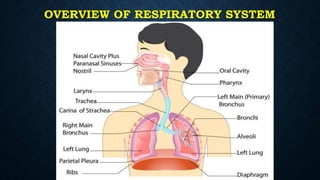
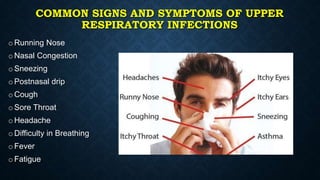
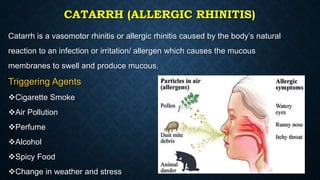
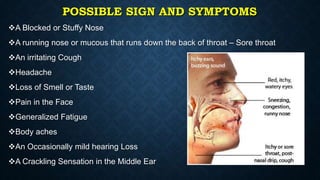
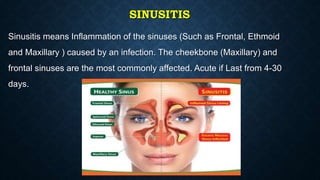
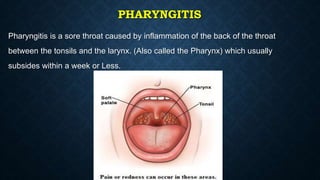
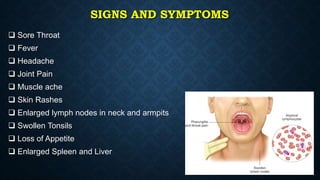
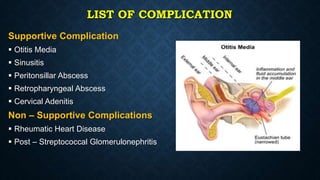
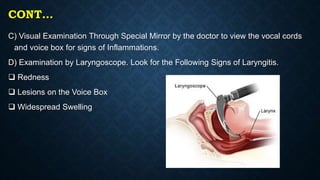
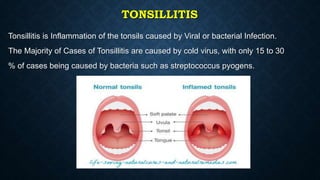
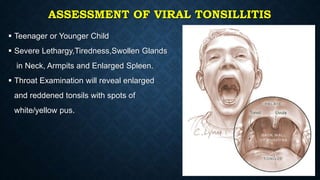
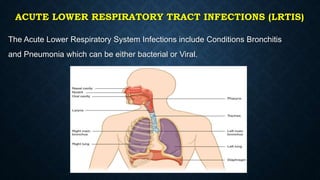
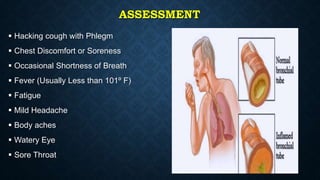
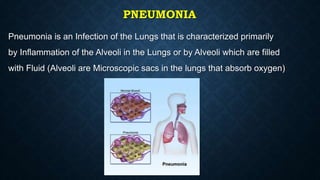
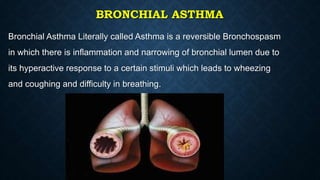
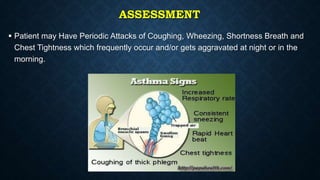
This document provides information on common respiratory conditions including upper and lower respiratory infections. It discusses conditions like the common cold, sinusitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, bronchitis and pneumonia. It outlines the causes, symptoms, risk factors and primary treatment measures for each condition. The document aims to help nursing students assess, identify and provide primary care for patients presenting with acute respiratory infections.