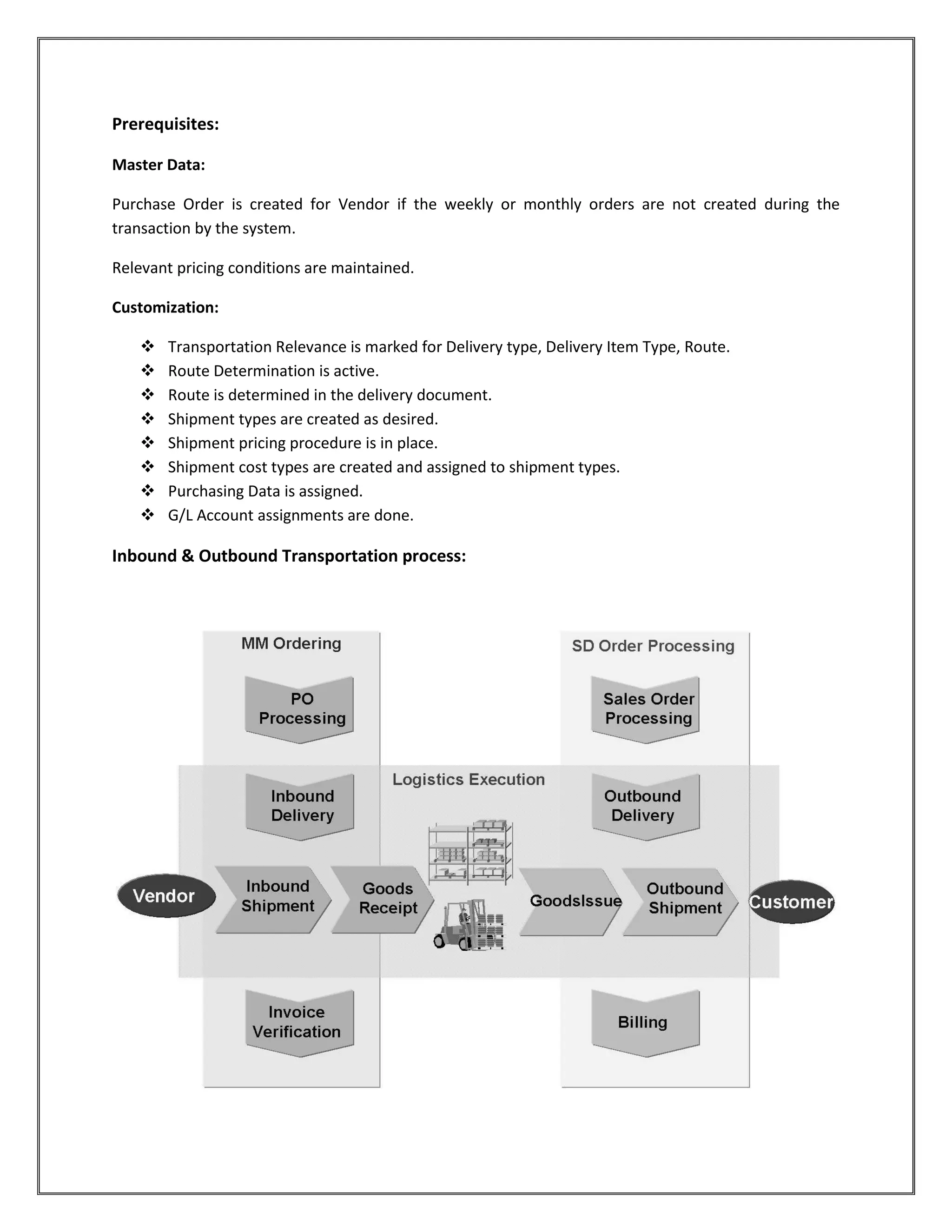
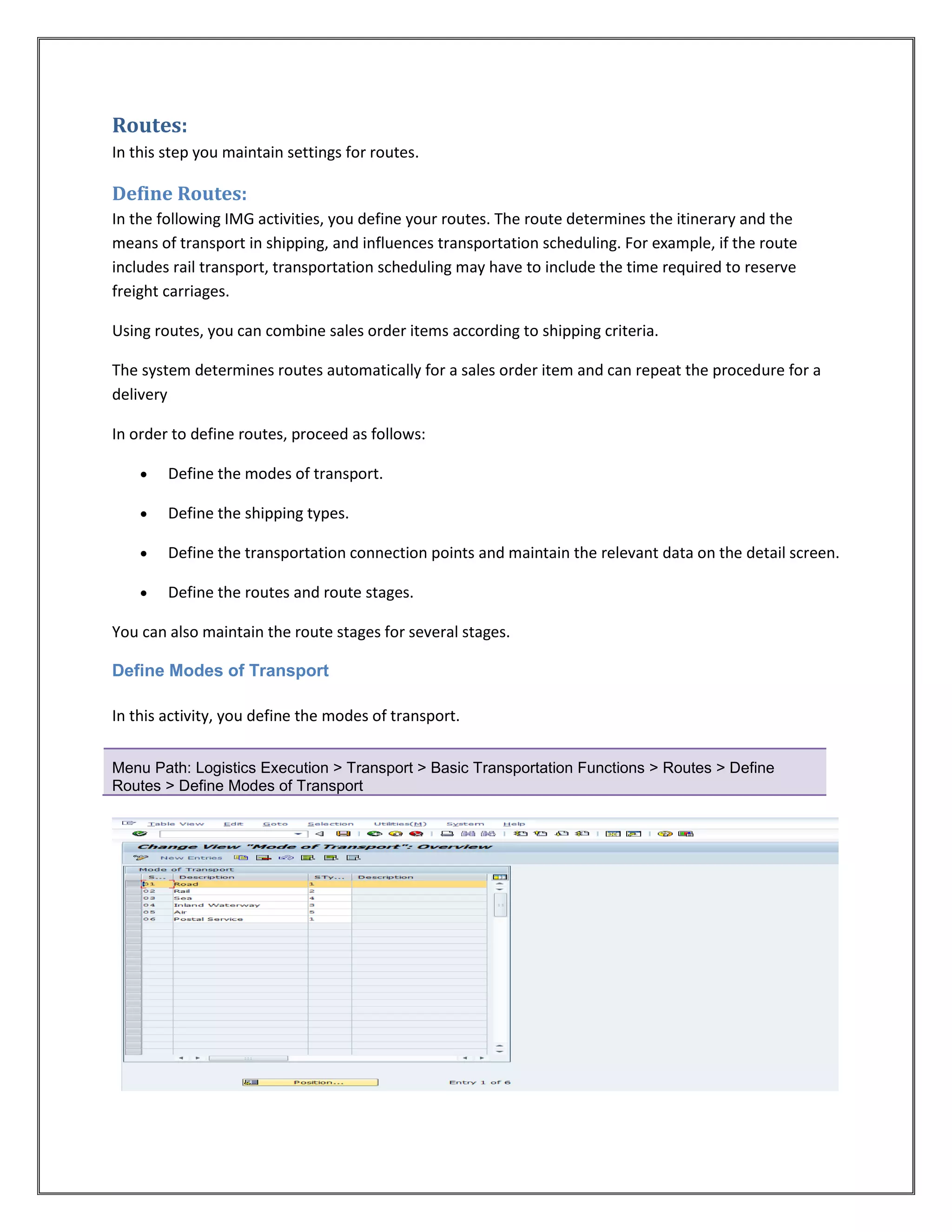
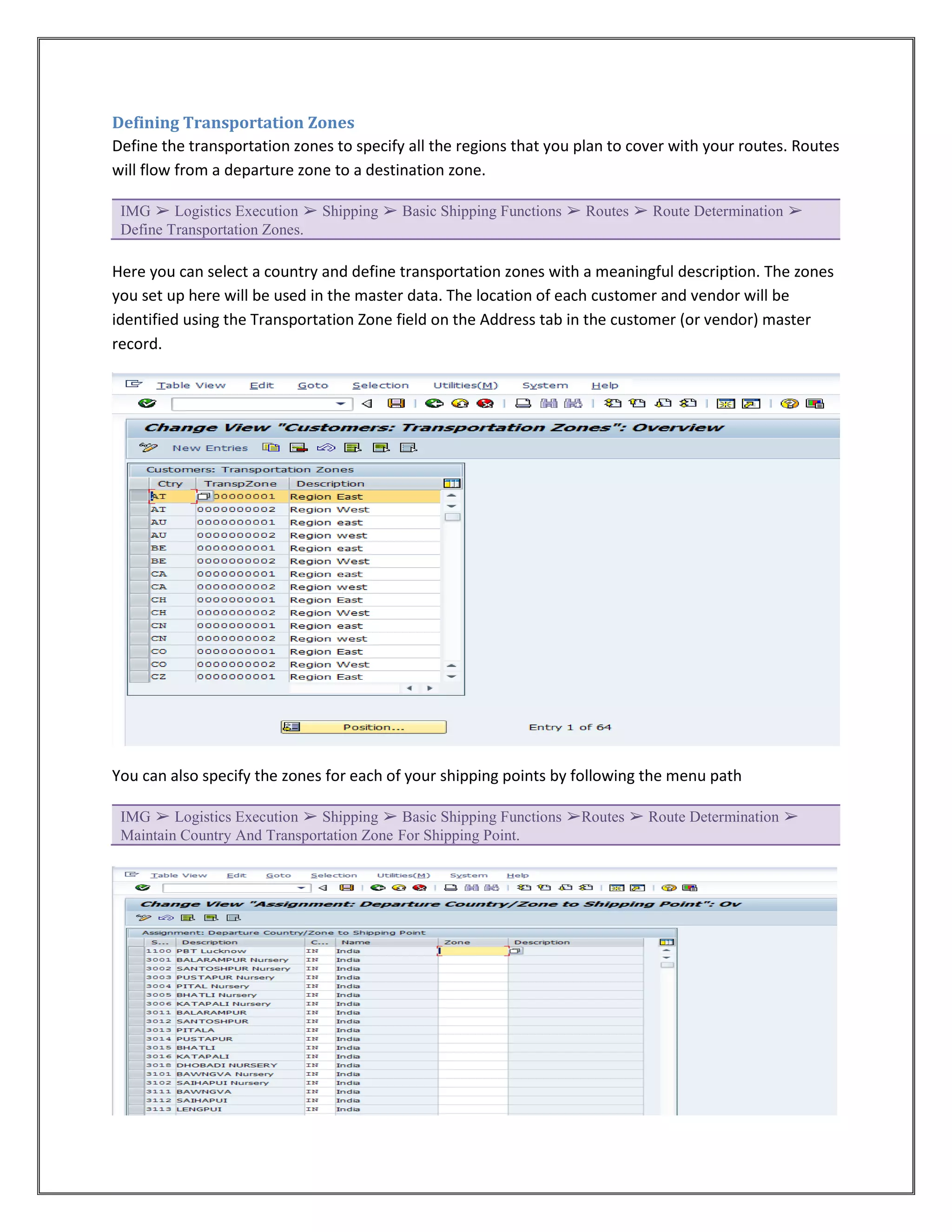
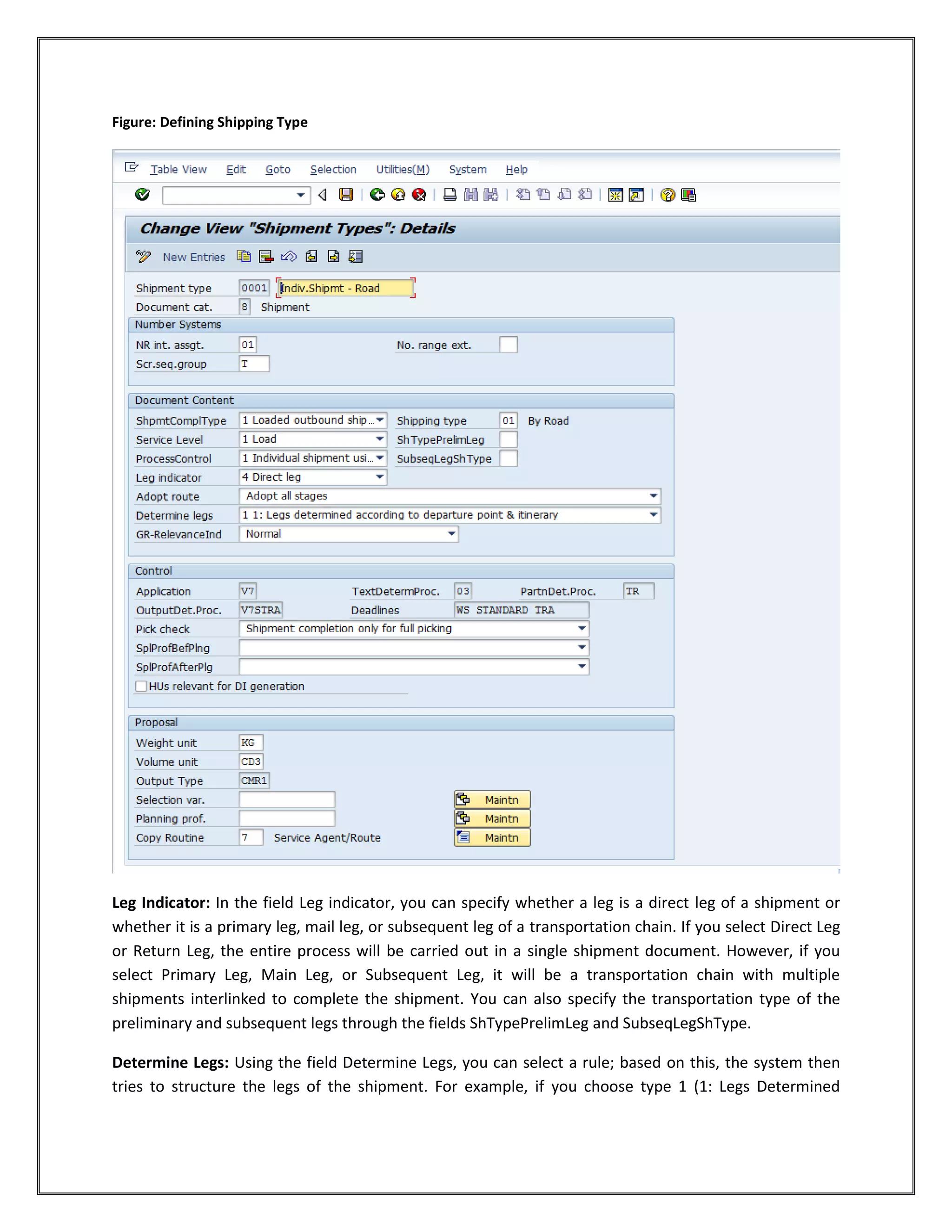
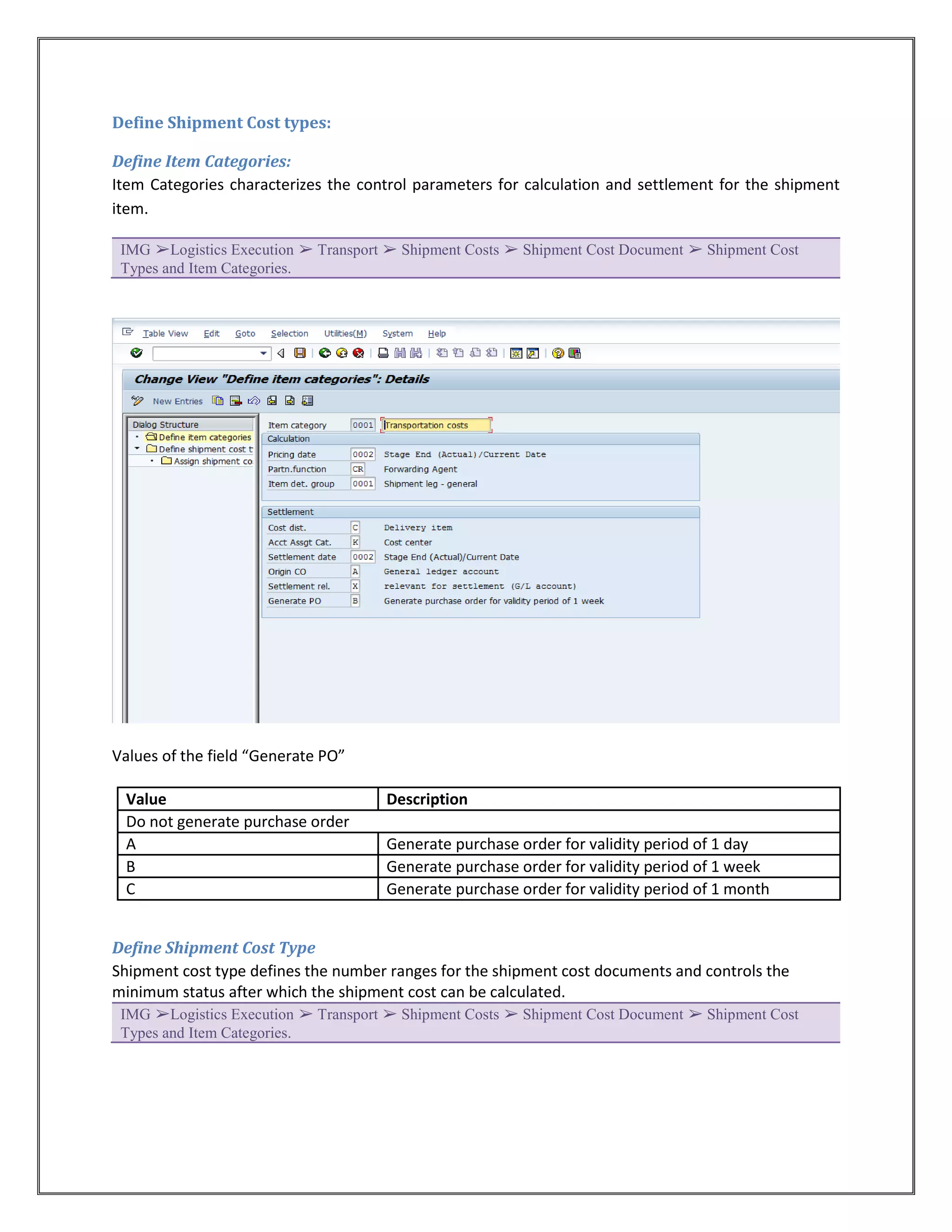
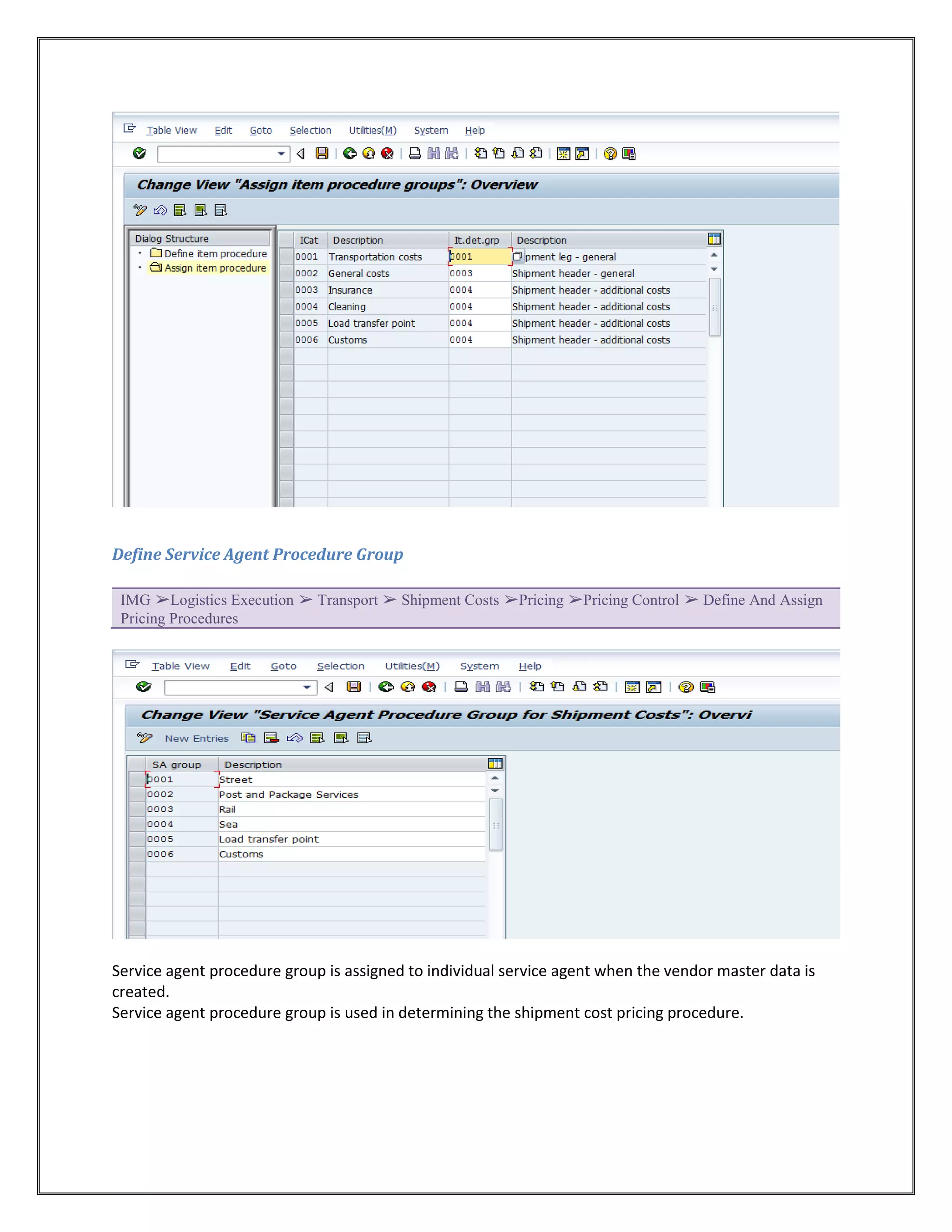
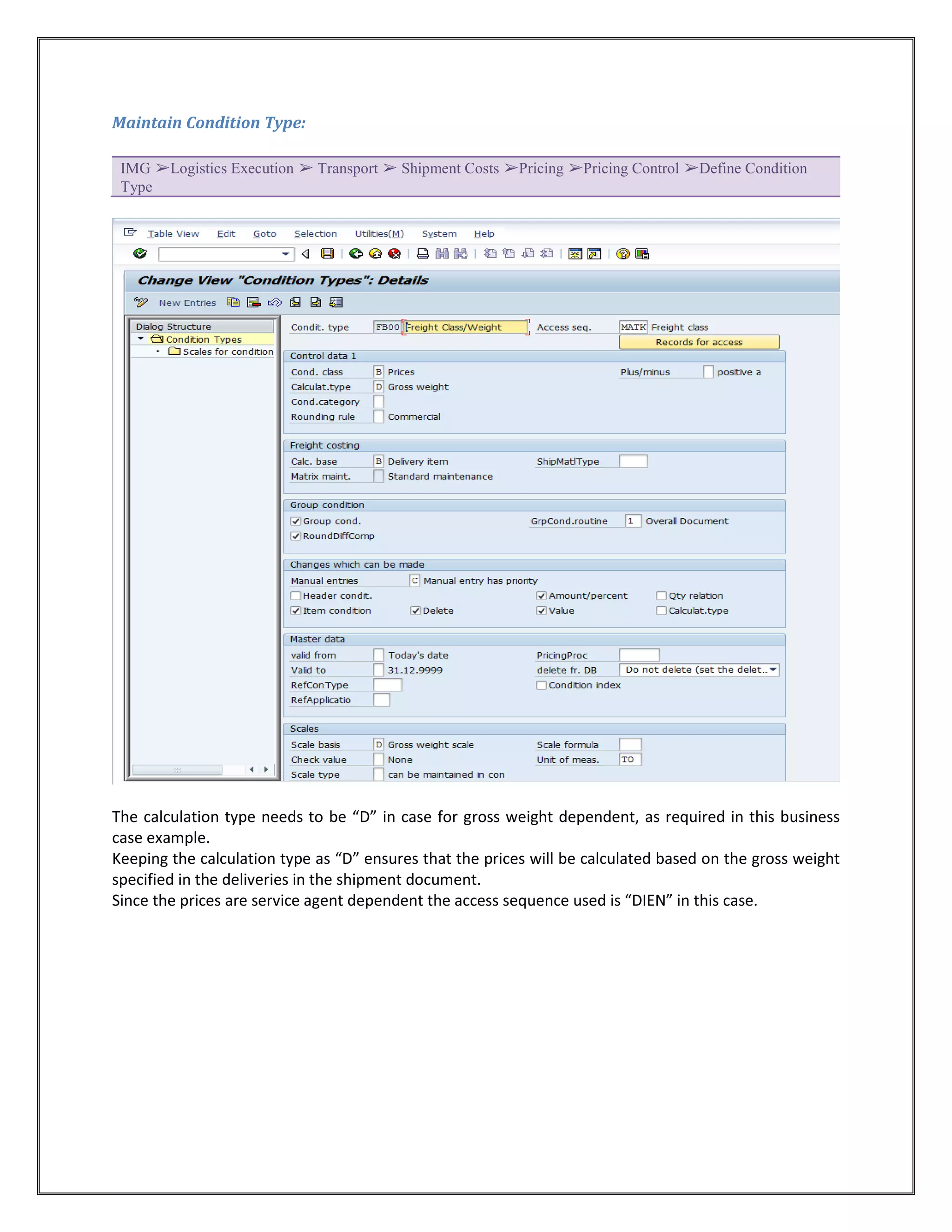
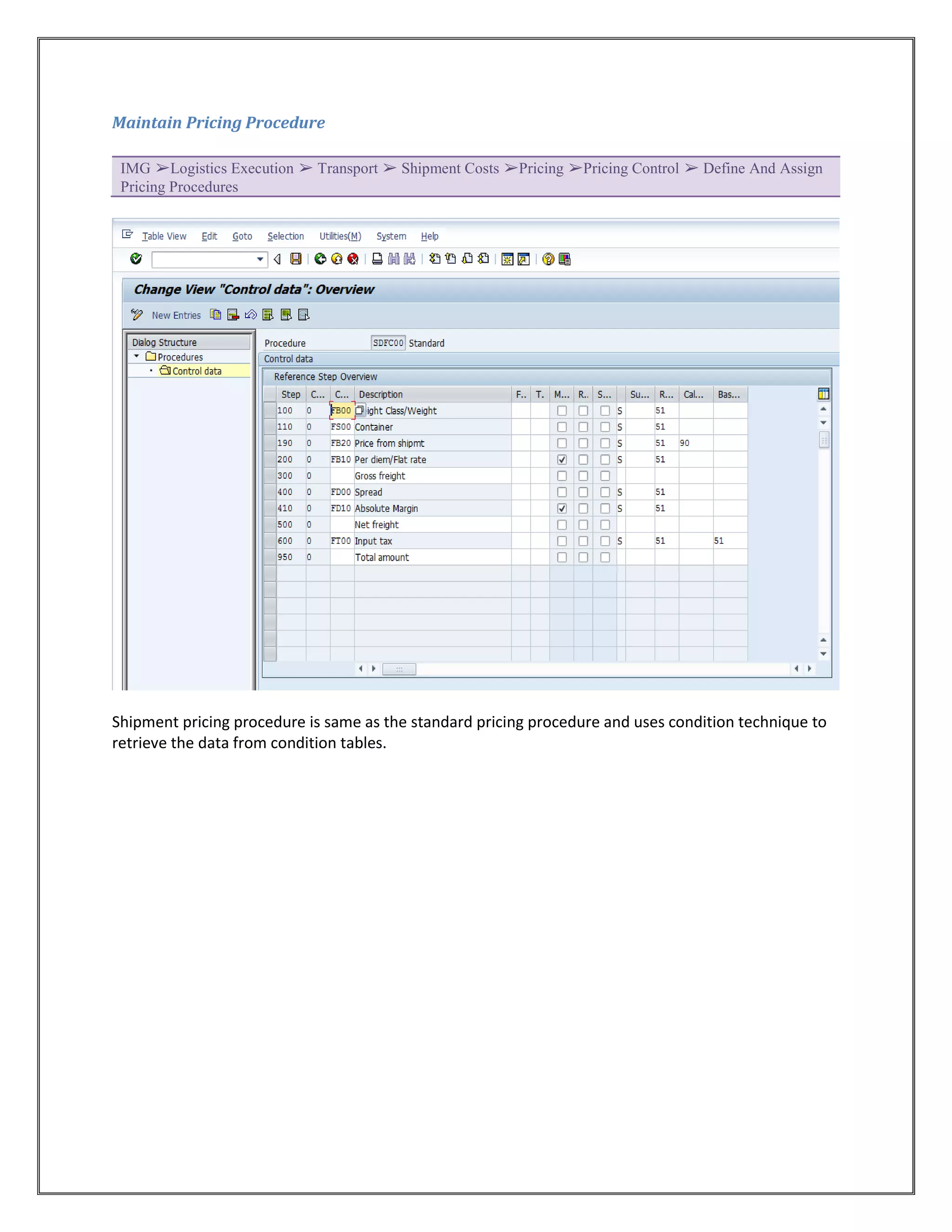
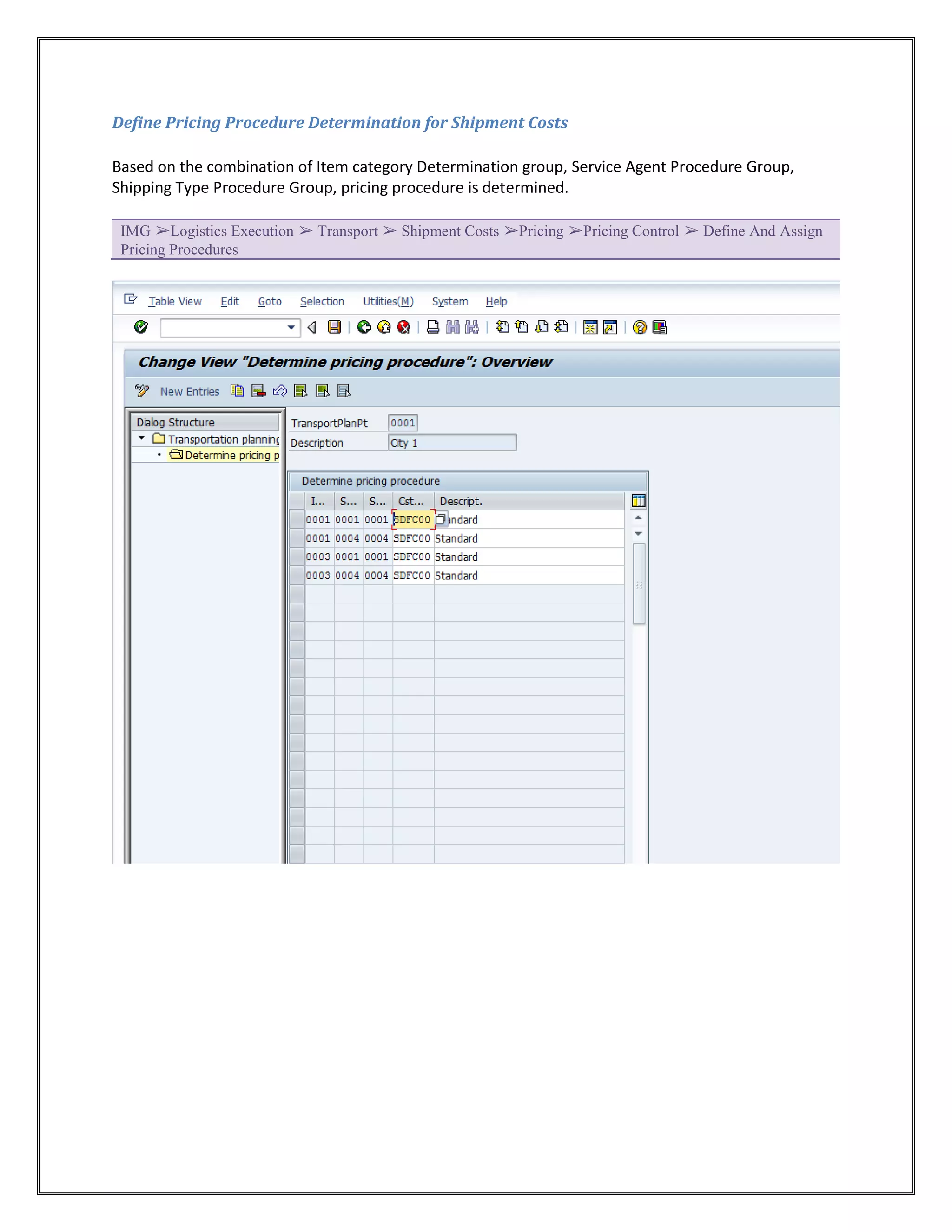
The document provides information on configuring outbound transportation in SAP. It discusses setting up transportation planning points, defining routes, shipment types, and activity profiles. The goal is to implement transportation management to ensure timely delivery to customers and reduce shipment costs. Key aspects covered include customizing route determination, defining modes of transport, shipping types, and configuring shipments.