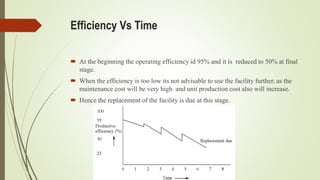
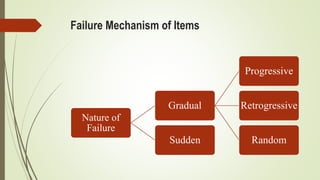
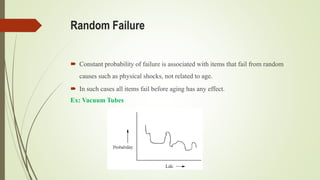
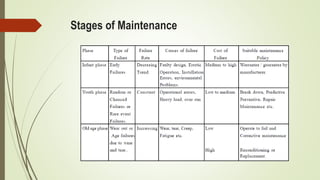
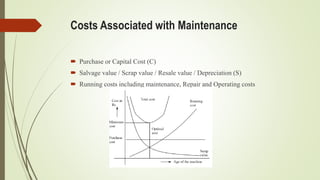
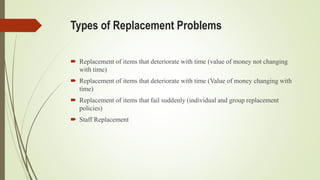
This document discusses replacement theory and models for determining optimal replacement times for equipment and components. It covers different types of failure mechanisms including gradual, sudden, progressive, and retrogressive failure. Key factors in replacement decisions are purchase costs, salvage values, maintenance costs, and operating costs. Optimal replacement minimizes total average costs over the lifetime of the item. Group replacement policies can be more cost effective than individual policies for items that fail suddenly by replacing items in a group before failures occur.