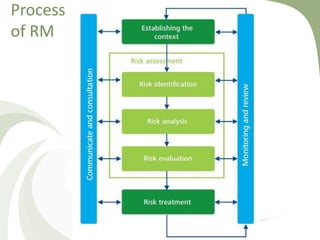
This document discusses risk management and risk treatment. It defines risk treatment as selecting and implementing responses to risks in line with an organization's risk approach and appetite. Common risk treatment methods include risk avoidance, reduction through internal controls, sharing through insurance, diversification, hedging and outsourcing, and acceptance. Risk reduction can lower the likelihood and severity of risks through activities like internal controls. Risk sharing transfers parts of risk through methods such as insurance, diversification of assets/activities, and hedging. The document also provides examples of a risk register and risk reporting.