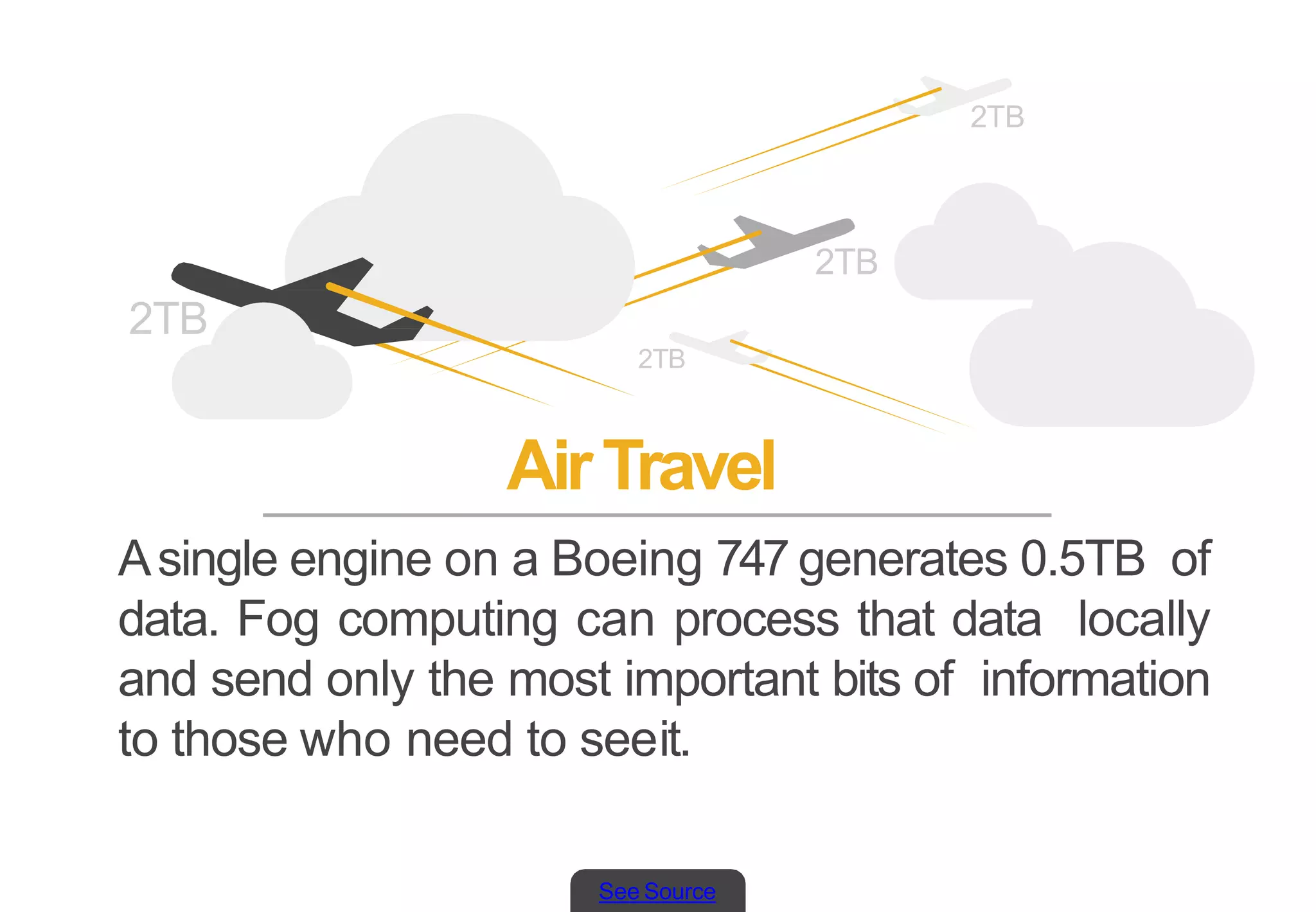
Fog computing emerges as a viable alternative to traditional cloud computing by processing data at the edge of the network, which leads to faster response times and lower bandwidth demands. This model is particularly beneficial in the context of the Internet of Things (IoT), where the expected surge in connected devices will require significant data handling capabilities. Notable applications of fog computing include smart city infrastructure and wearable technology, both of which benefit from local data processing.