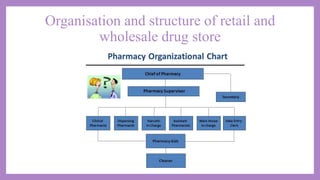
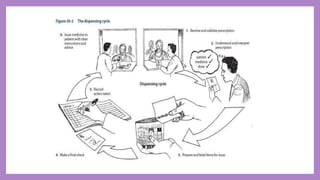
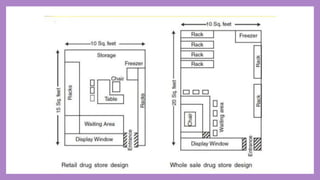
Community pharmacies, also known as retail pharmacies, serve as essential facilities for dispensing and supplying medications, requiring pharmacists to have specific qualifications and registrations. They provide a wide range of services, including patient counseling, drug distribution, and medication management while adhering to legal and professional standards. The management of community pharmacies includes site selection, layout design, staff selection, and maintaining accurate records to ensure effective operations and compliance with regulations.