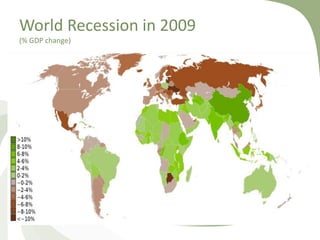
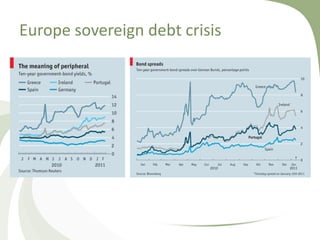
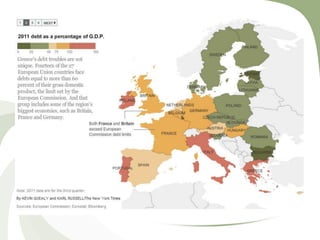
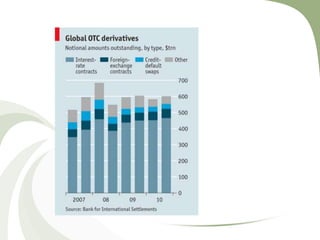
This document discusses the major financial crises of the 20th and early 21st centuries, including the Great Depression, various stock market crashes, the Asian Financial Crisis, and the Global Financial Crisis of 2007-2009. It outlines the phases of the recent crisis, from the bursting of the US housing bubble to the recession and sovereign debt crisis. Key events of 2008 that exacerbated the crisis are described, such as the collapse of Lehman Brothers and bailouts of major financial institutions. The roots of the crisis are analyzed from a risk management perspective, including deregulation, low interest rates, unregulated derivatives, and incentives for short-term gains.