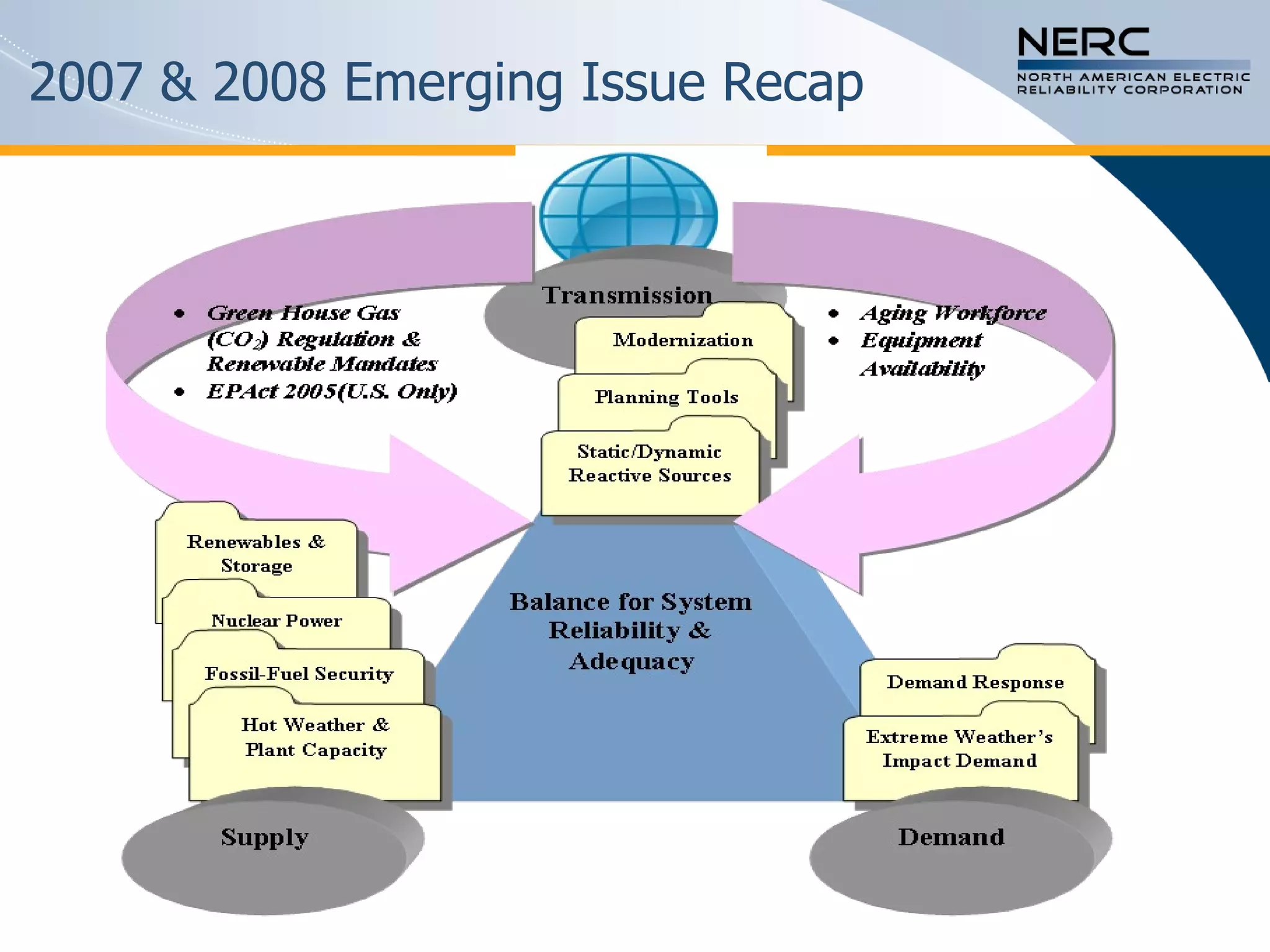
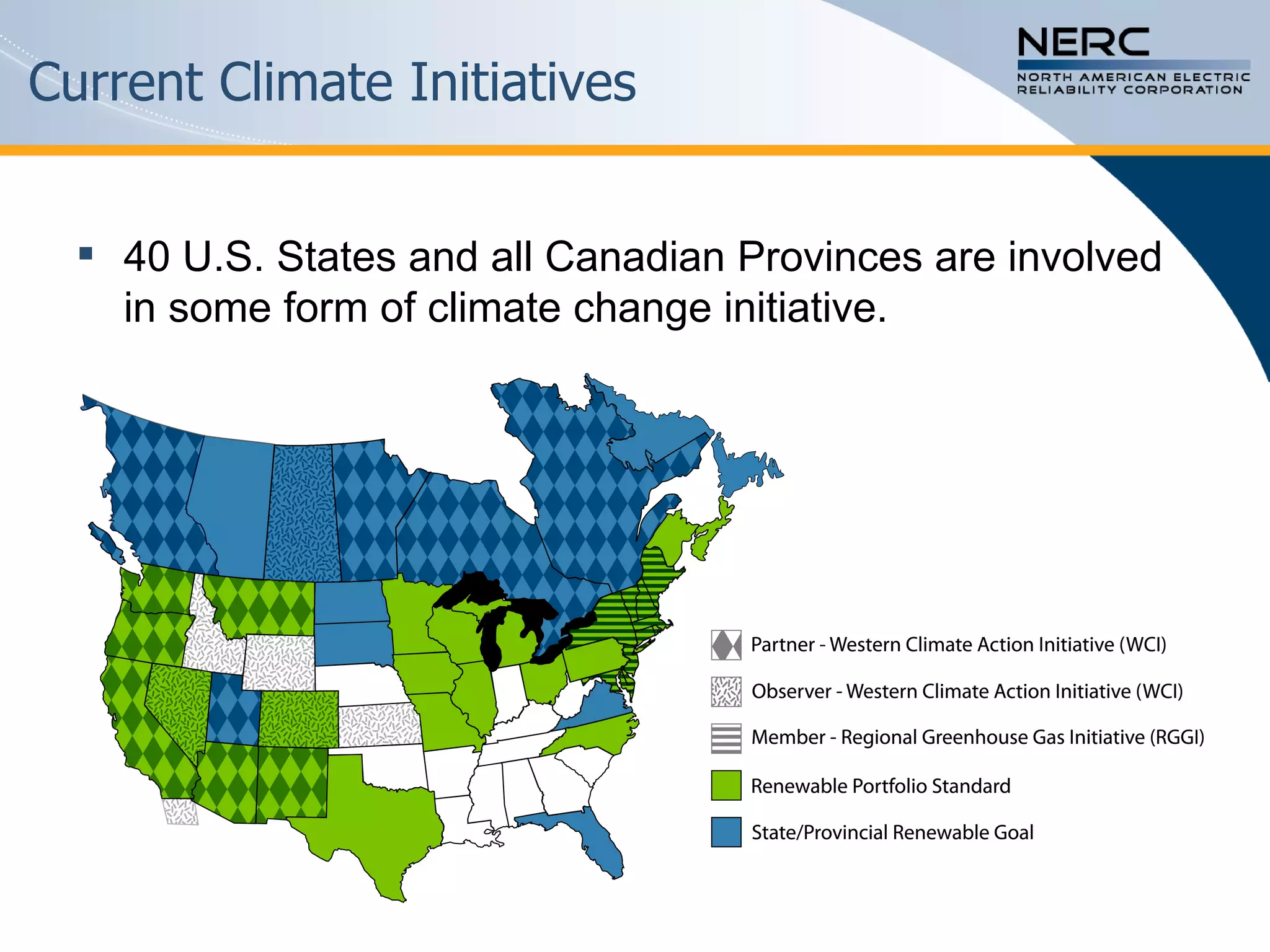
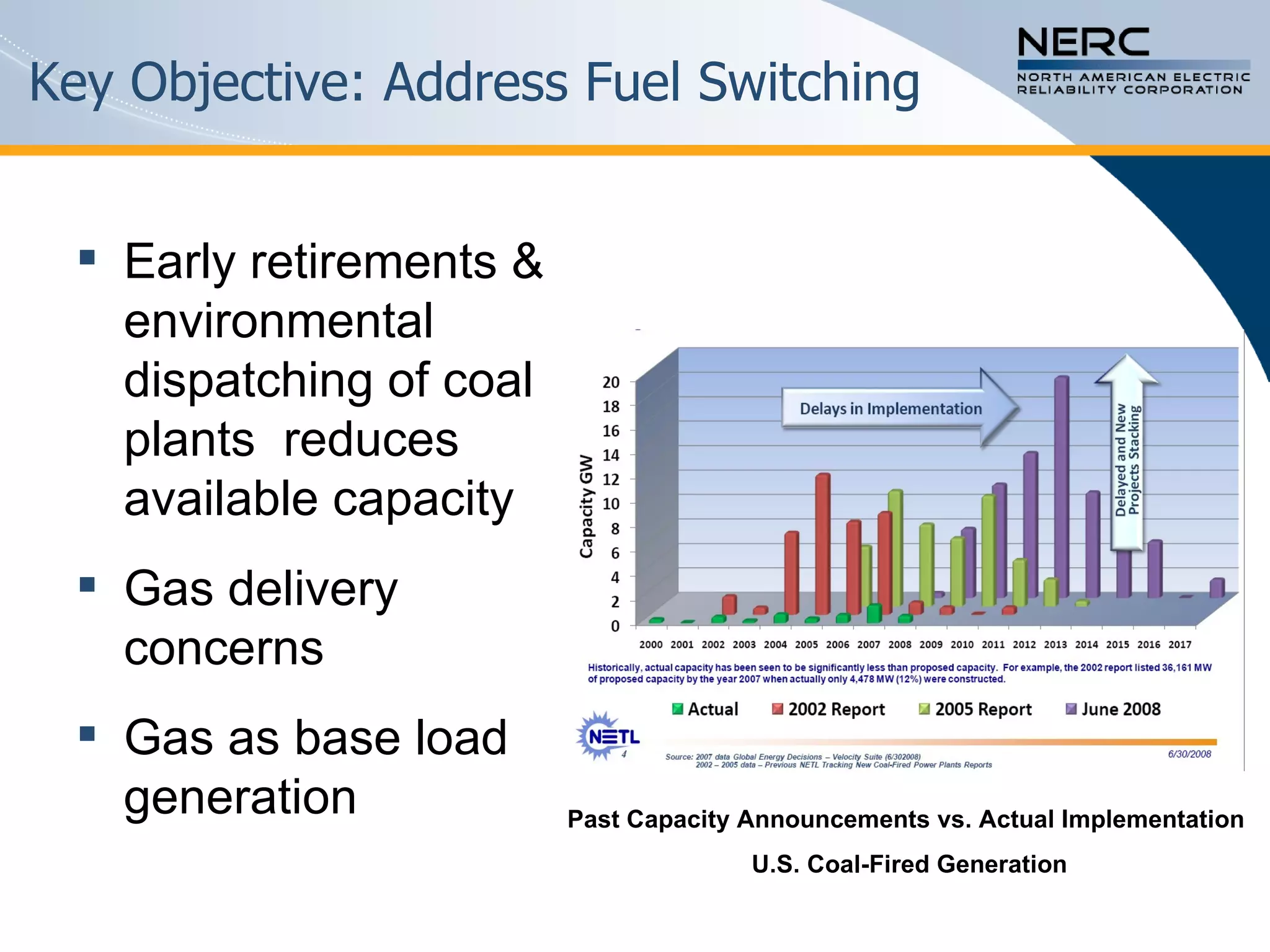
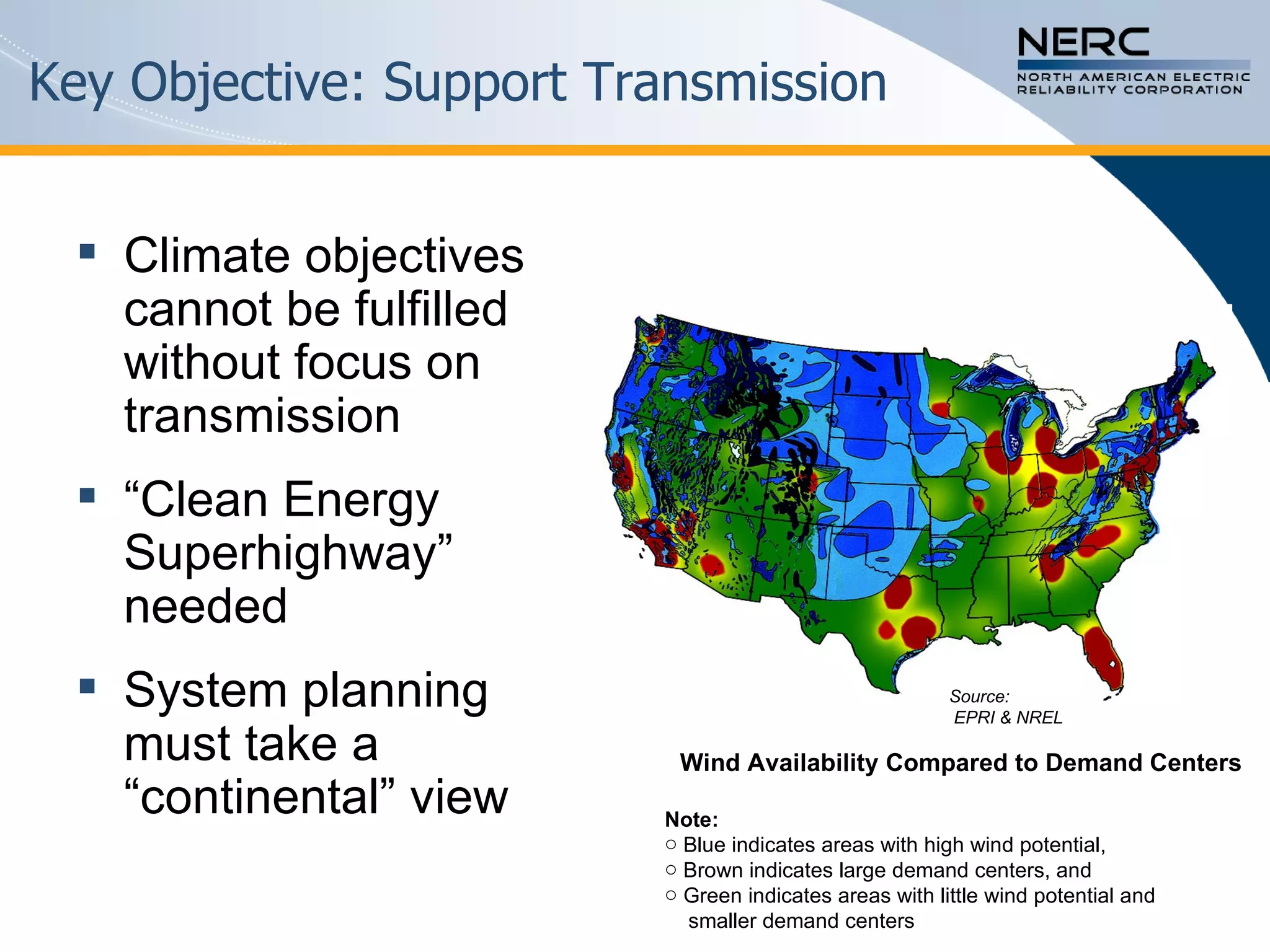
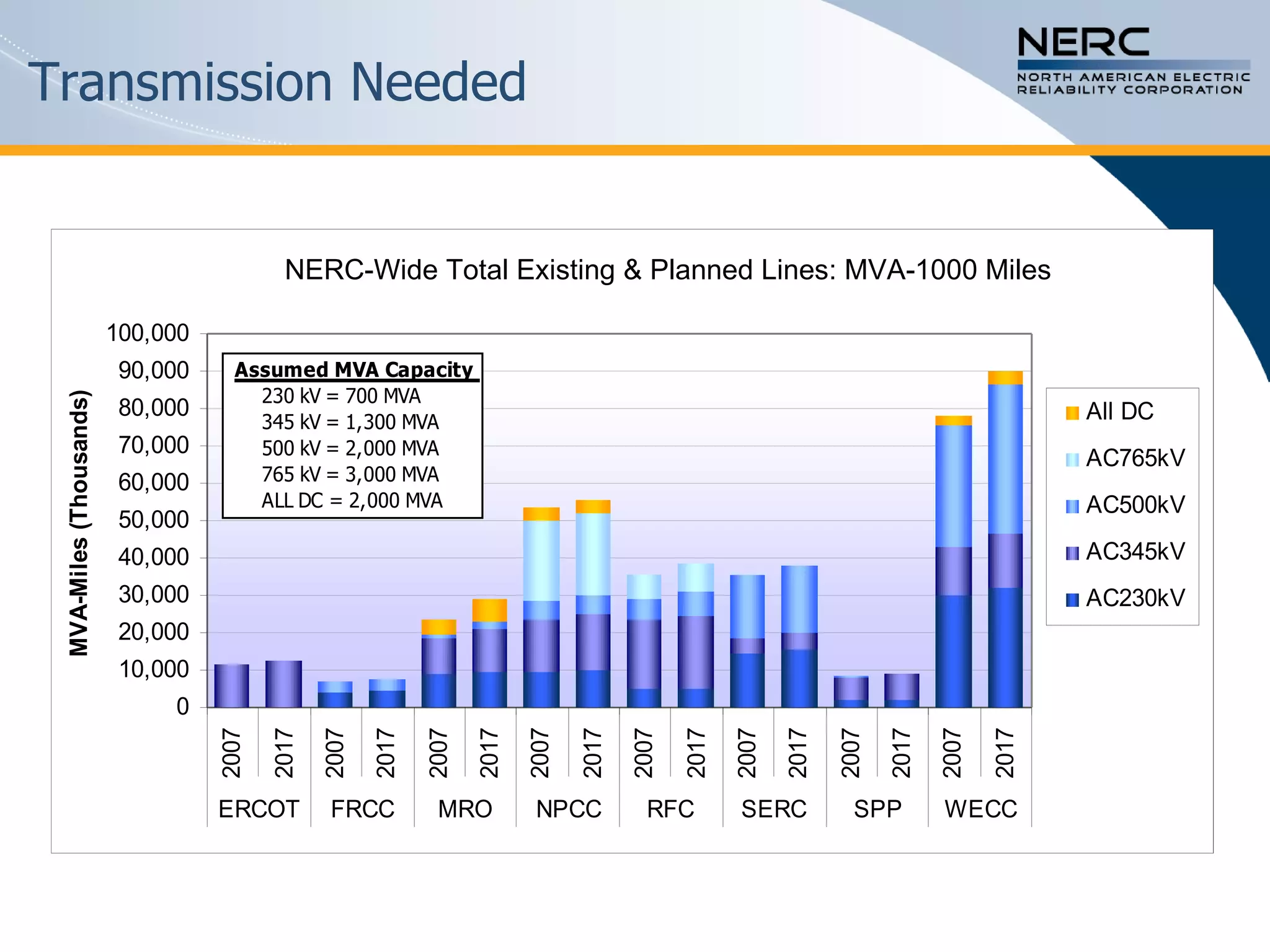
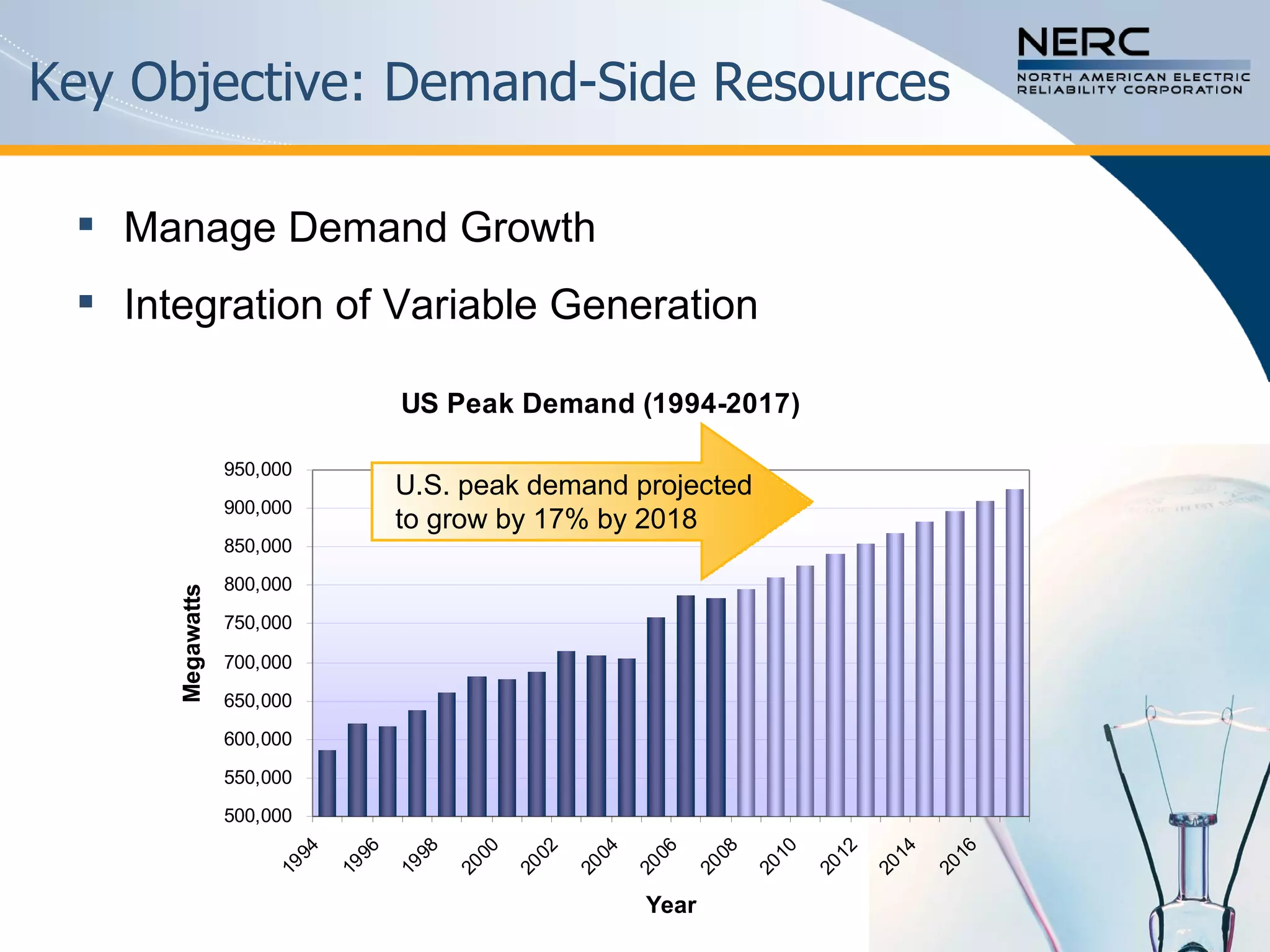
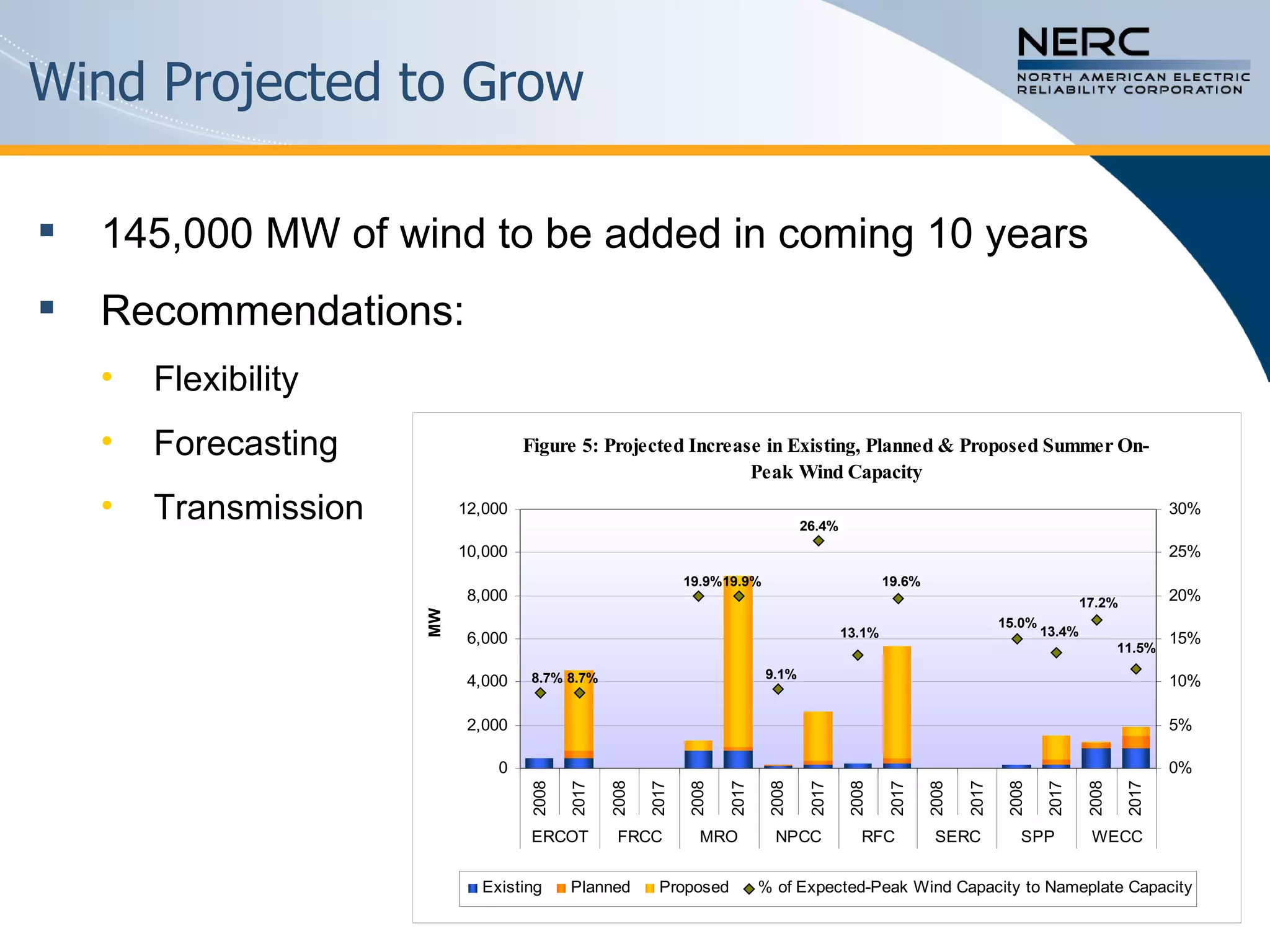
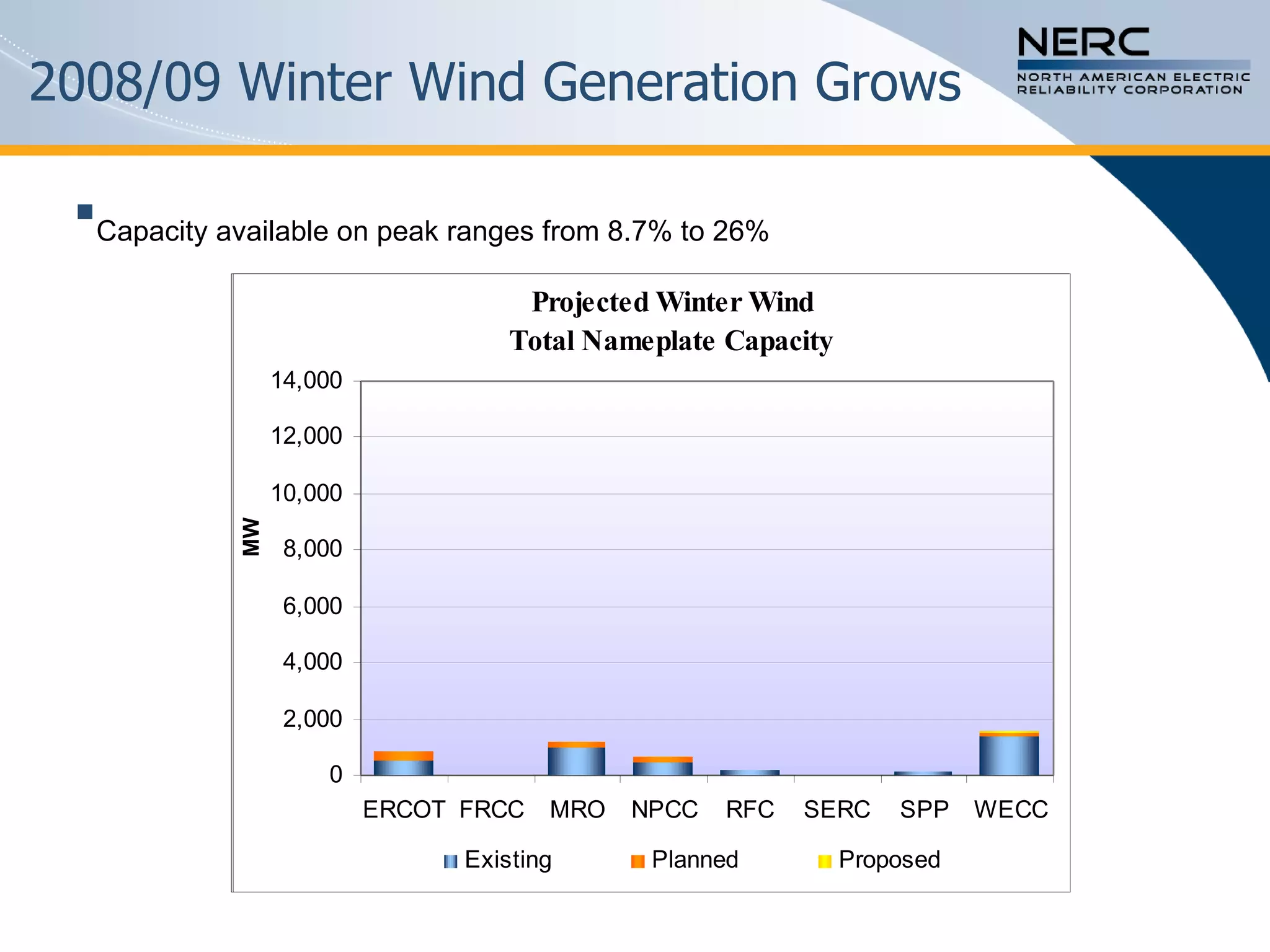
The document discusses the challenges and strategies for enhancing the reliability of the North American bulk power system in the context of renewable energy integration and climate initiatives. It emphasizes the need for improved transmission infrastructure, a diversified fuel mix, and advanced grid technologies to manage growing energy demands and variable generation. Key recommendations include fostering regulatory certainty, enhancing flexibility, and promoting smart grid developments to support reliability and resource management.






![Thank you [email_address] North American Electric Reliability Coordination Director, Inter-Governmental Relations, 202-393-3998](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renewablenc-123974477489-phpapp01/75/Renewable-Nc-18-2048.jpg)