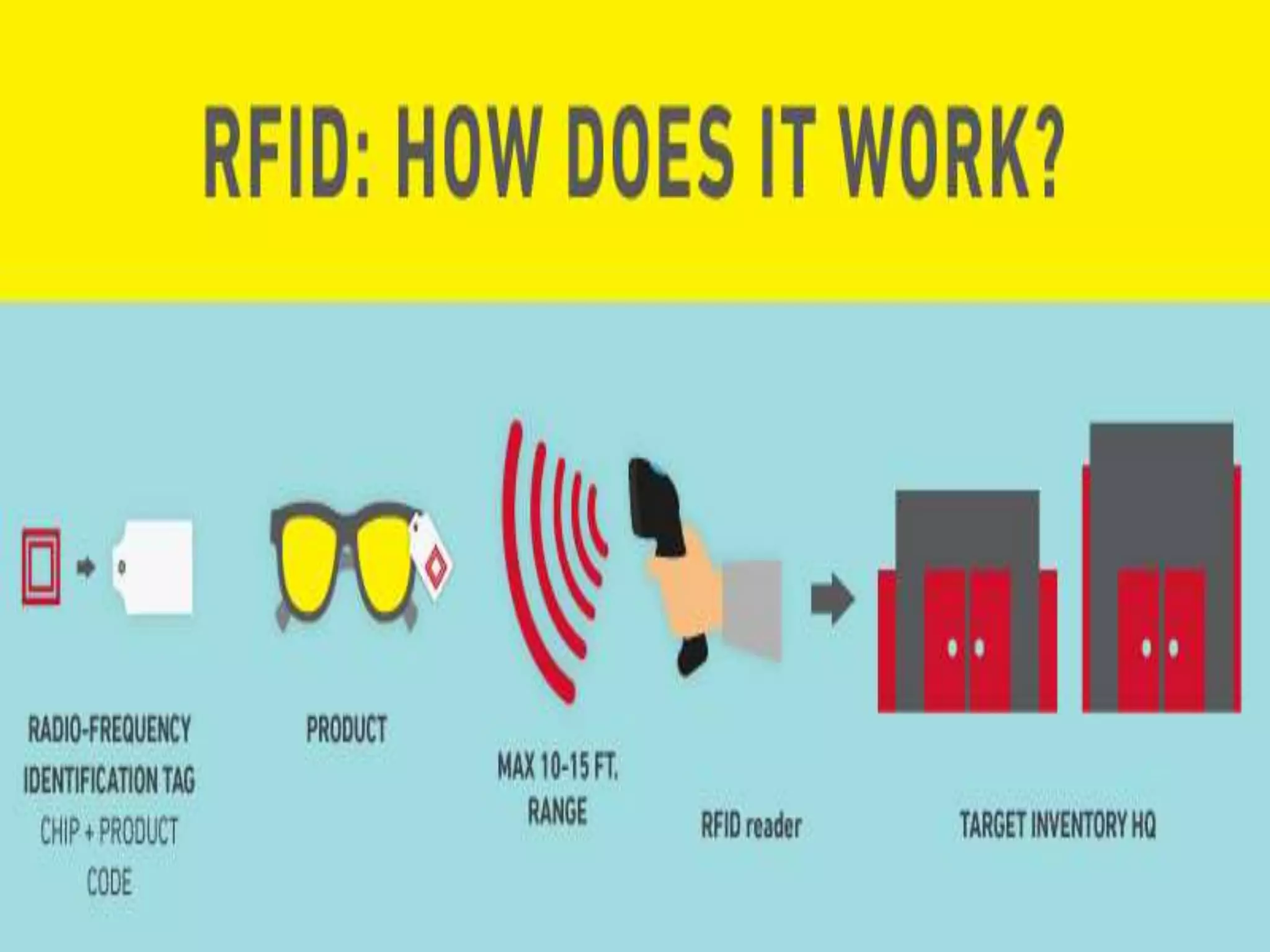
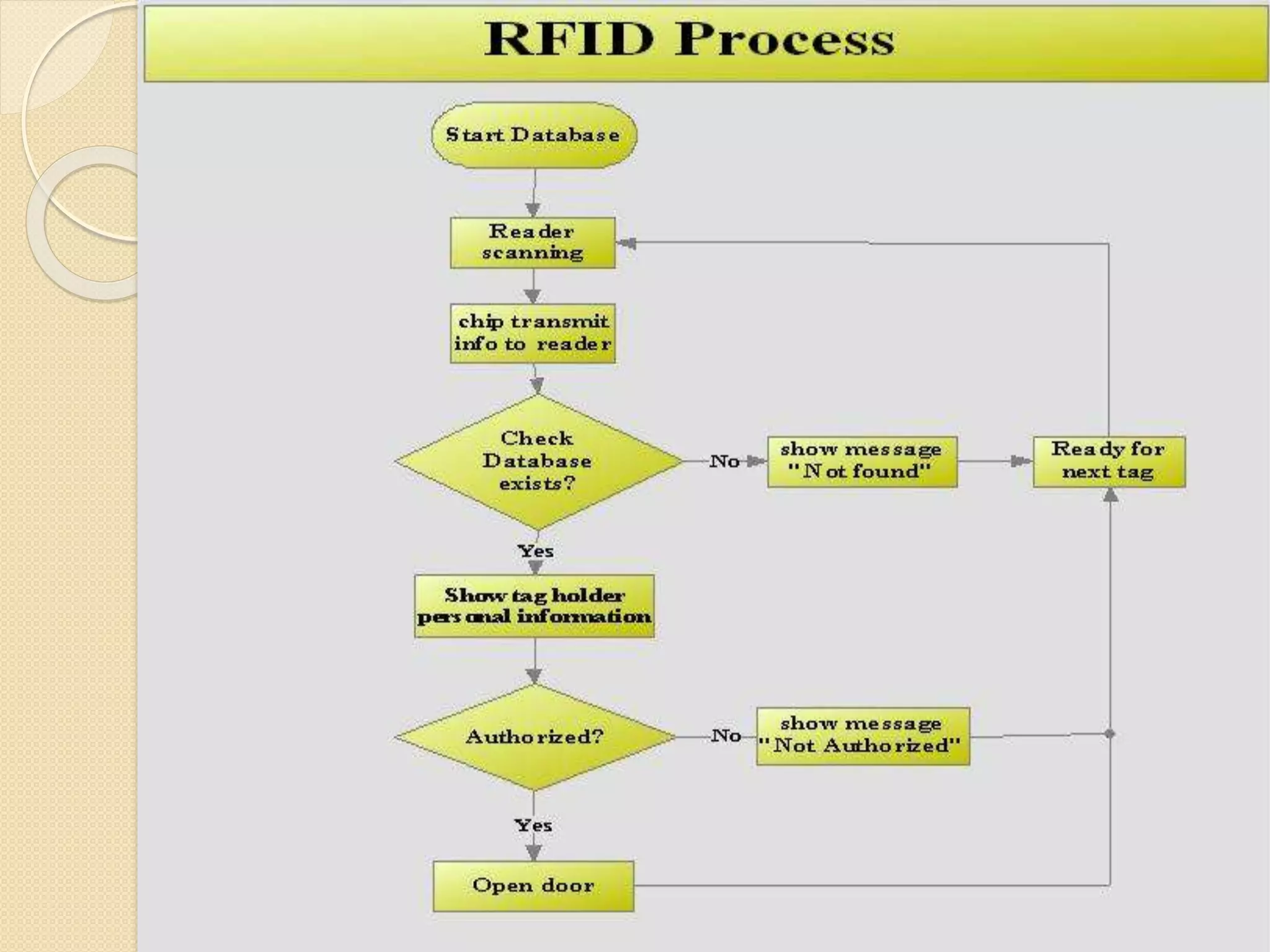
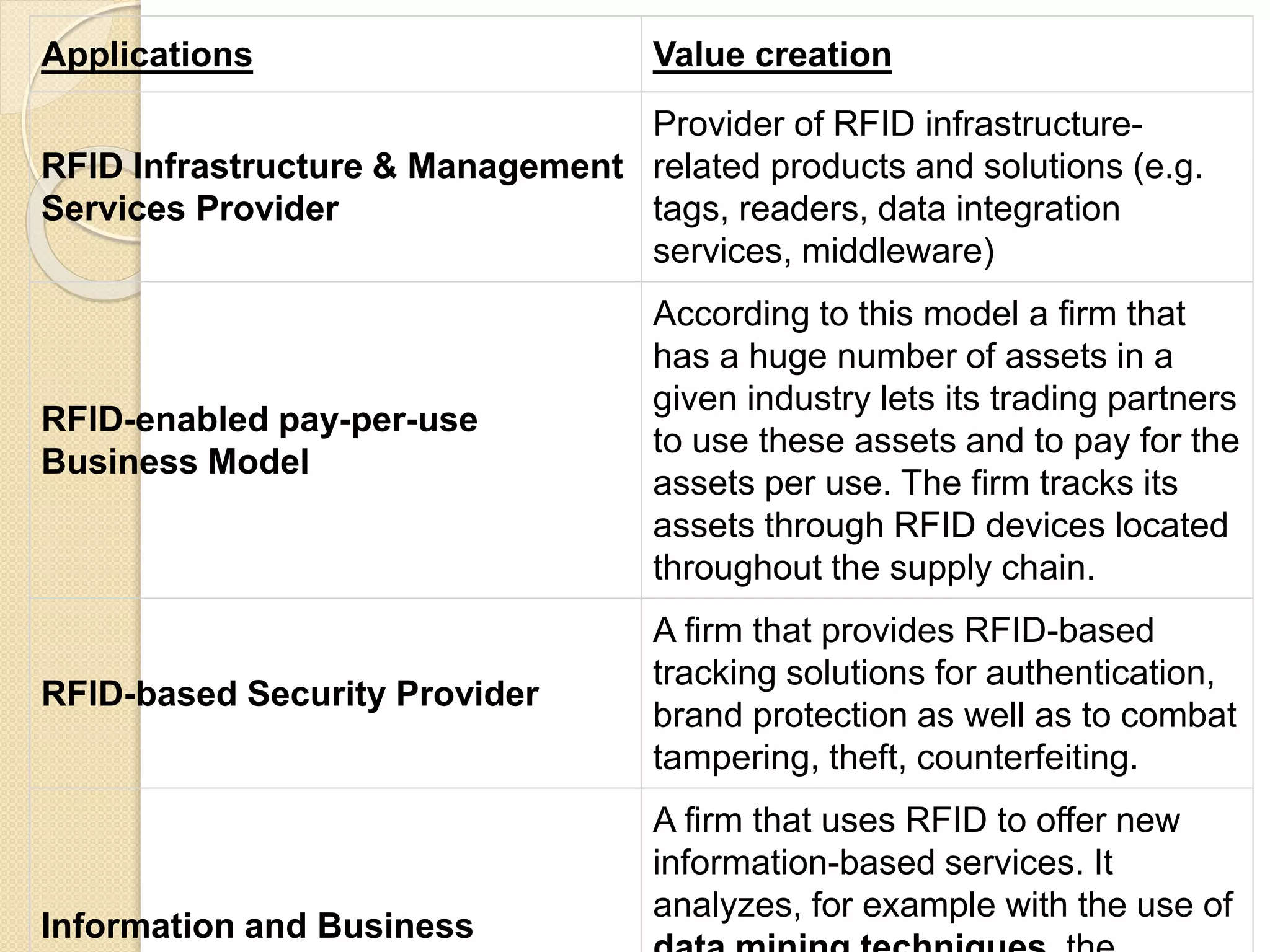
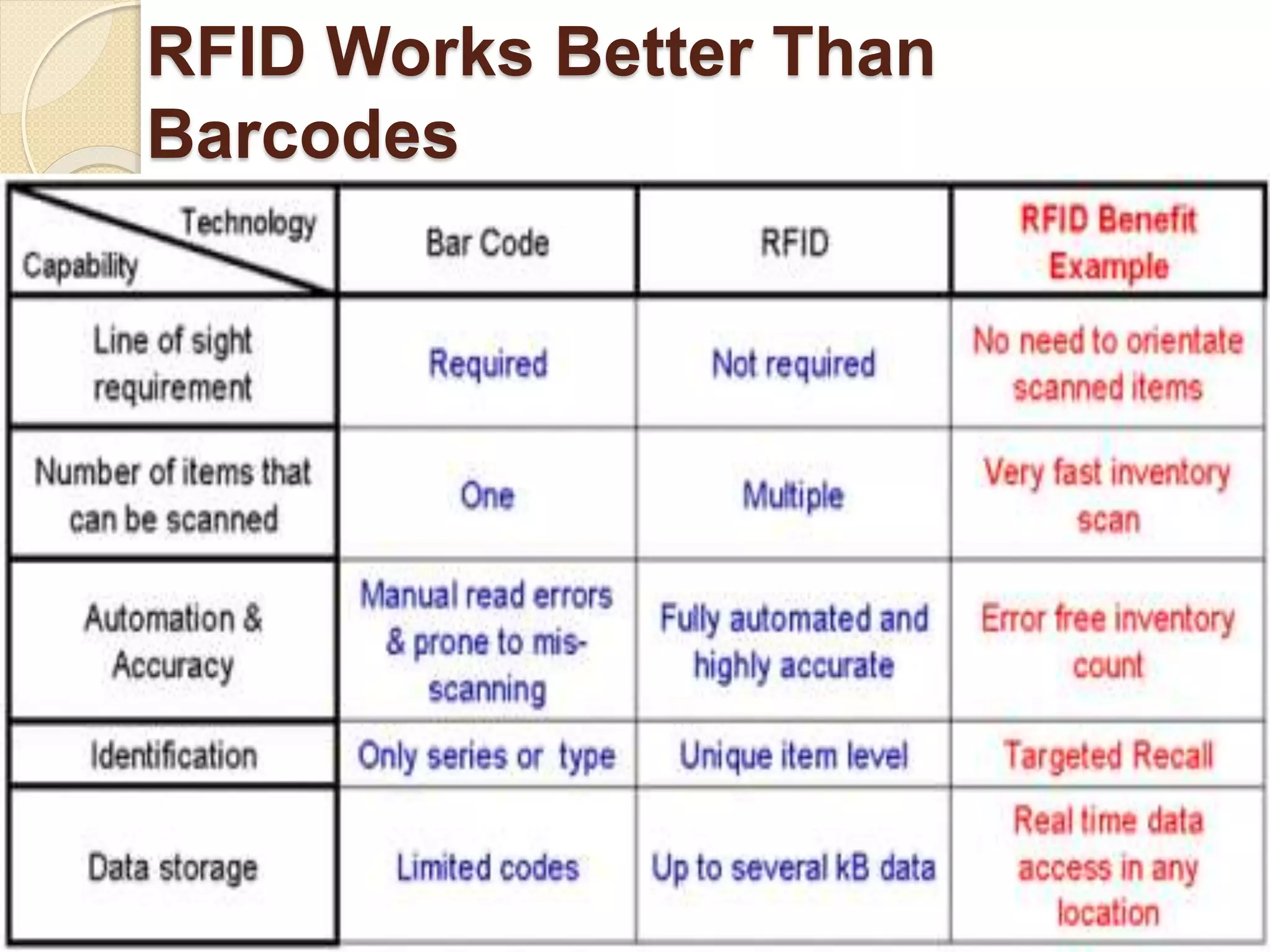
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. It can help create value for businesses in several ways. RFID allows for automatic scanning of products during purchase instead of manual scanning, improving efficiency. It also helps reduce failure rates and costs while improving on-time delivery. RFID provides real-time tracking of inventory and assets throughout the supply chain. Some applications of RFID that create value include supply chain management, security and access control, asset tracking, and automated identification.