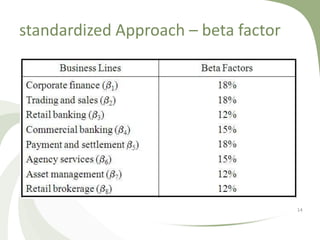
This document discusses operational risk management. It defines operational risk as losses from failed internal processes, people, or systems or external events. It identifies types of operational risks such as people risk, process risk, technology risk, and external risks. It also lists common causes of operational risk like fraud, workplace safety issues, and system failures. Finally, it outlines three approaches used in banking to measure and hold capital reserves for operational risk: the Basic Indicator Approach, Standardized Approach, and Advanced Measurement Approach.