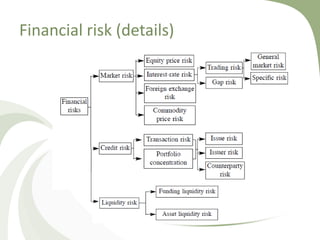
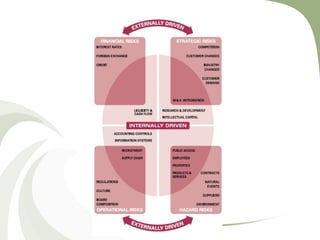
This document discusses risk management. It defines risk as the probability of a negative event and the potential consequences. It distinguishes between risk, which can be quantified with probabilities, and uncertainty, which cannot be quantified. The main categories of risk are strategic, financial, and operational. Financial risk includes market, credit, liquidity, and other risks. The document traces the history of risk concepts from ancient times through modern developments in probability theory and risk management as a discipline.