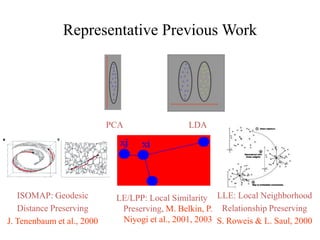
This document discusses dimensionality reduction algorithms and proposes a unified framework. It summarizes previous algorithms like PCA, LDA, ISOMAP and describes how they can be viewed as special cases of a general formulation involving intrinsic and penalty graphs. A new algorithm, Marginal Fisher Analysis, is introduced that utilizes label and local manifold structure information for tasks like face recognition. Experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness. The document also outlines future work on machine learning, event recognition, biometrics and multimedia content analysis.