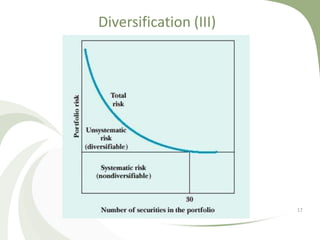
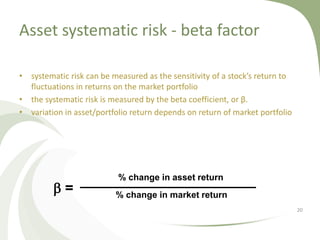
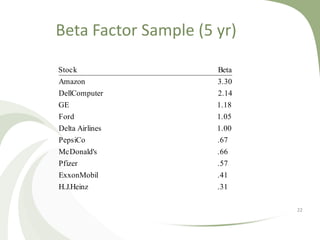
The document discusses financial risk management. It defines three main sources of financial risk: market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk. It then provides details on specific types of market risk, including equity price risk, interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, and commodity price risk. It also discusses how diversification across different asset classes can help reduce overall portfolio risk through lowering specific risk, though not systematic risk. The beta factor is introduced as a measure of an asset's systematic risk relative to the overall market.










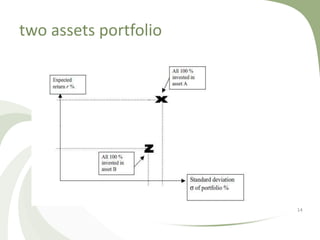
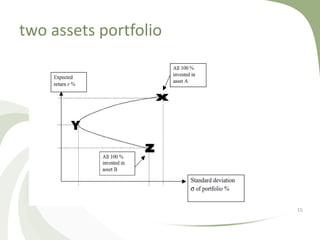
![diversification (I)
• diversification means reducing risk by investing in a variety of
assets
• it means: don't put all your eggs in one basket
• diversified portfolio will have less risk than the weighted
average risk of its elements
• often less risk than the least risky of its parts
• crucial element is selection of assets with low correlation
• correlaton values:[-1,1]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rm-07-v1-120403001018-phpapp01/85/Rm-07-v1-13-320.jpg)