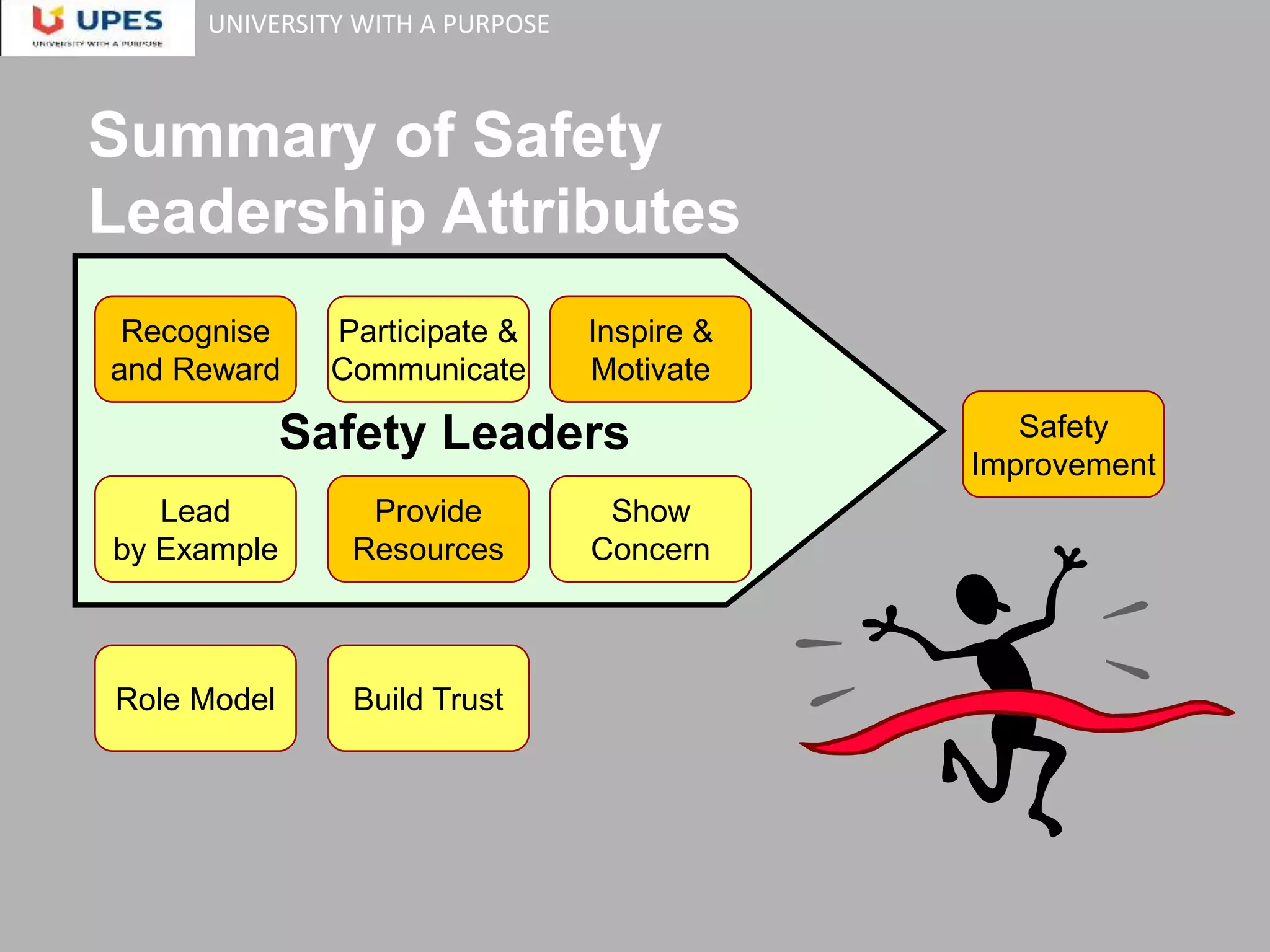
This document discusses leadership and safety culture. It begins by outlining the objectives of exploring concepts of leadership and how they can be applied to workplace health and safety. It then discusses what leadership is not, such as power, status, authority, or management. True leadership shapes culture and influences performance outcomes. As a safety leader, visible commitment and leadership in the field are keys to achieving safety success. The document provides tools for safety leaders, including understanding behavior using the ABC model, influencing others positively through RAS questions, and leading effective toolbox talks. It emphasizes that safety leaders must lead by example, recognize workers, and inspire others to behave safely.