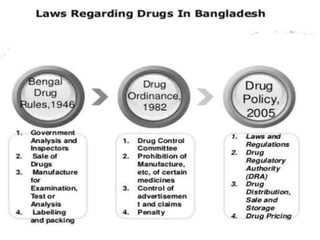
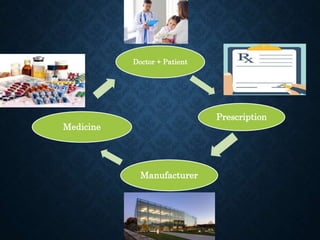
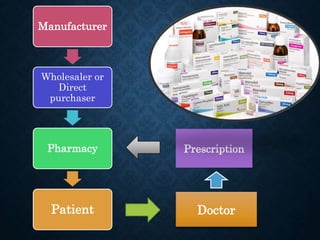
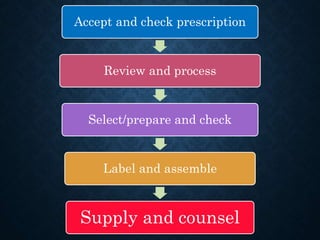
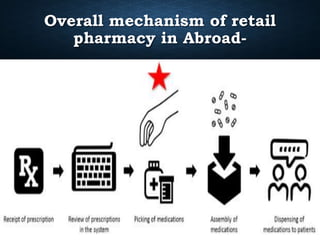
The presentation discusses retail pharmacy practices in Bangladesh and abroad, highlighting the roles and responsibilities of retail pharmacists, as well as the regulatory framework in Bangladesh. It details the mechanisms of drug delivery, including direct and indirect methods, and emphasizes the socio-economic contributions of retail pharmacies globally. Finally, the presentation outlines the process of prescription management and pharmacist counseling in international contexts, including salary expectations.