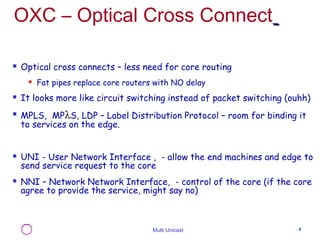
The document discusses the evolution of optical networking, emphasizing the need for agile reconfiguration of light paths to support new services and applications. It highlights the significant bandwidth demands of streaming media, the cost-effectiveness of multi unicast over traditional WAN, and the importance of moving intelligence from the optical core to the network edge. Additionally, it addresses the ongoing challenges and bottlenecks in optical networking, particularly at the first mile.