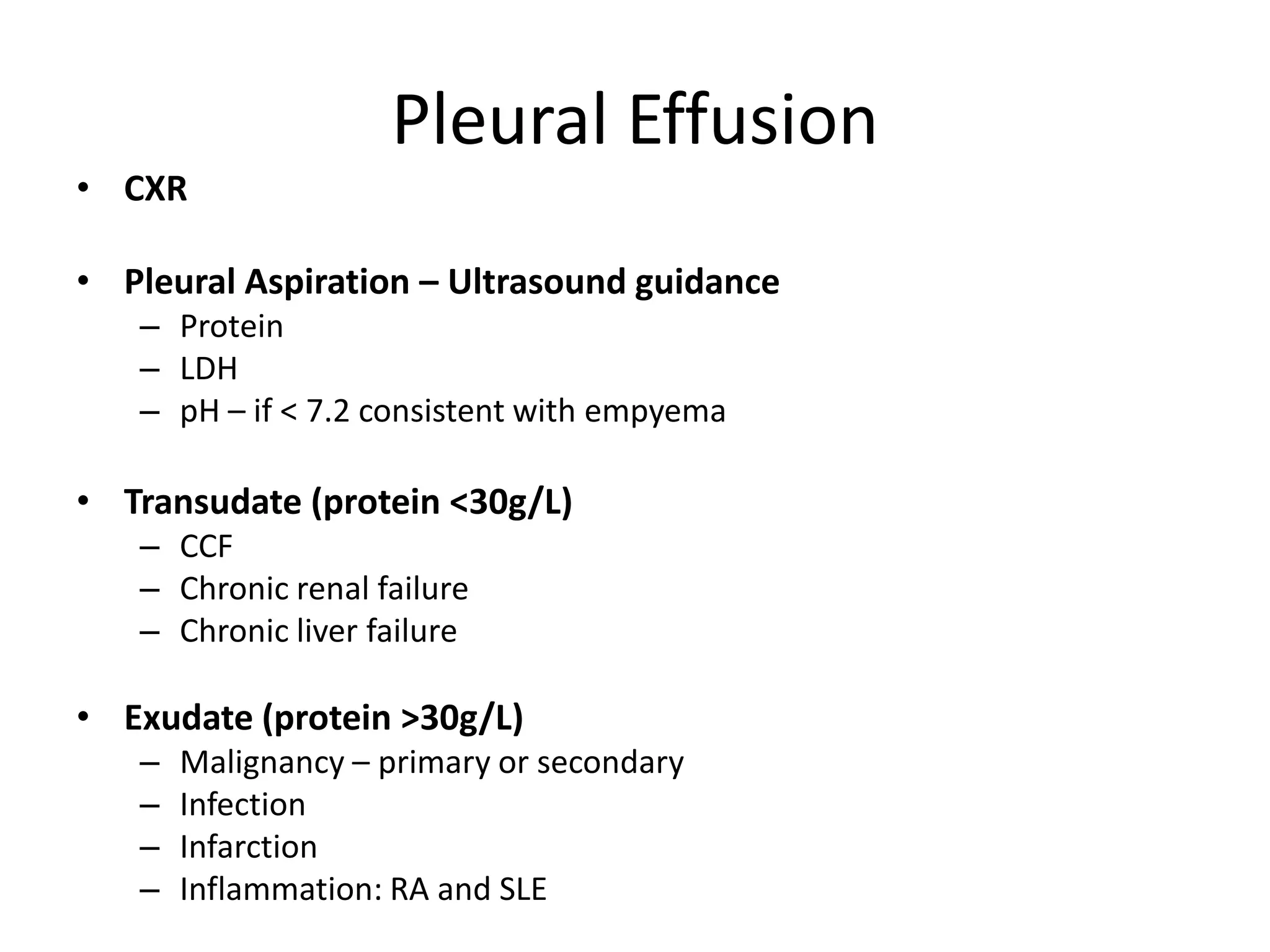
This document provides an overview of conducting a respiratory OSCE station, including examining common signs, conditions, investigations, and management strategies. Key areas of focus are the respiratory examination, common signs and causes of conditions like clubbing, crackles, and reduced breath sounds, investigating and treating issues like pneumonia, COPD, and lung cancer. The goal is to thoroughly examine patients and utilize clinical clues and testing to accurately diagnose and manage respiratory diseases.