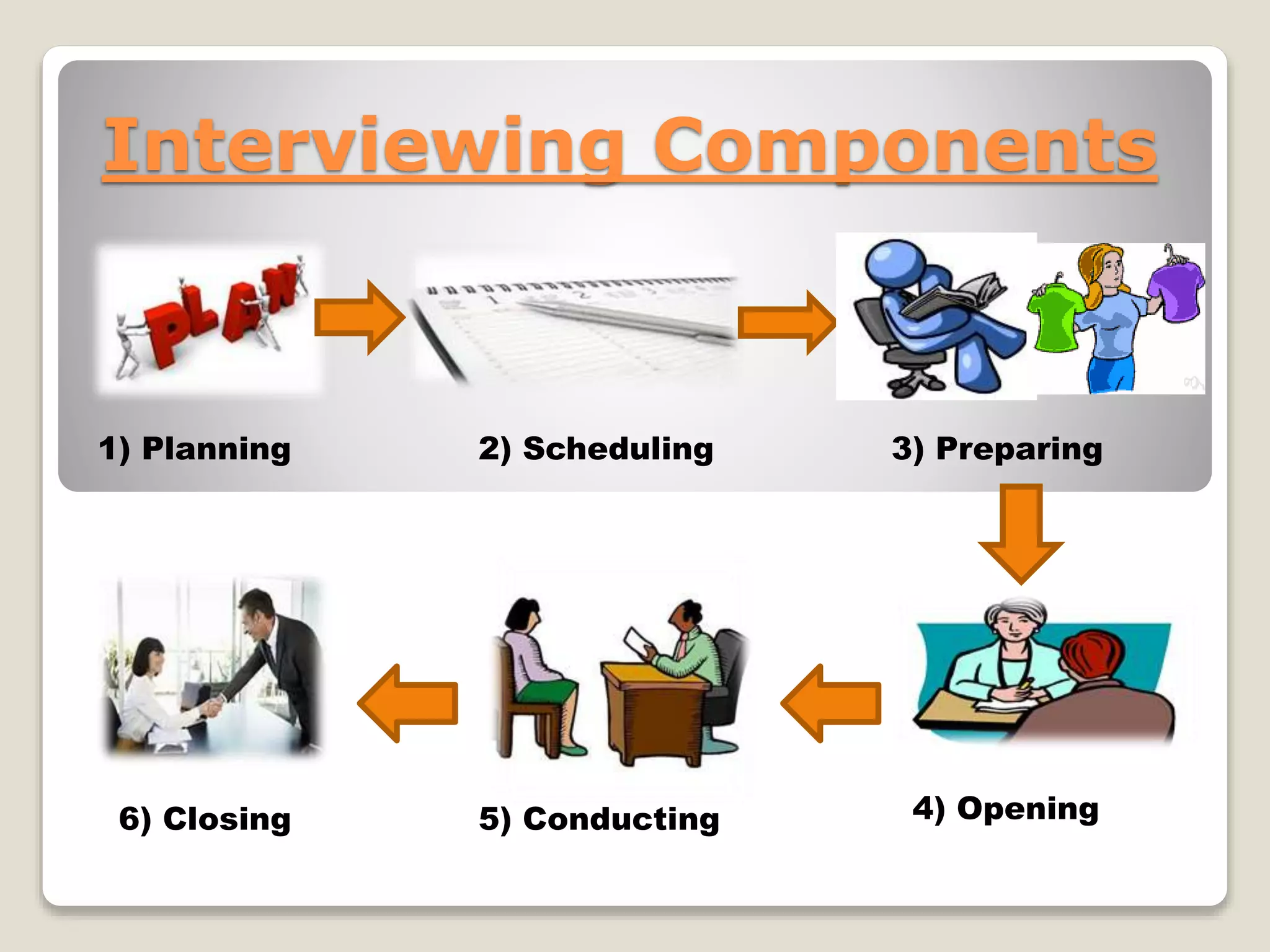
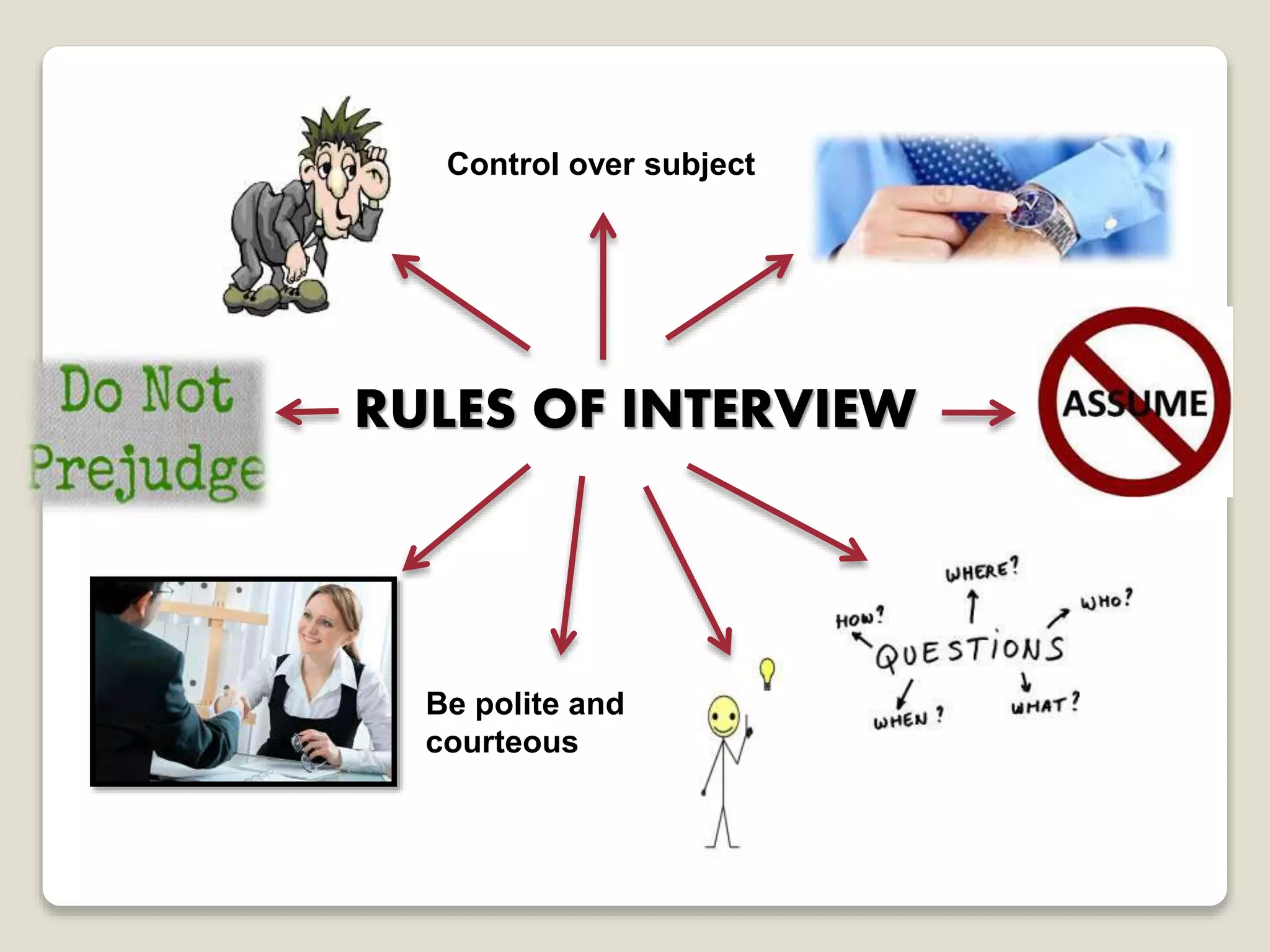
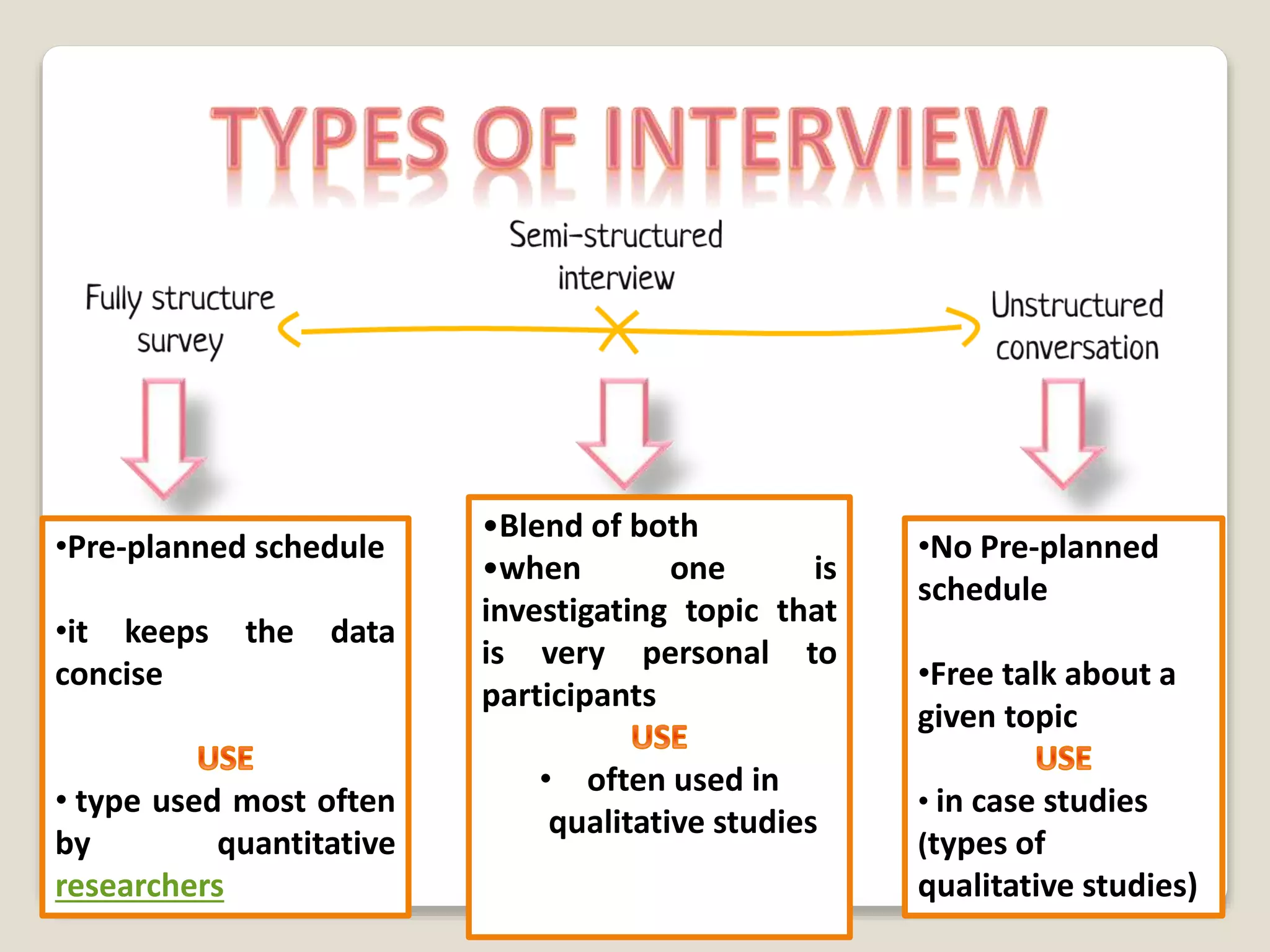
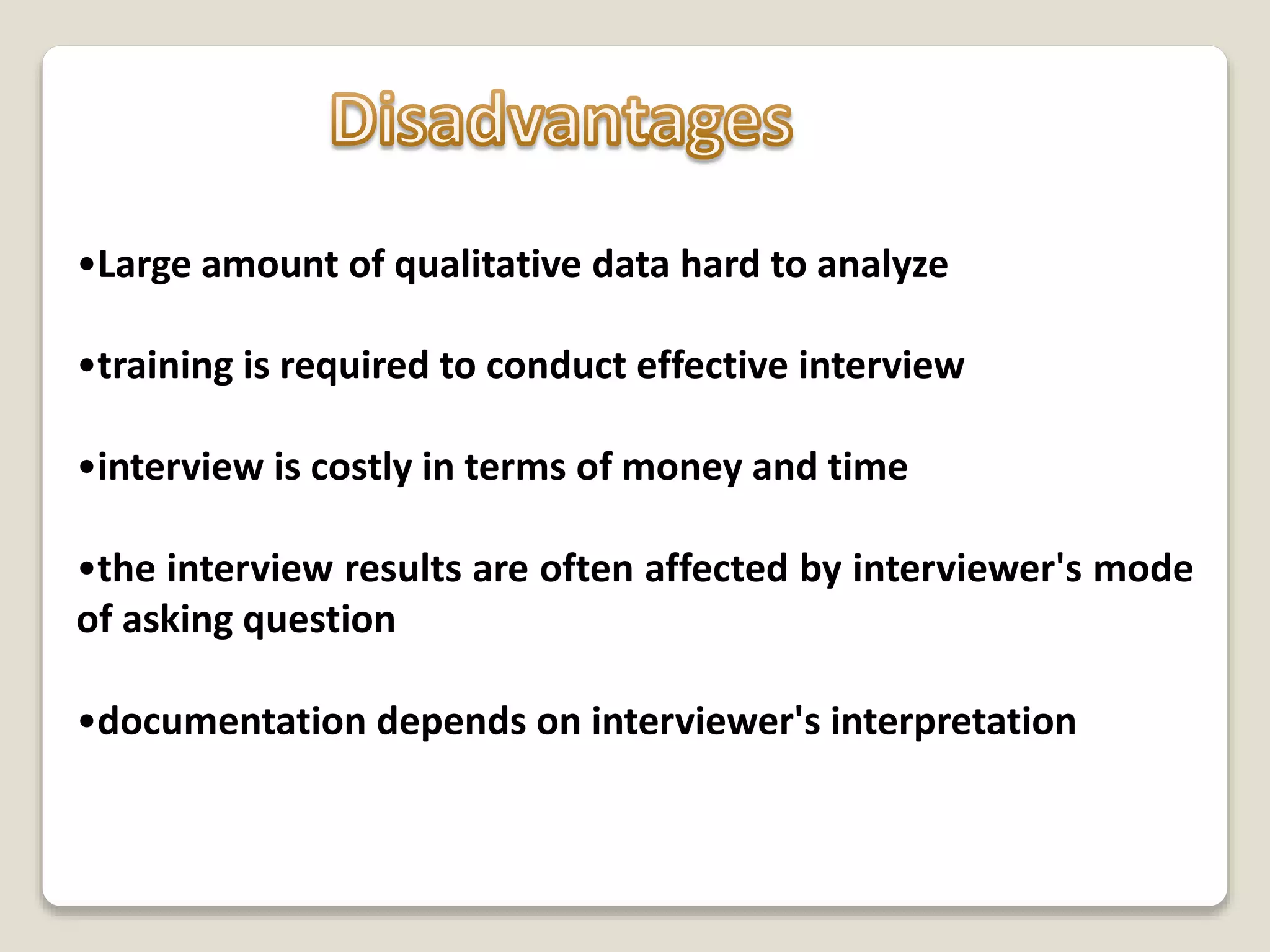
The document discusses the 'one on one interview' technique for requirement elicitation, emphasizing its definition, purpose, components, and the skills necessary for effective information gathering. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of interviews, including their ability to gather qualitative data and the potential challenges of cost and time. Additionally, it highlights the importance of planning and executing interviews with care to gather accurate and useful information.