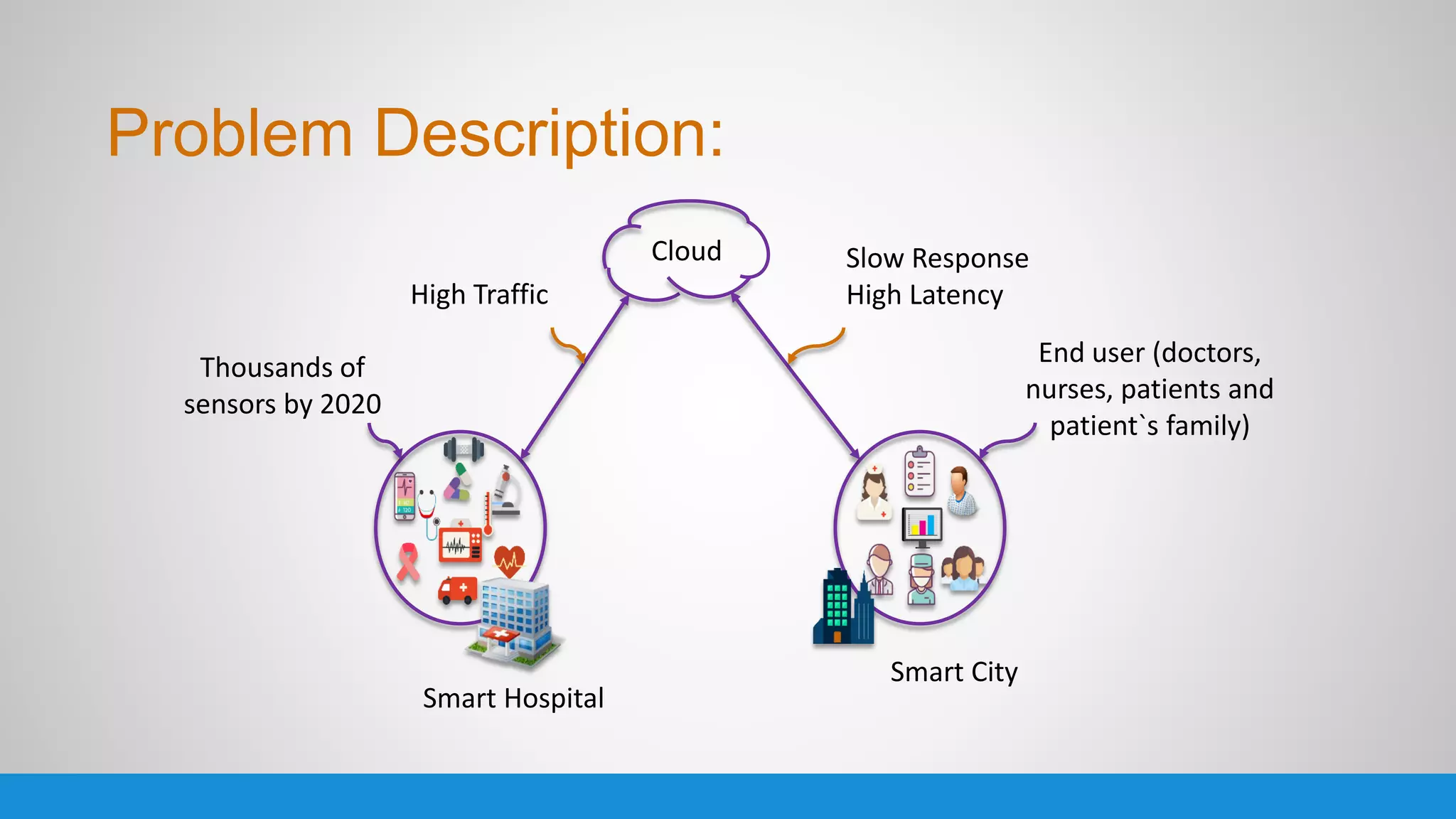
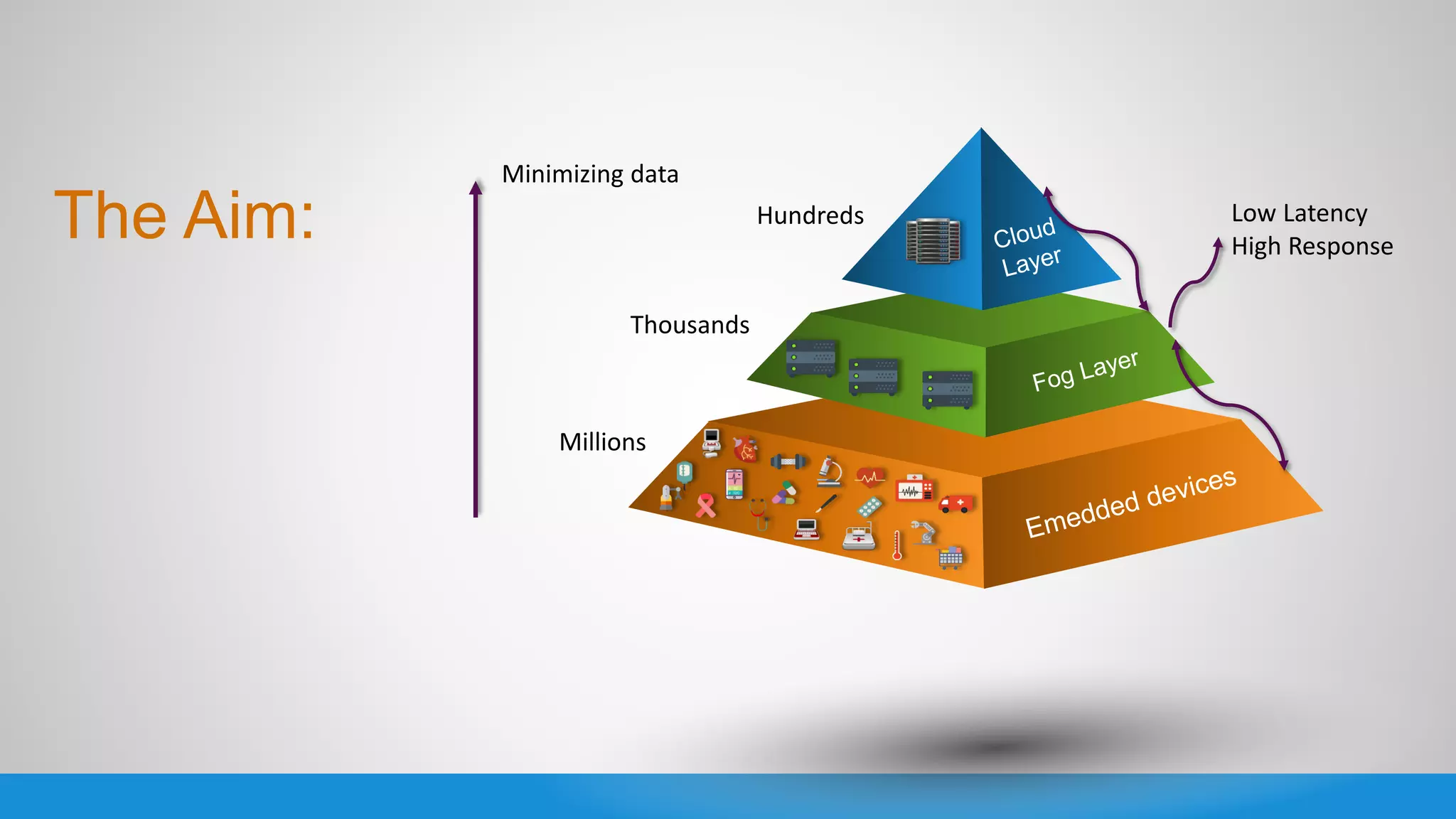
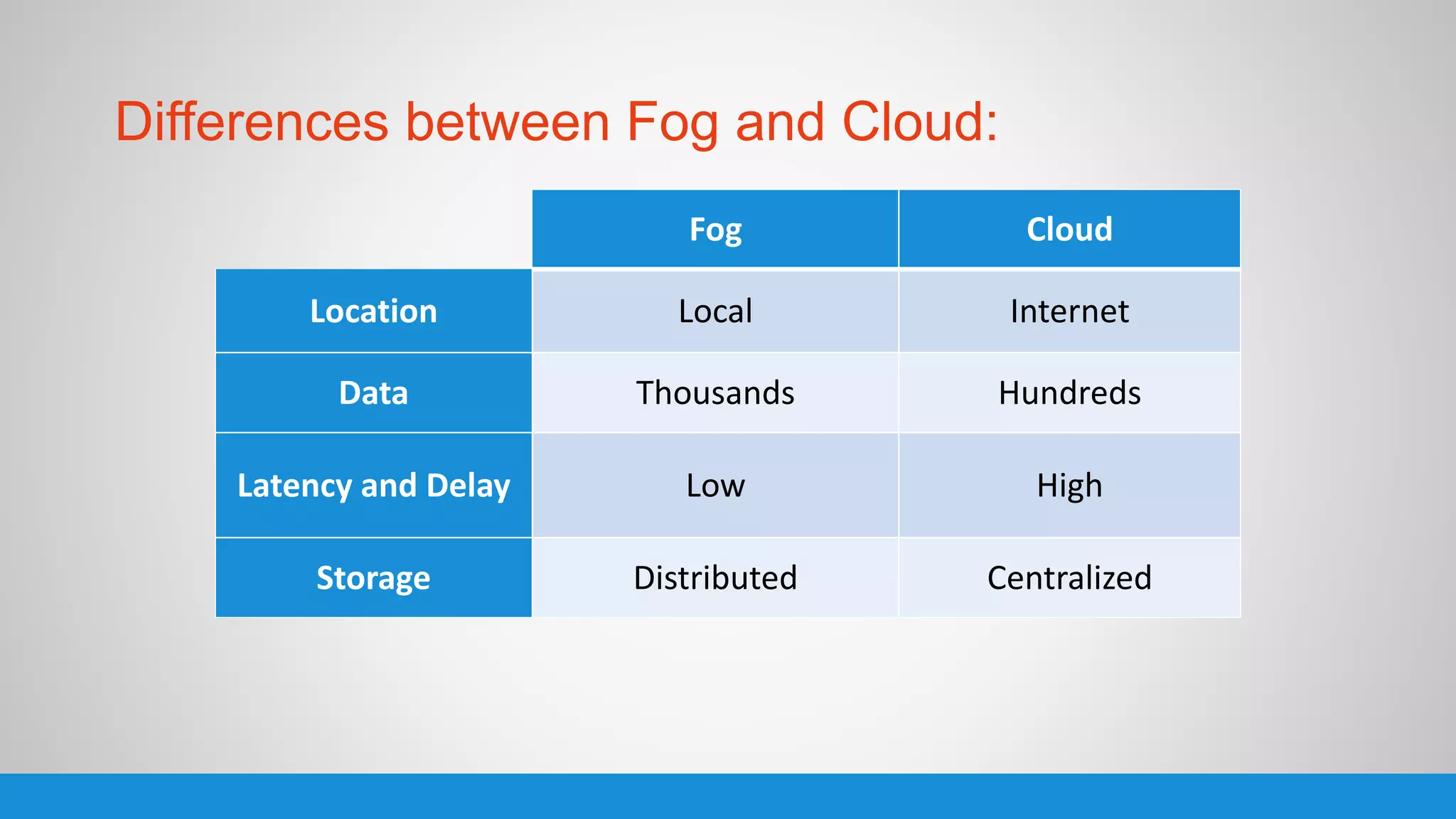
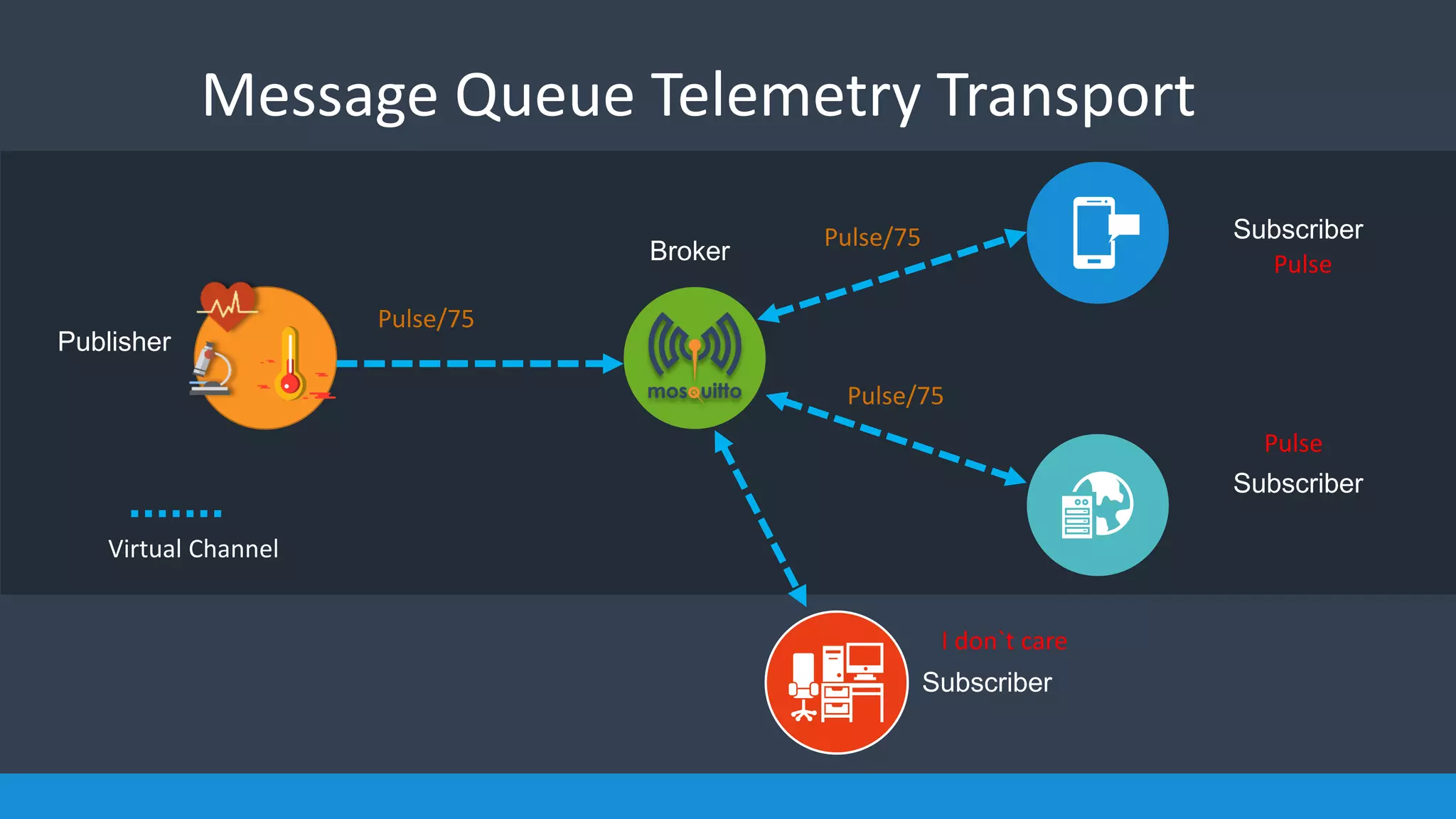
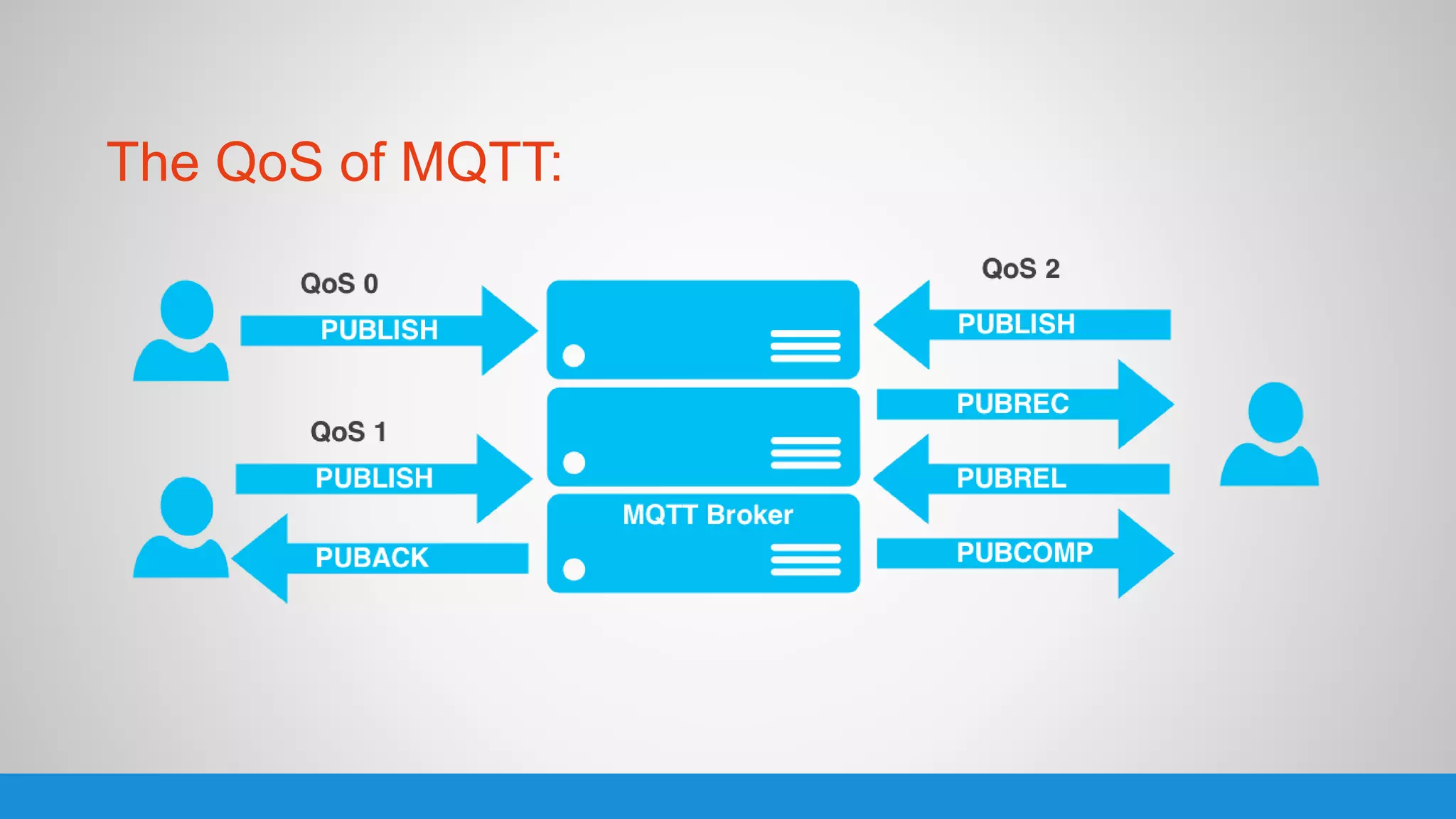
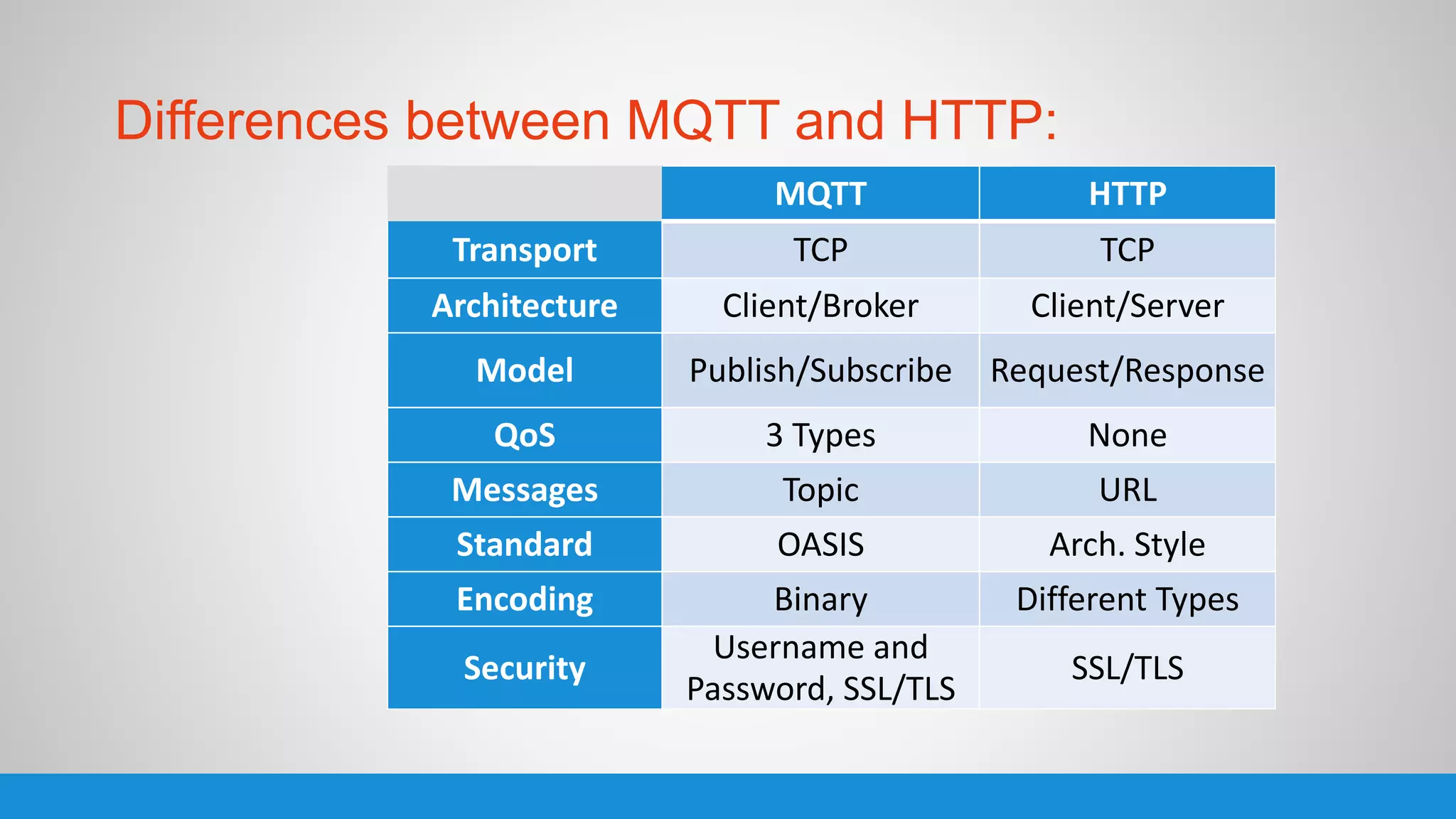
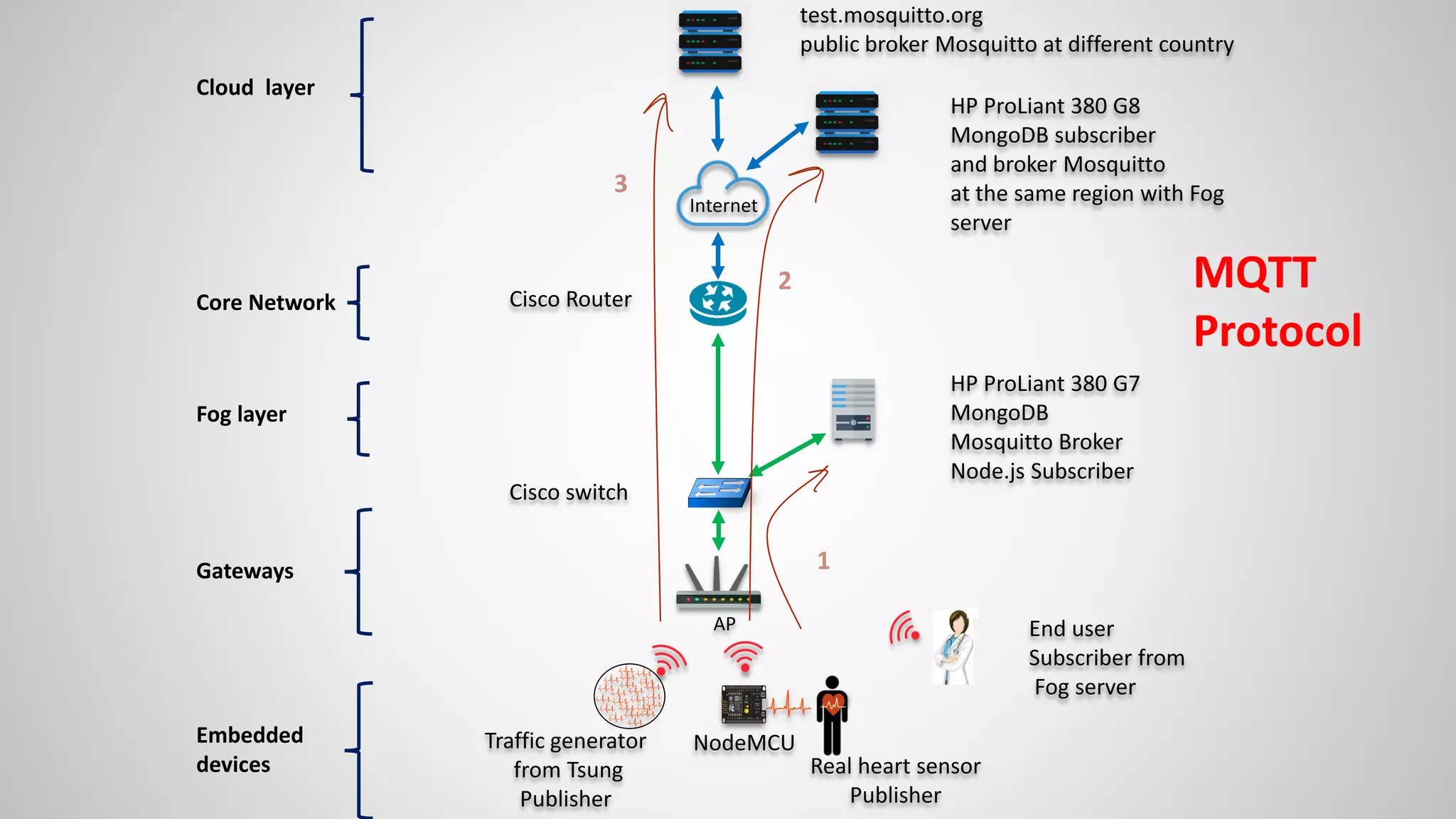
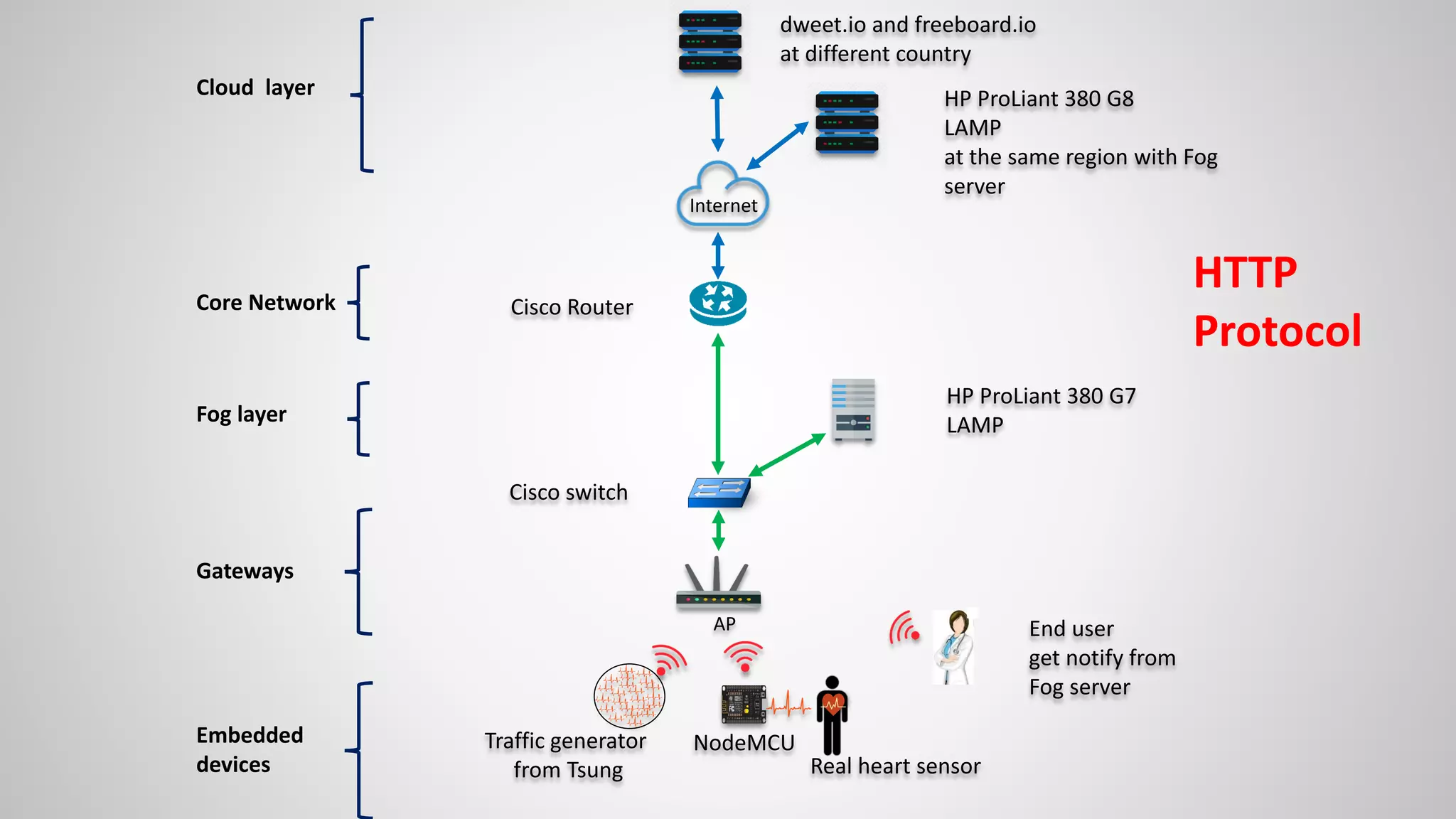
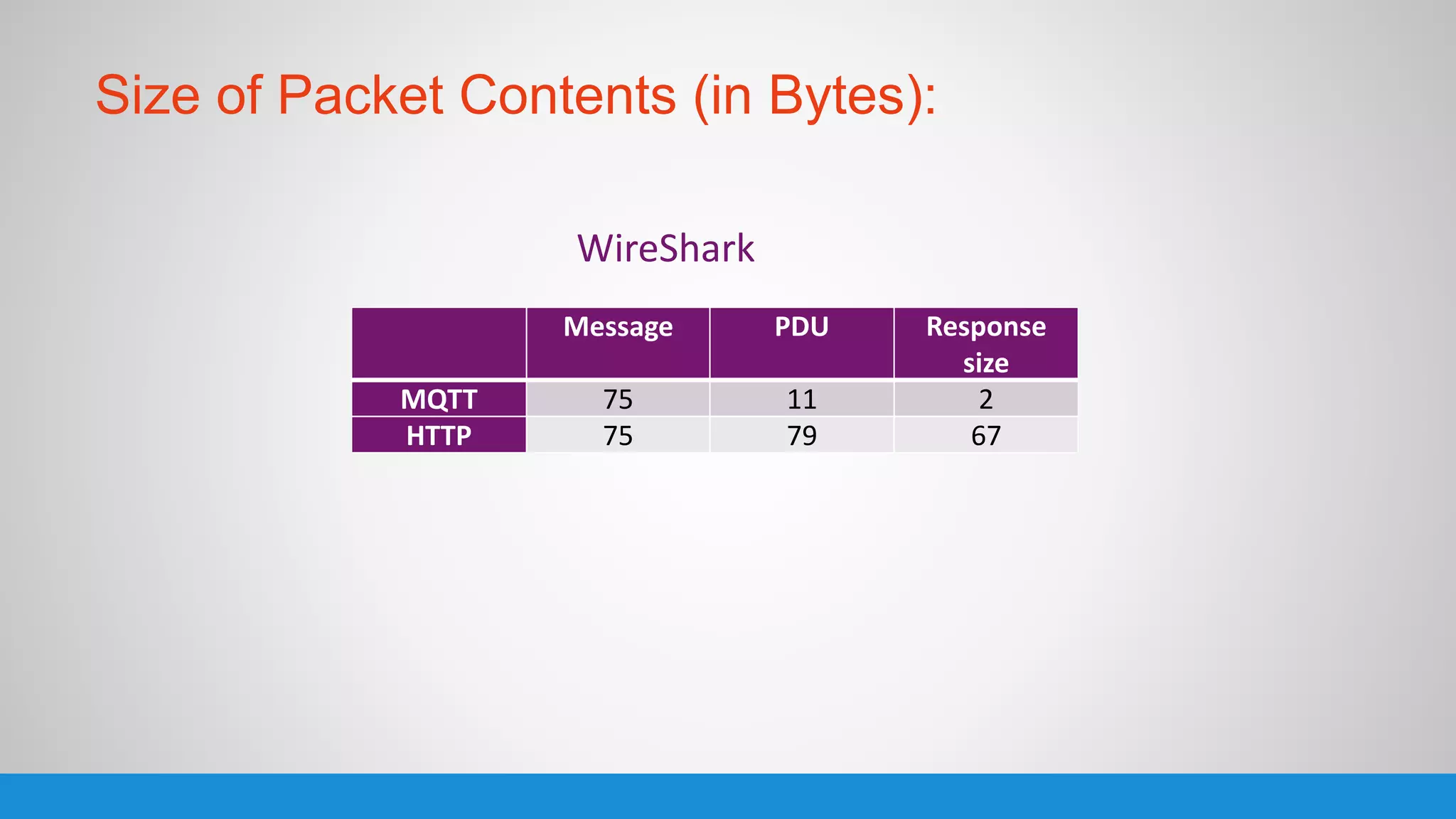
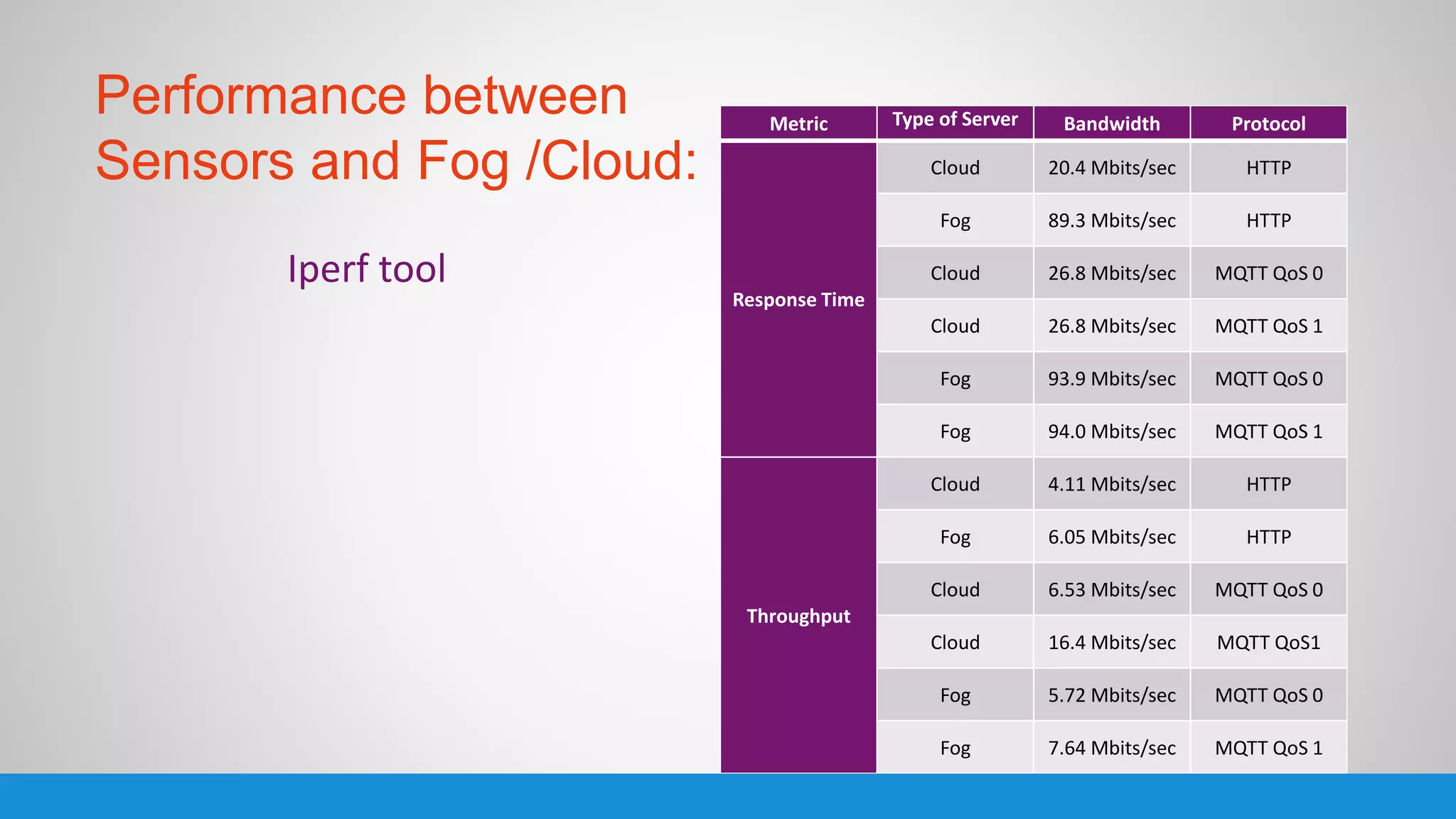
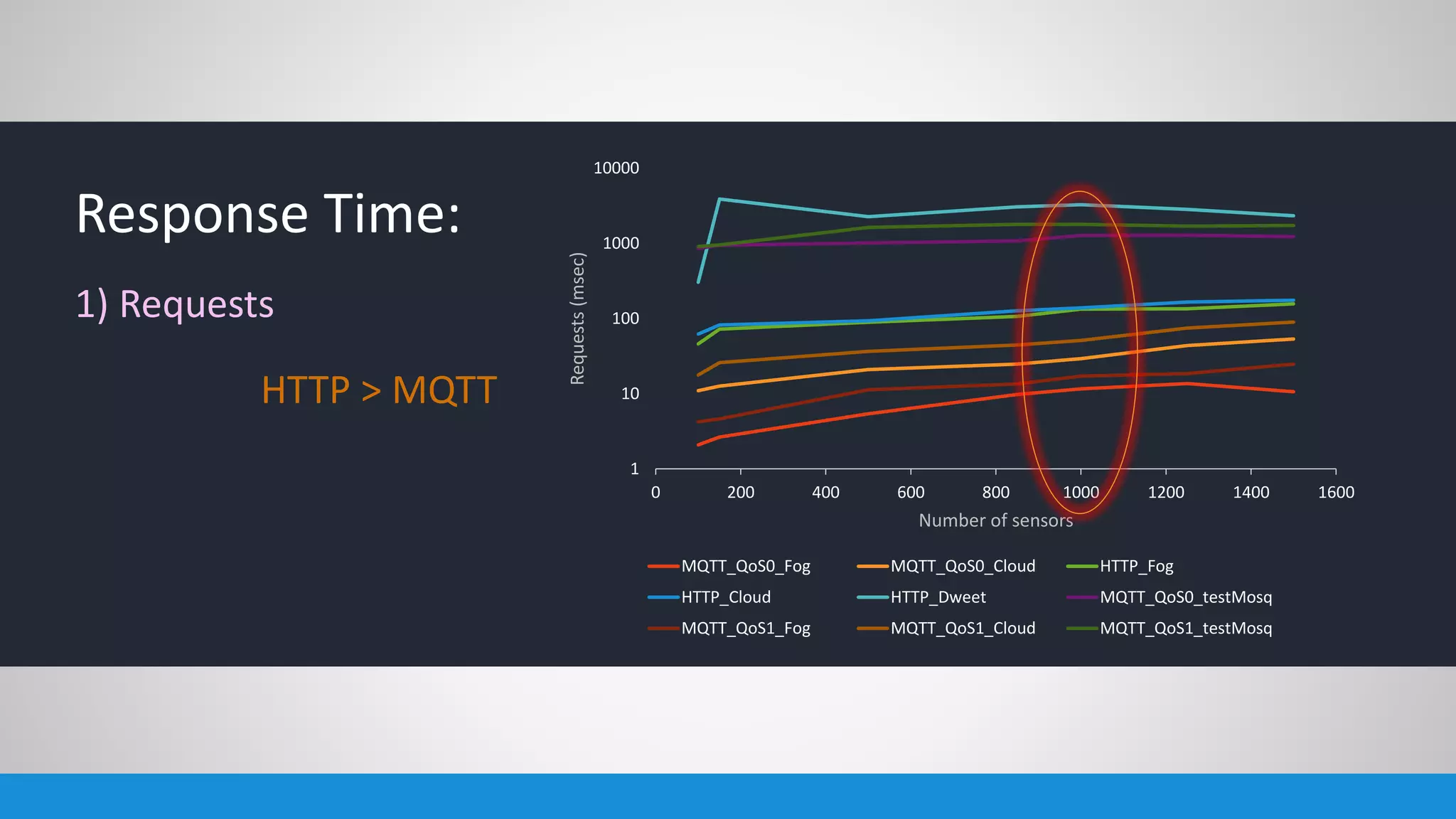
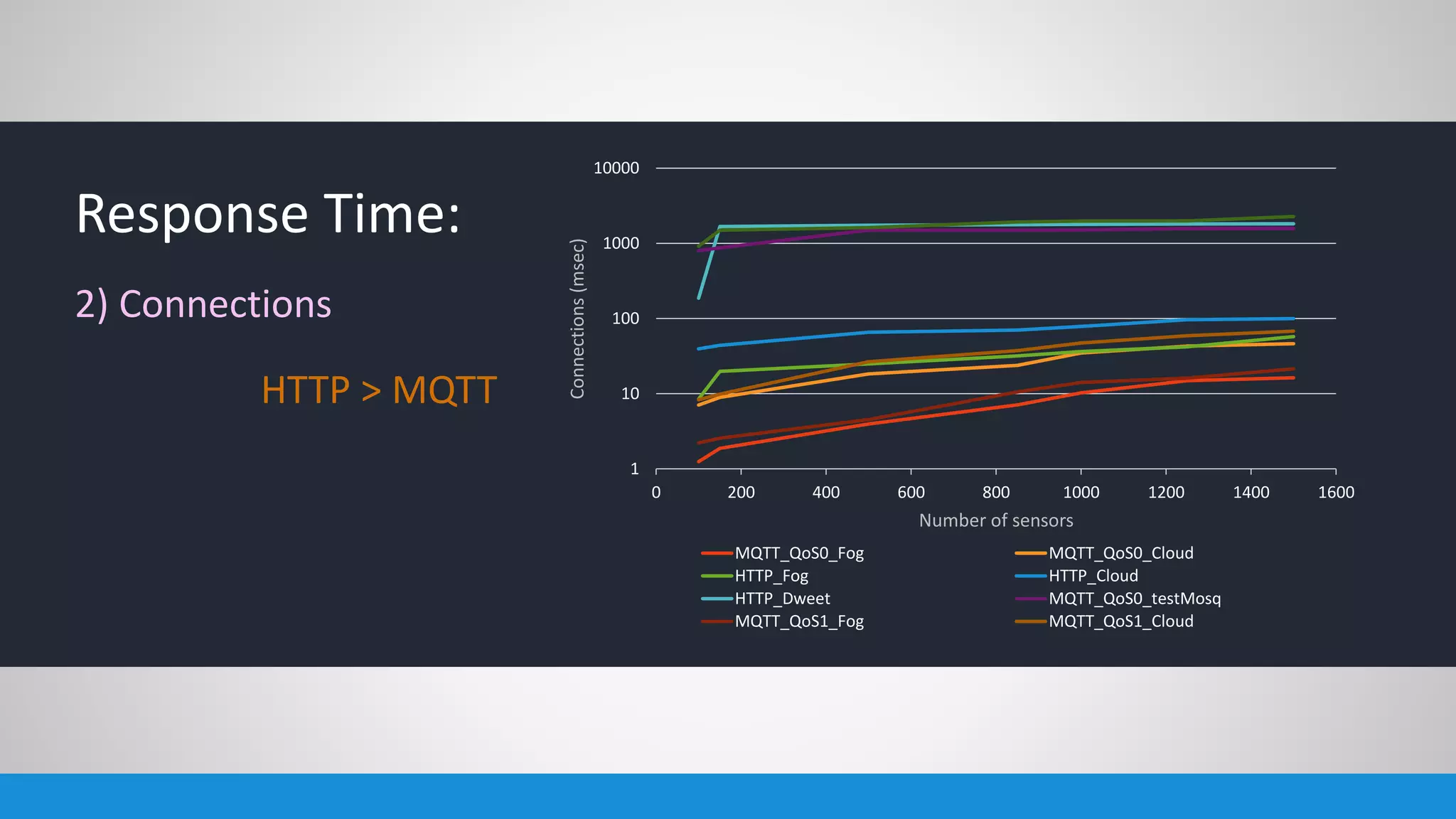
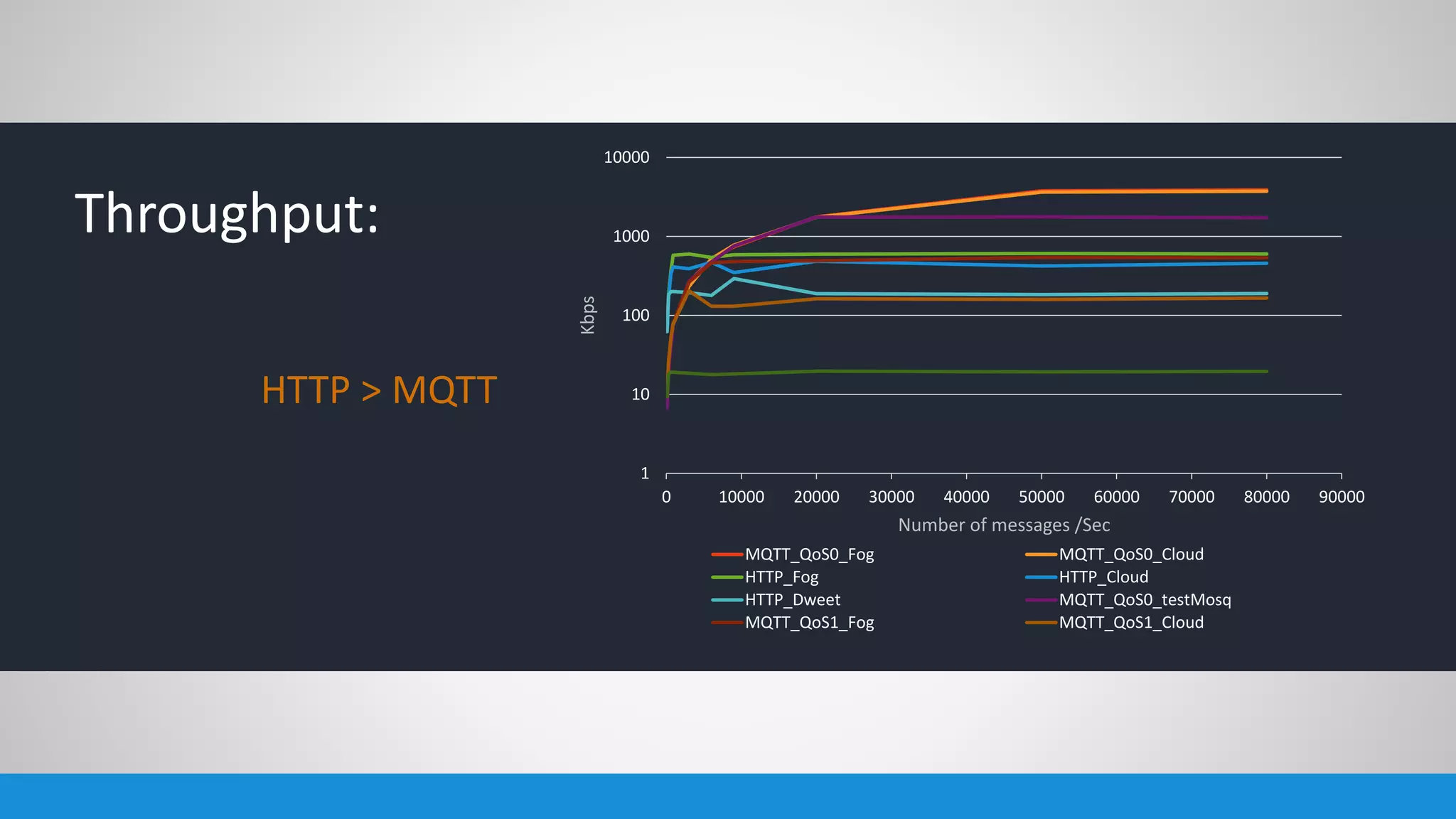
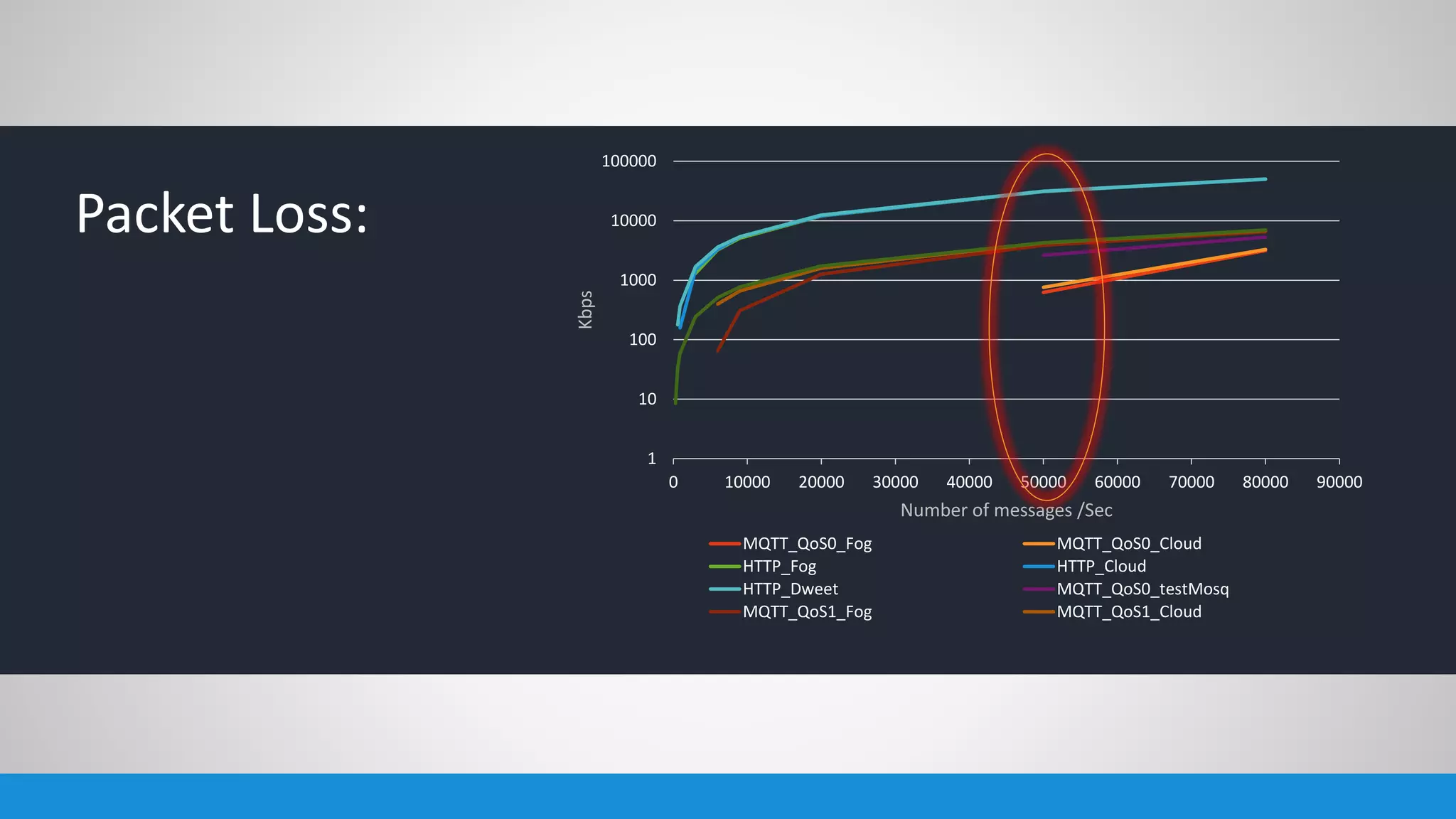
The document analyzes the performance of Internet of Things (IoT) protocols like MQTT and HTTP when used with fog and cloud computing over high traffic networks. The research tests response time, throughput, and packet loss for different IoT protocols (MQTT with QoS 0 and 1) and transmission methods (fog vs cloud) using realistic IoT sensors and traffic loads. The results showed MQTT generally had lower response times and higher throughput than HTTP, especially when using fog computing rather than cloud. MQTT QoS 1 also outperformed QoS 0 in most tests. Overall, fog computing with MQTT QoS 1 was found to have the best performance for high traffic IoT applications.