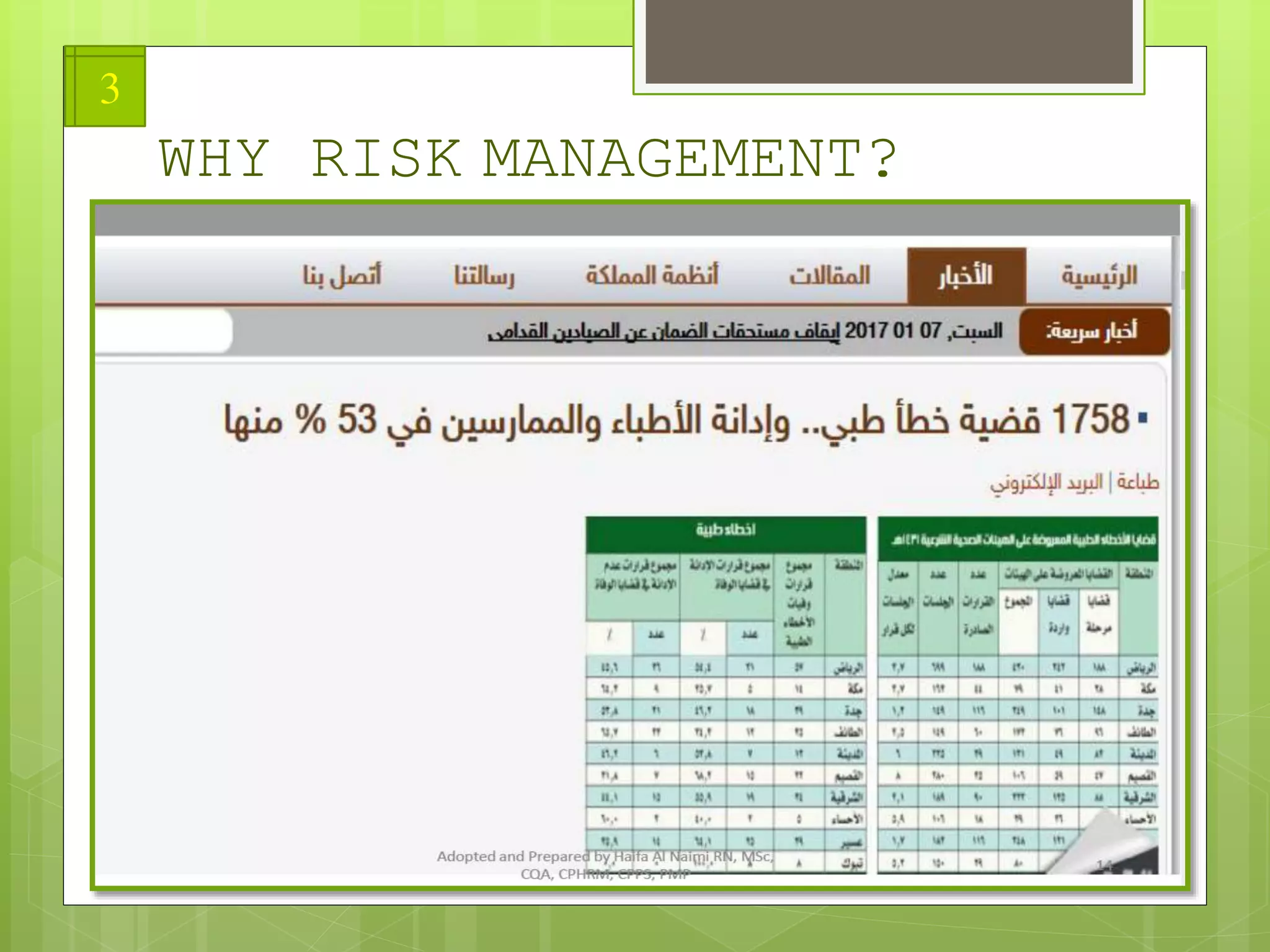
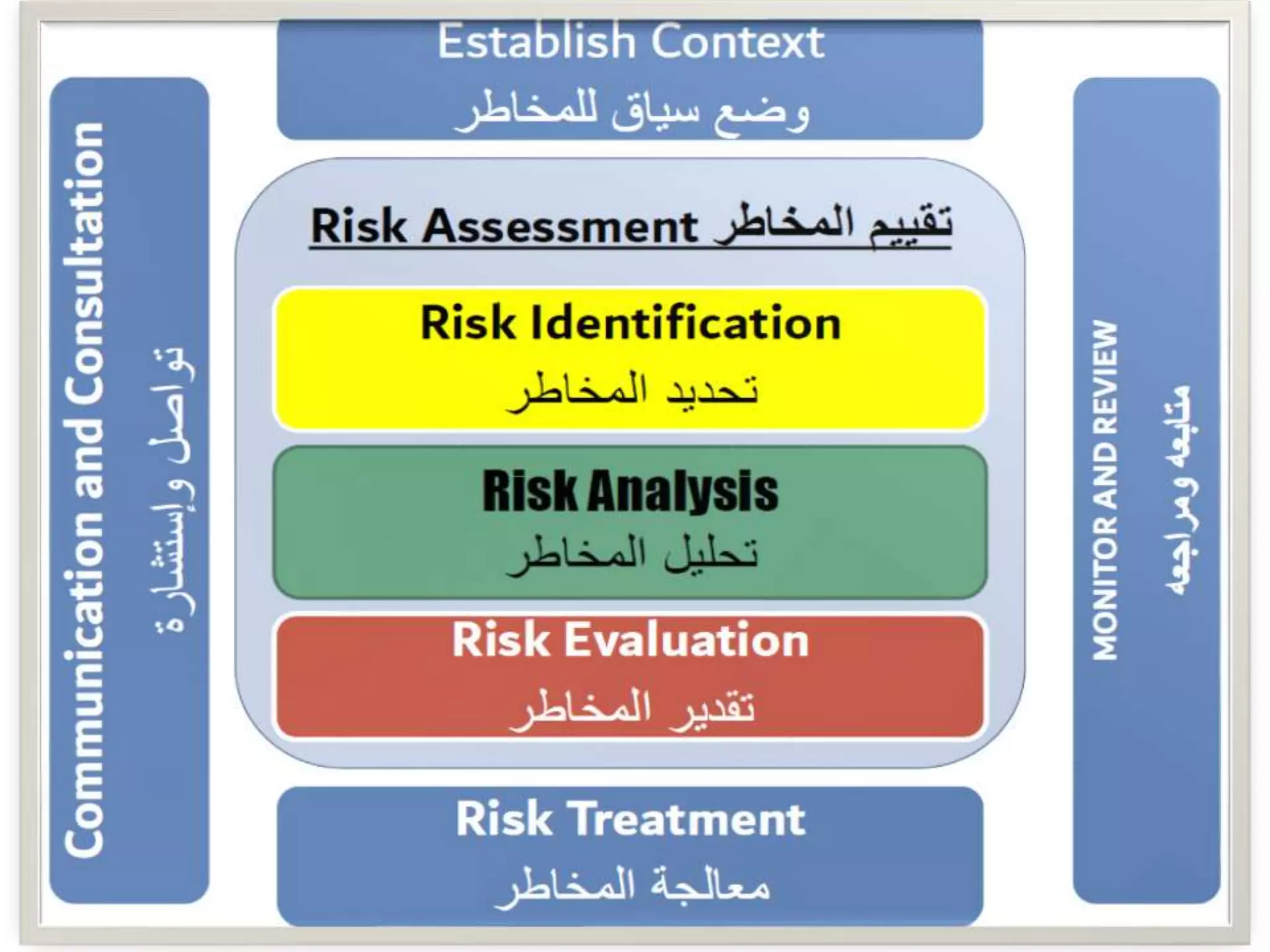
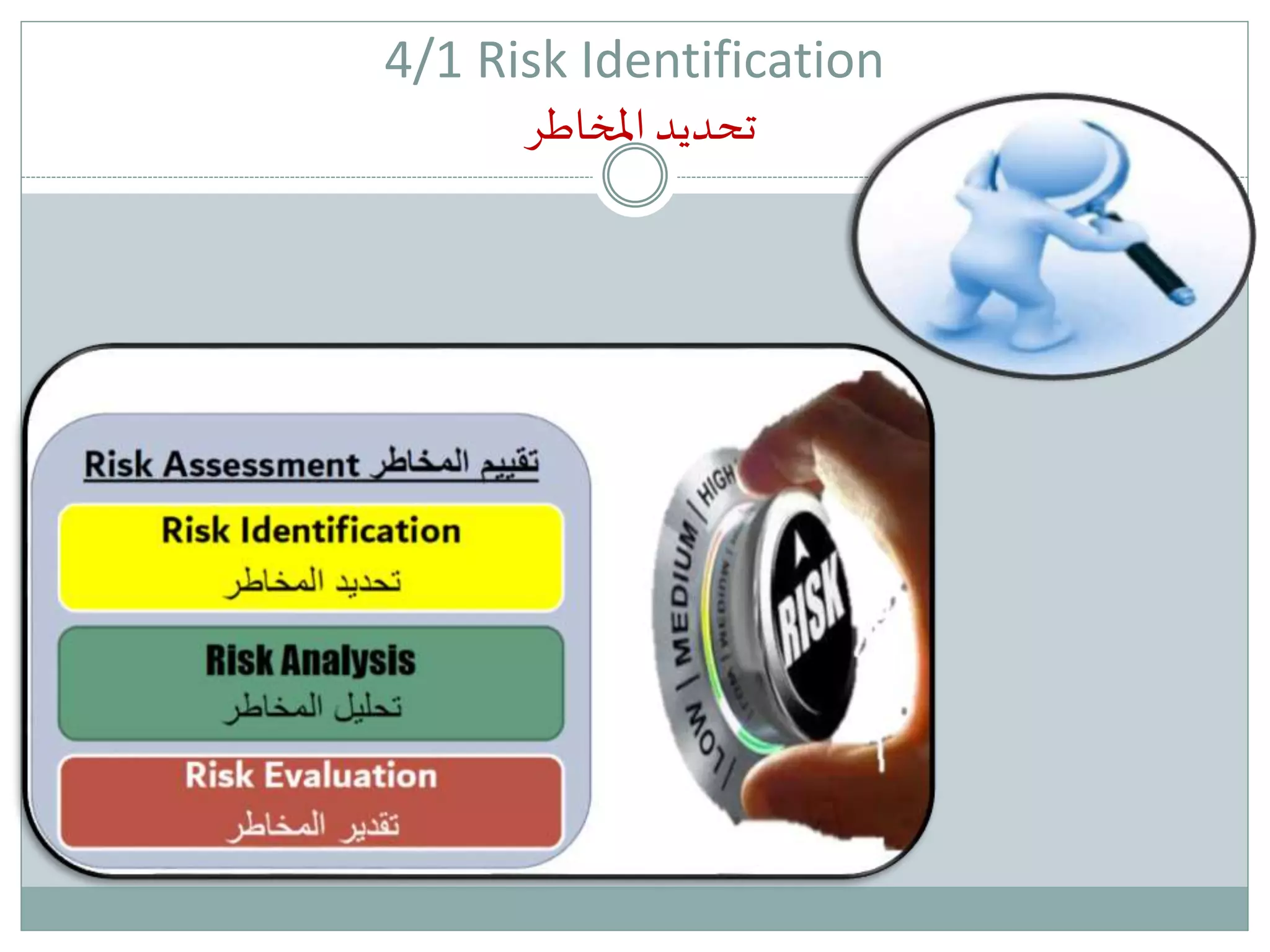
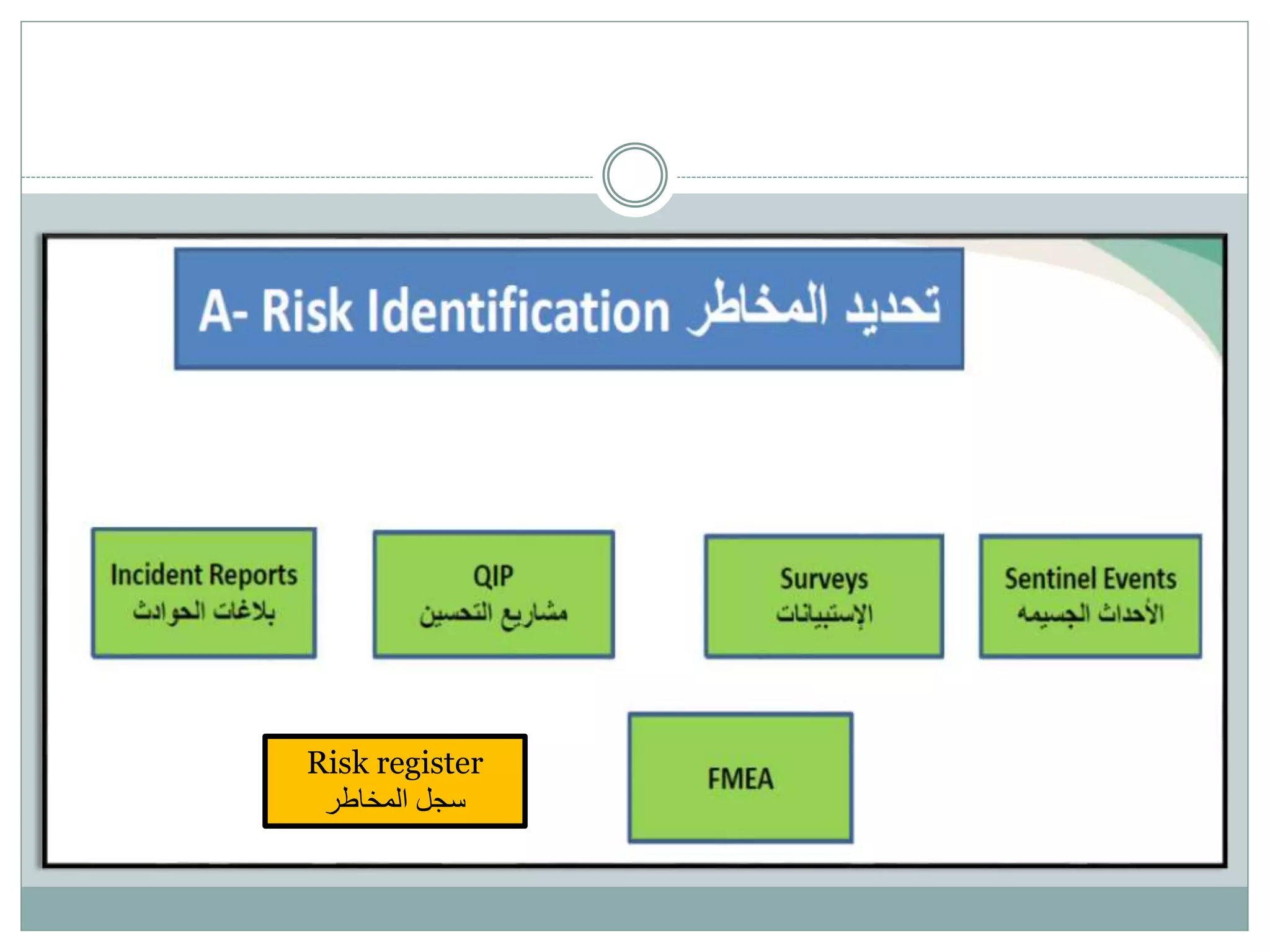
The document provides an overview of risk management in healthcare, defining risk and outlining its importance for patient safety and organizational integrity. It categorizes risks into several types, including operational, financial, human capital, strategic, legal, technology, and environmental hazards, and discusses expected outcomes for effective risk management. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for systematic identification and management of risks while adapting to changes in healthcare demographics and regulatory environments.