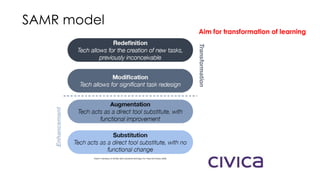
This document provides ideas for using technology in the classroom to enhance learning. It introduces the SAMR model for integrating technology, which includes substitution, augmentation, modification, and redefinition of learning tasks. Examples are given for using audio, audiovisual tools, e-readers, digital storytelling, Twitter, and game-based learning. Teachers are encouraged to test new technology ideas against learning models, aim for transformation of learning, and get support or feedback before implementing activities.