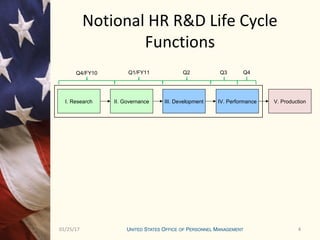
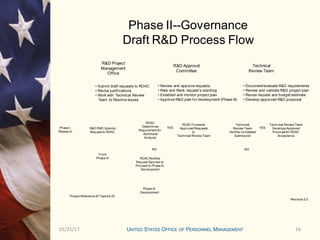
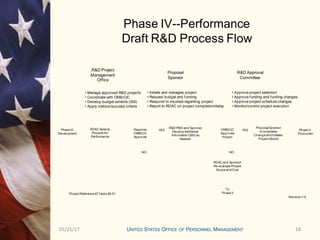
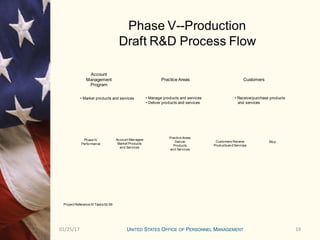
This document outlines the research and development program for fiscal year 2012 at the Center for Emerging Solutions and HR Innovations. It provides details on the current state of ongoing R&D projects, criteria for new project requests, funding mechanisms, and the approval process and timeline. The R&D program management office oversees 24 ongoing projects with a total estimated cost of $X.X million and evaluates project performance on a monthly and quarterly basis through a research and development approval committee.