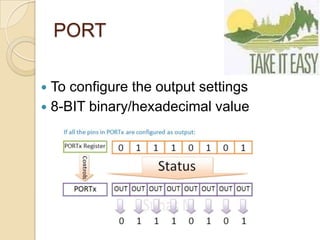
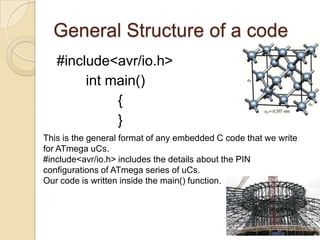
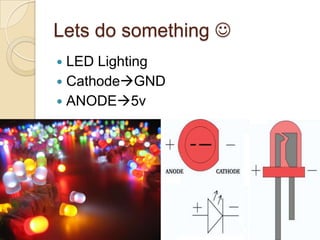
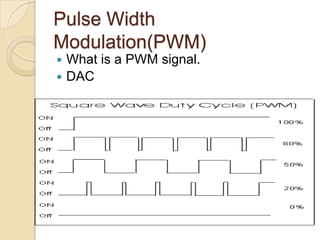
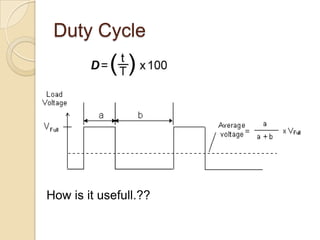
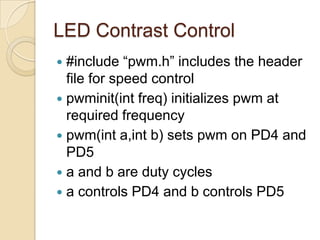
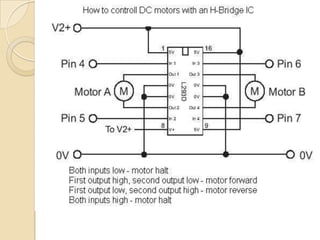
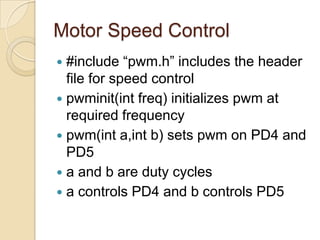
This document provides an overview of a workshop on basic robotics and embedded systems simulation. It discusses microcontrollers and some popular models like the AVR ATmega16. It describes the ATmega16's features like memory, I/O ports, timers and interfaces. It also explains concepts like I/O registers, binary-hexadecimal conversion, and using embedded C to code for the microcontroller. Examples provided include blinking an LED, pulse width modulation for LED contrast control, and motor speed control.