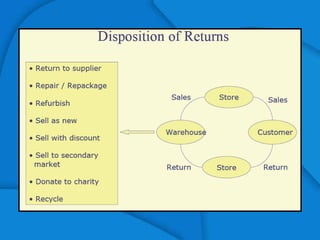
The retail supply chain is a large and evolving industry globally and in India. Retail formats have evolved from traditional village markets to modern convenience stores, supermarkets, hypermarkets, and shopping malls. There are over 12 million retail outlets in India, making it one of the most densely populated retail markets. Emerging technologies like RFID and information systems are becoming the backbone of retail supply chain operations by automating processes, increasing visibility and efficiency, and reducing costs. For example, Walmart estimated potential annual savings of $8.35 billion from implementing RFID across its supply chain through benefits like reduced inventory levels, shrinkage, and labor costs.