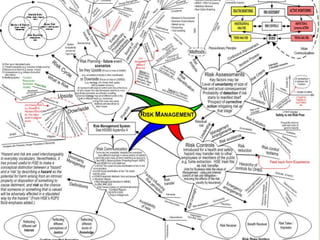
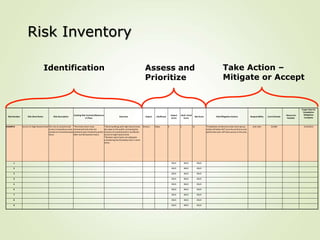
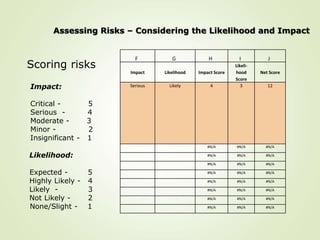
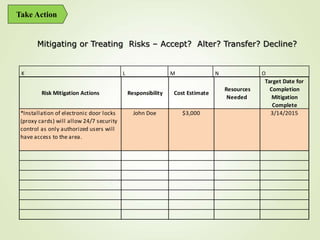
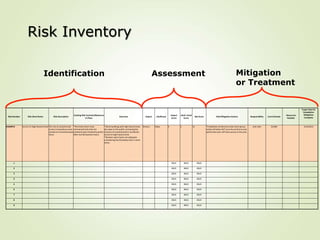
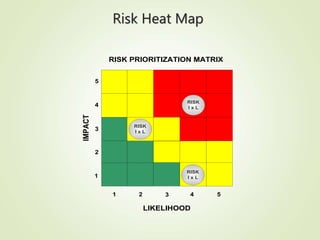
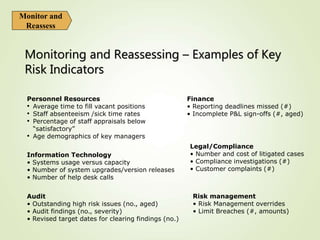
This document provides an overview of Part One of a three-part training program on strategic risk management. It discusses key concepts in risk management including identifying risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, prioritizing risks, and developing mitigation strategies. A risk inventory template is also presented to catalog identified risks. Participants are encouraged to consider how they would implement strategic risk management in their own work areas to improve decision-making and better achieve organizational objectives.