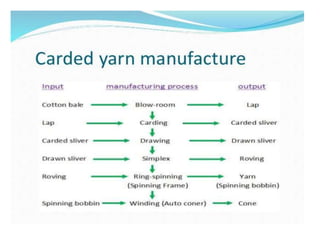
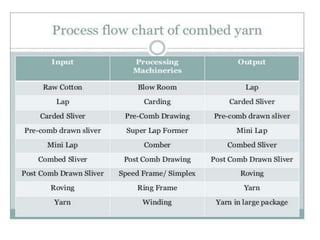
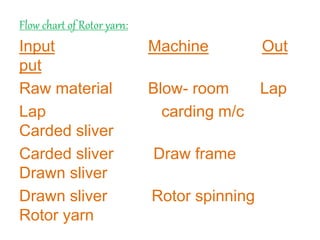
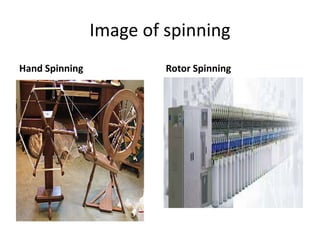
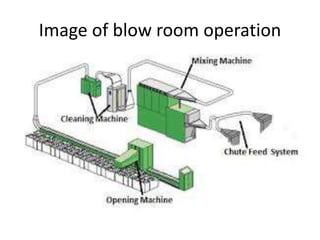
Yarn is produced by twisting fibers together. There are different types of yarns including rotor yarn, which is produced using a rotor spinning machine. The properties of cotton fibers that are important for spinning include fineness, length, strength and cleanliness. These properties affect the quality and characteristics of the resulting yarn. The blow room is the first processing stage, where bales of cotton fibers are opened, blended, cleaned and formed into laps to prepare them for further processing into yarn.