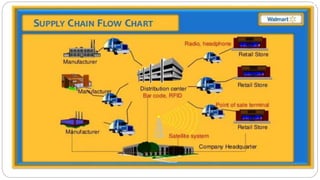
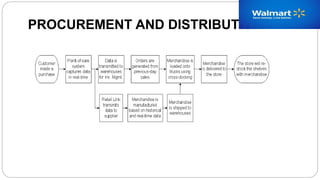
Walmart was founded in 1962 in Rogers, Arkansas. It is now the largest retailer in the world with over 11,000 stores across 27 countries. Walmart uses advanced logistics systems like barcodes, RFID, and satellite communication to track inventory in real-time across its extensive global supply chain. It has over 158 distribution centers in the US that use conveyor belts and trucks to deliver goods to stores within a 200 mile radius. Walmart maintains strict control over its vast network of suppliers to ensure the lowest prices.