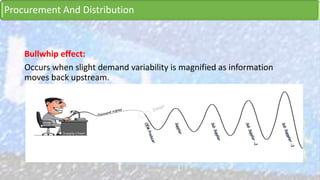
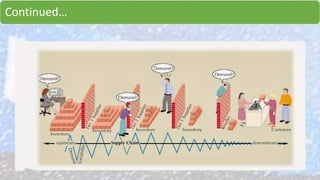
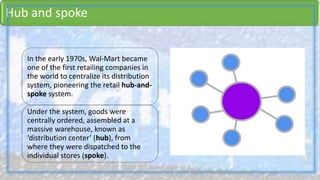
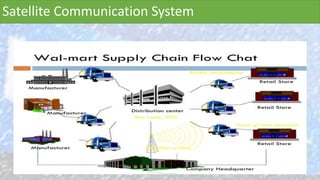
Walmart has highly effective supply chain management practices that have contributed significantly to its success. It uses procurement strategies like direct sourcing from manufacturers and vendor managed inventory. Logistically, it employs cross-docking and a hub-and-spoke distribution model. Walmart also pioneered the use of IT in supply chain management, developing systems for inventory tracking, replenishment, and collaboration with suppliers. These integrated IT systems and data-driven practices help Walmart maintain low inventory levels while still ensuring high product availability.