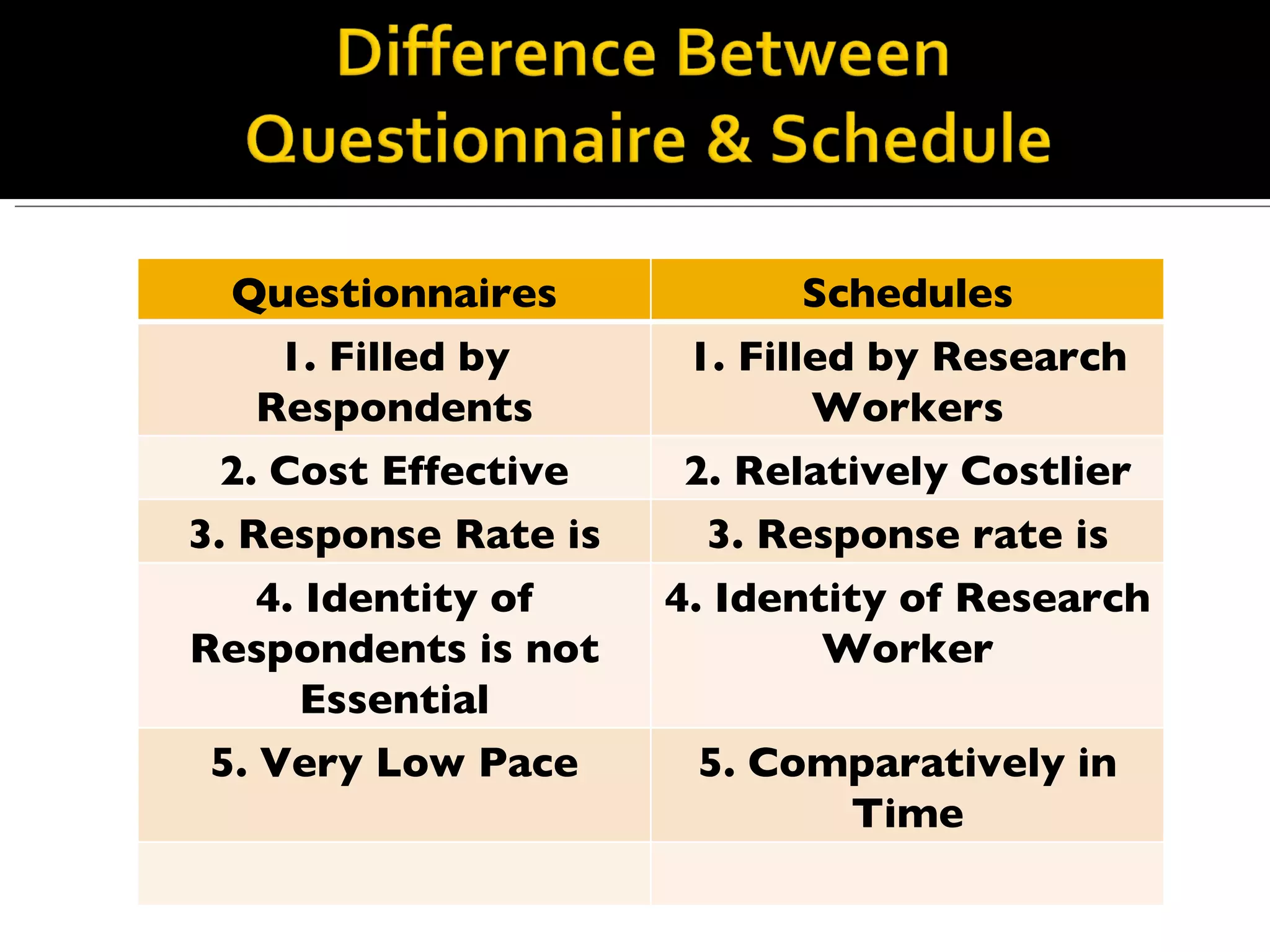
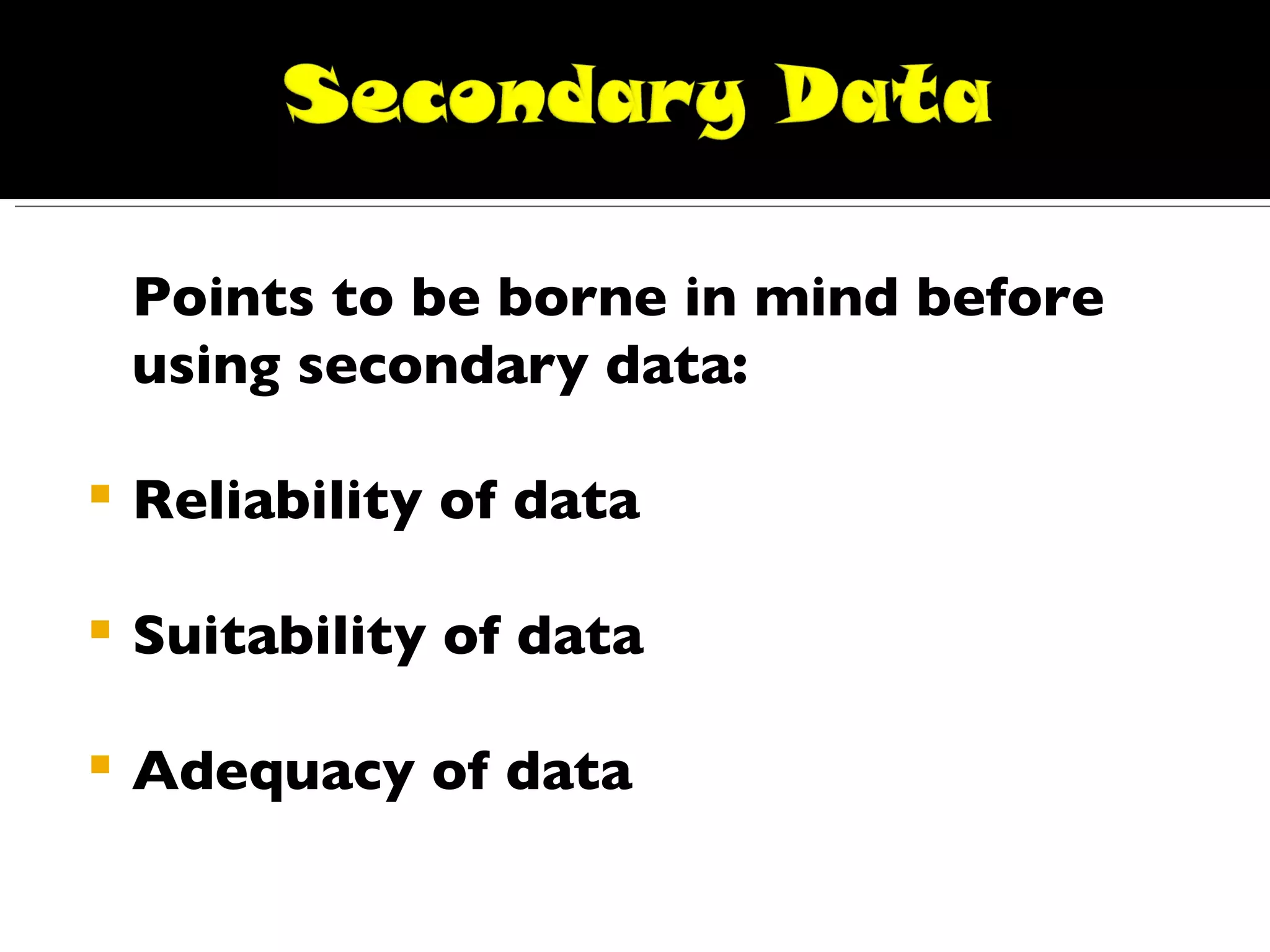
The document discusses different types of data and research methods used to collect data. It summarizes that there are two main types of data: primary data collected directly by researchers, and secondary data that has already been collected. It then outlines various methods for collecting primary data, including observation, interviews, and questionnaires. Some key advantages and disadvantages of questionnaires and schedules are provided. Lastly, it notes some important considerations for using secondary data.