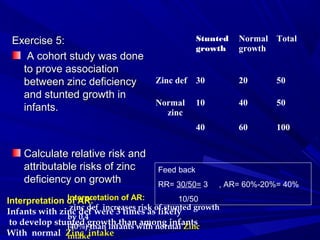
The document discusses risk assessment and various measures used to quantify risk such as relative risk, attributable risk, odds ratio, prevalence rate, and incidence rate. It provides examples of how to calculate these measures from cohort and case-control study data and interpret the results. Key points are that relative risk is used for cohort and experimental studies, odds ratio for case-control studies, and prevalence and incidence rates help measure disease burden. Attributable risk helps identify excess risk from an exposure. The examples help illustrate how to apply these concepts to public health practice.