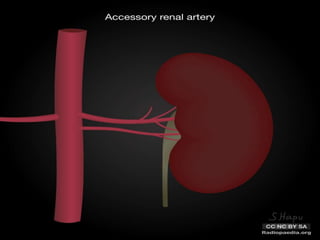
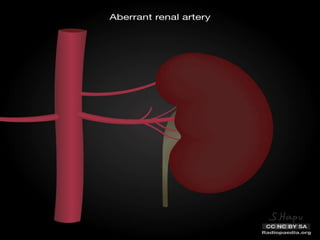
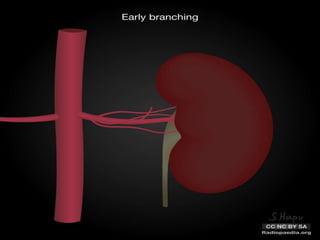
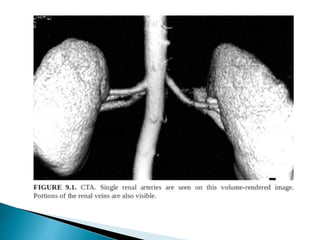
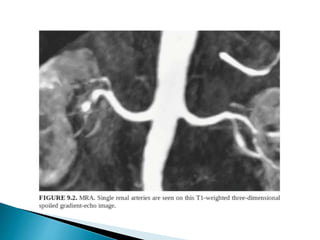
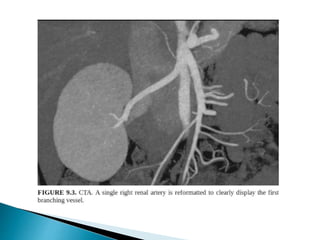
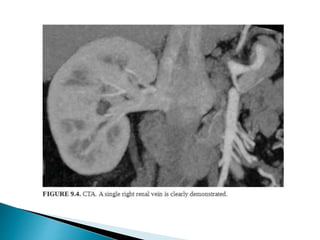
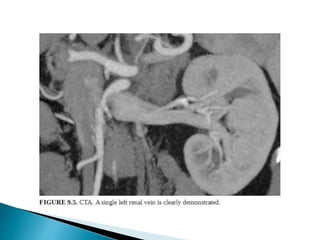
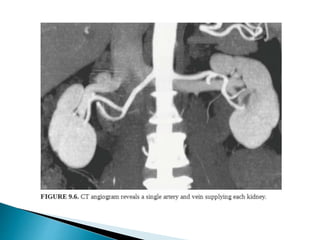
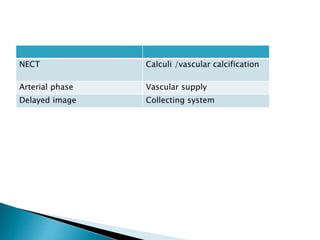
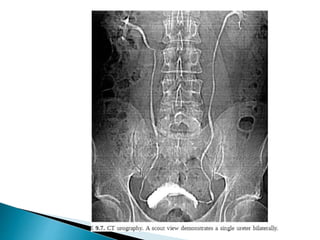
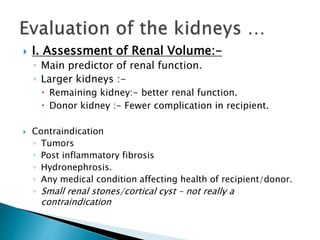
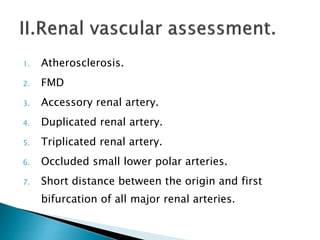
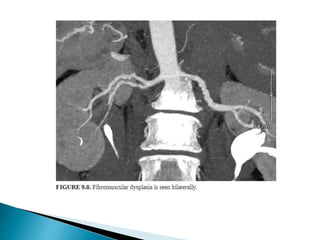
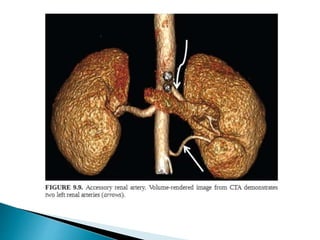
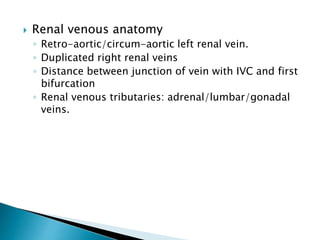
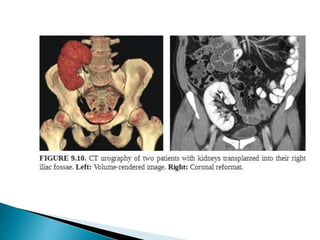
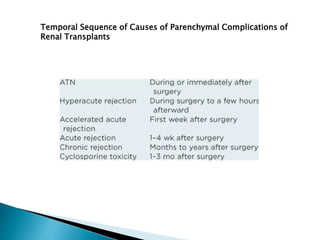
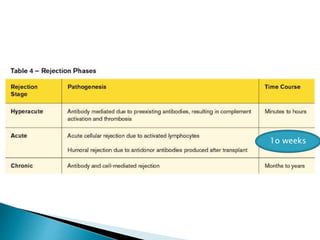
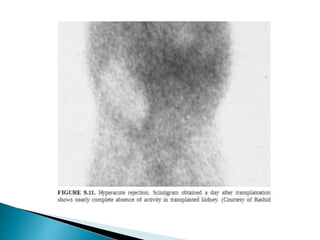
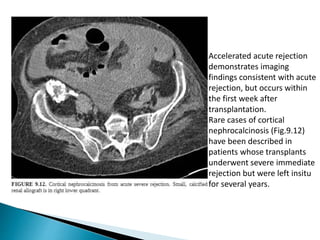
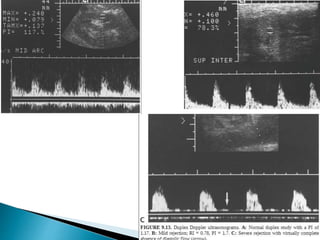
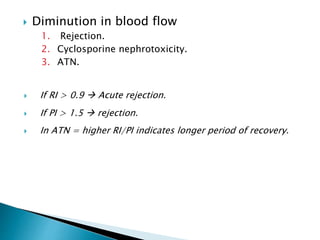
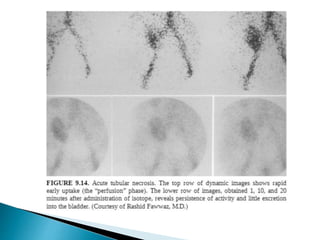
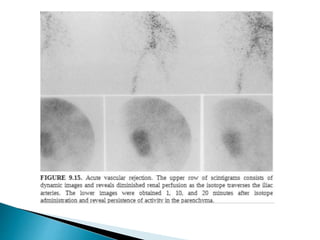
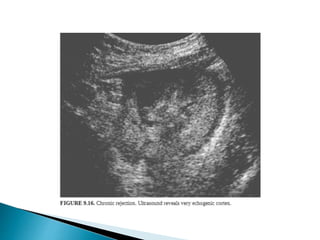
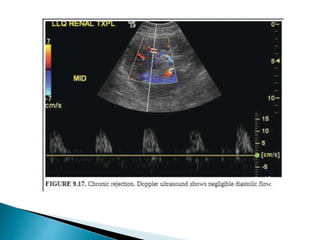
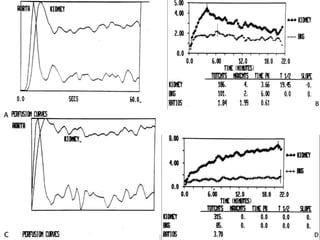
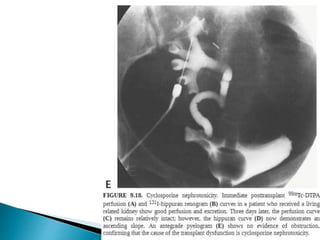
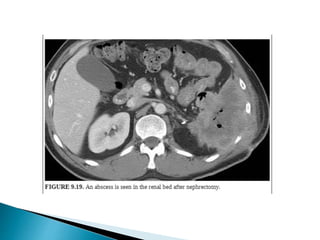
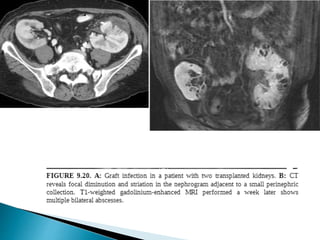
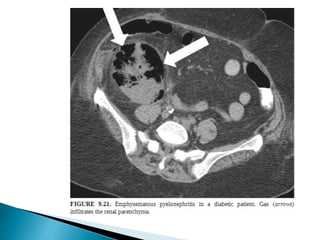
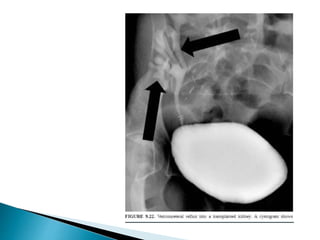
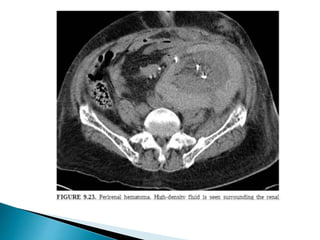
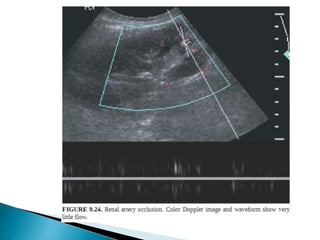
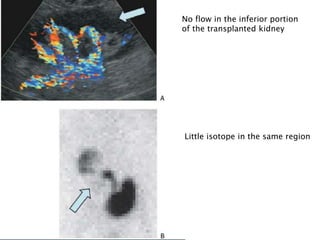
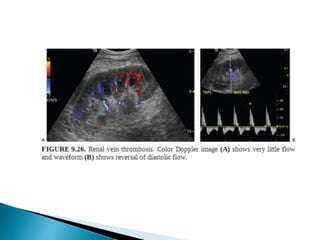
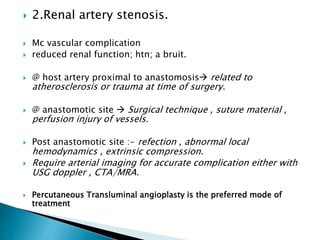
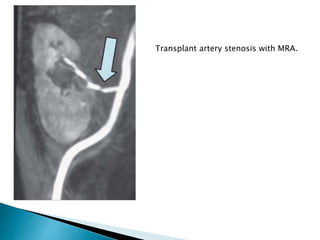
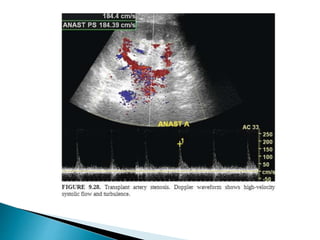
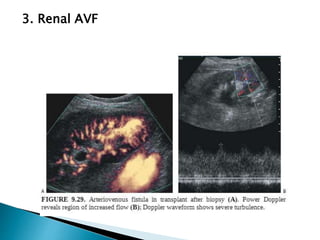
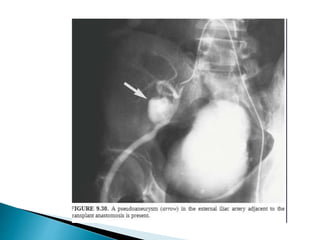
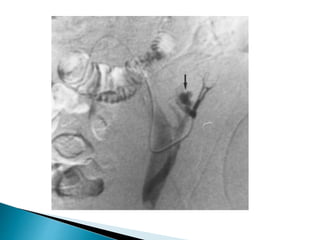
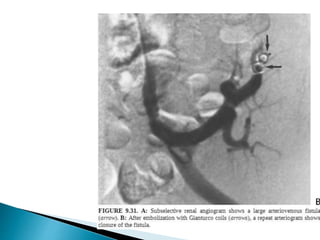
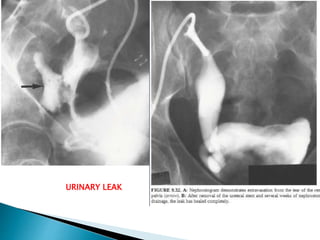
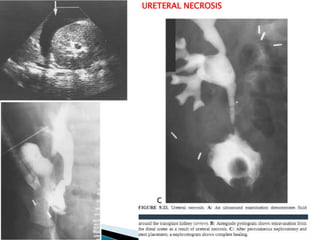
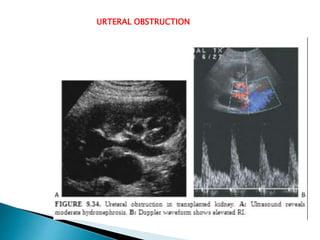
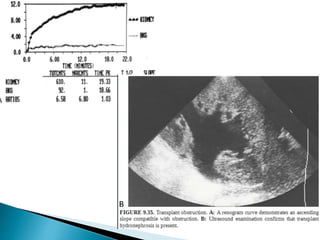
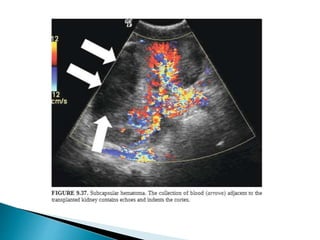
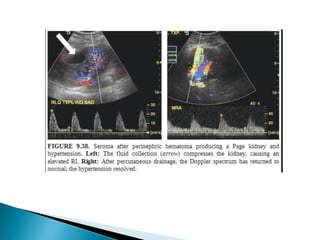
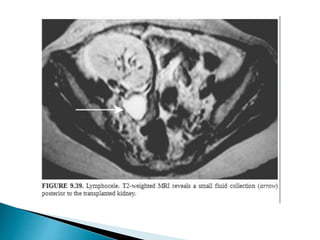
Renal transplantation is the most desirable treatment for end-stage renal disease. Kidneys can come from cadaveric or living donors. A successful transplant depends on careful recipient and donor selection and evaluation, immunosuppression, HLA matching, and the transplant team's skills. Most recipients survive the first year, though long-term function beyond 10 years is less common. Complications include acute tubular necrosis, acute rejection, vascular issues like thrombosis or stenosis, urinary leaks, and increased cancer risk due to immunosuppression. Imaging plays a key role in evaluating donors and recipients and detecting post-transplant complications.