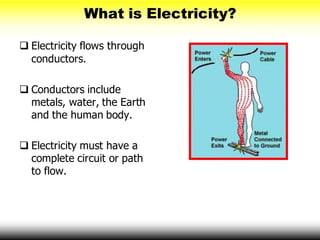
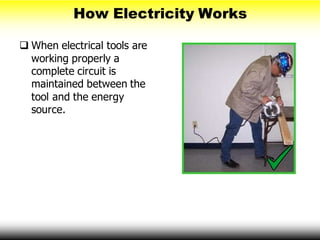
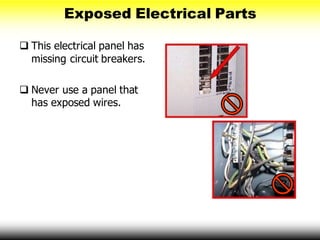
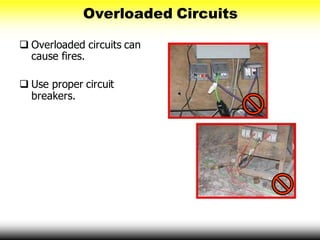
This document provides information on electrical hazards, which are one of the biggest hazards on construction sites. It discusses common electrical hazards such as improper grounding, exposed electrical parts, inadequate wiring, overloaded circuits, damaged tools and equipment, wet conditions, and overhead power lines. It emphasizes the importance of accident prevention methods like using personal protective equipment, inspecting tools and cords, ground fault circuit interrupters, and lock-out/tag-out procedures. The document aims to help workers recognize electrical hazards and prevent electrical accidents and injuries.