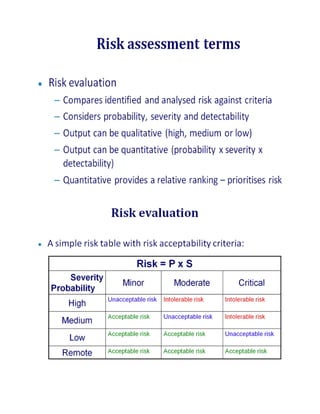
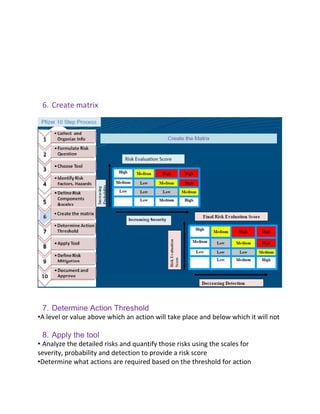
This document outlines a risk-based approach for classifying deficiencies found during inspections. Deficiencies are described as instances of non-compliance and are classified based on whether they result from a defective system or a failure to comply with the system. Deficiencies can be critical, major, or minor/other observations. Critical observations pose a significant risk of patient harm, while major observations indicate major deviations from good practices. The document also describes Pfizer's 10-step process for conducting a quality risk management assessment, which includes identifying risks, defining risk components and scales, applying a risk analysis tool, defining risk mitigation measures, and documenting the assessment.