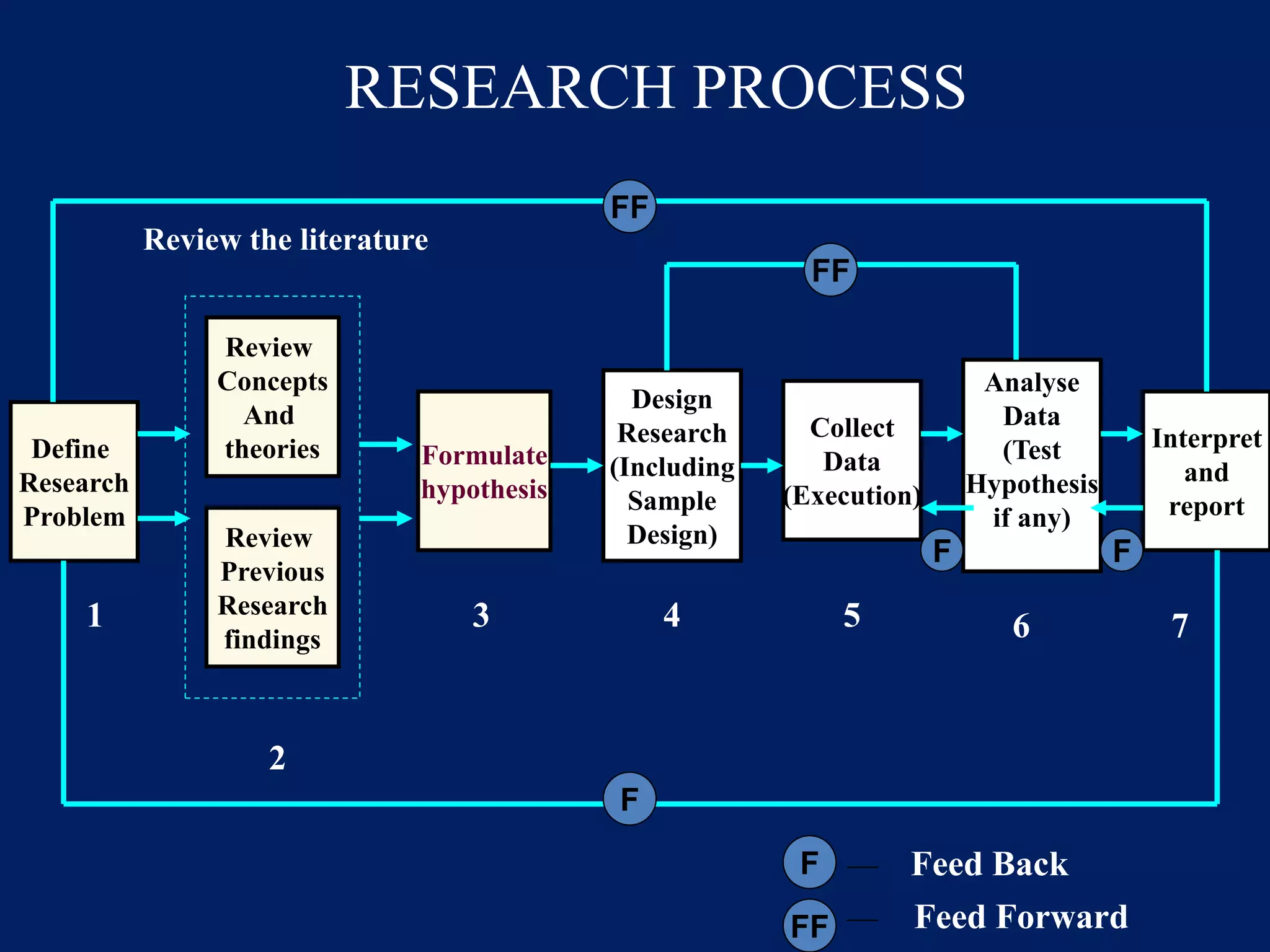
The document provides an overview of the research methodology process. It discusses defining the research problem, reviewing literature, formulating hypotheses, and establishing research objectives. The key steps are:
1) Defining the research problem by identifying and selecting a problem to study based on criteria like interest and feasibility.
2) Reviewing relevant literature to understand previous work and identify gaps.
3) Formulating testable hypotheses about relationships between variables based on theories and findings from the literature.
4) Establishing clear and achievable research objectives to directly answer the research problem.


























![1. Descriptive Hypothesis
These are assumptions that describe the characteristics
(such as size, form or distribution) of a variable. The variable
may be an object, person, organisation, situation or event.
2. Relational Hypothesis [Explanatory Hypothesis]
These are assumptions that describe the relationship
between two variables. The relationship suggested may be
positive, negative or causal relationship.
TYPES OF HYPOTHESIS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/researchmethodologyipr-ii-210326042121/75/Research-Methodology-IPR-II-28-2048.jpg)


