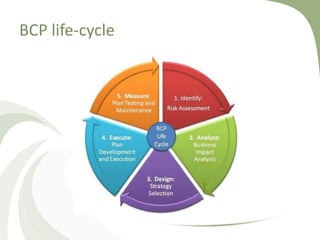
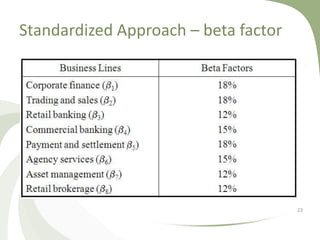
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events. It is categorized into people, processes, systems/technology, and external risks. Key risk indicators are metrics used to monitor identified operational risks over time and provide early warnings. Banks use three approaches to operational risk management - the basic indicator approach, standardized approach, and advanced measurement approach - which require banks to hold capital reserves proportional to their operational risk exposure based on business lines and historical loss data.