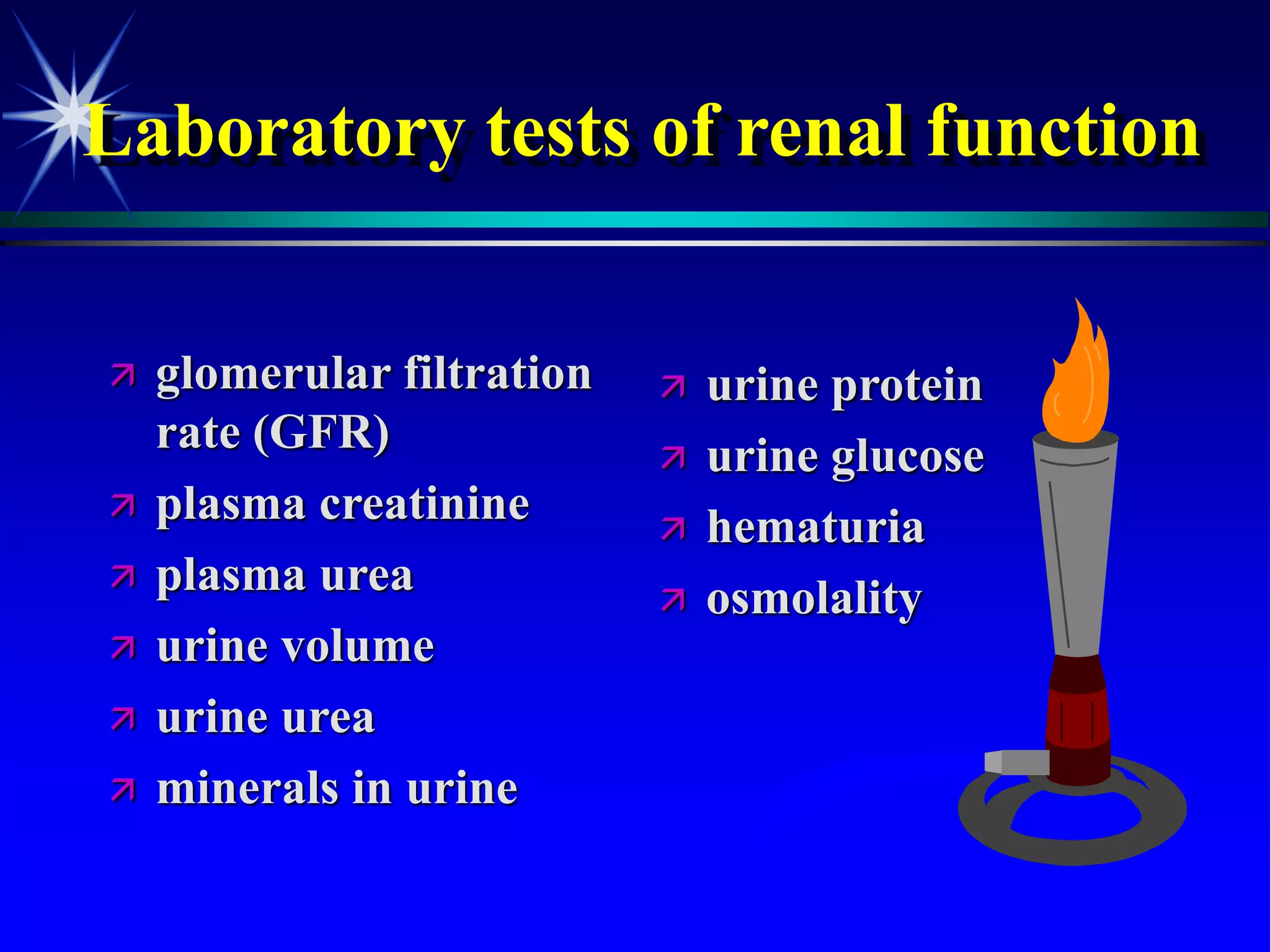
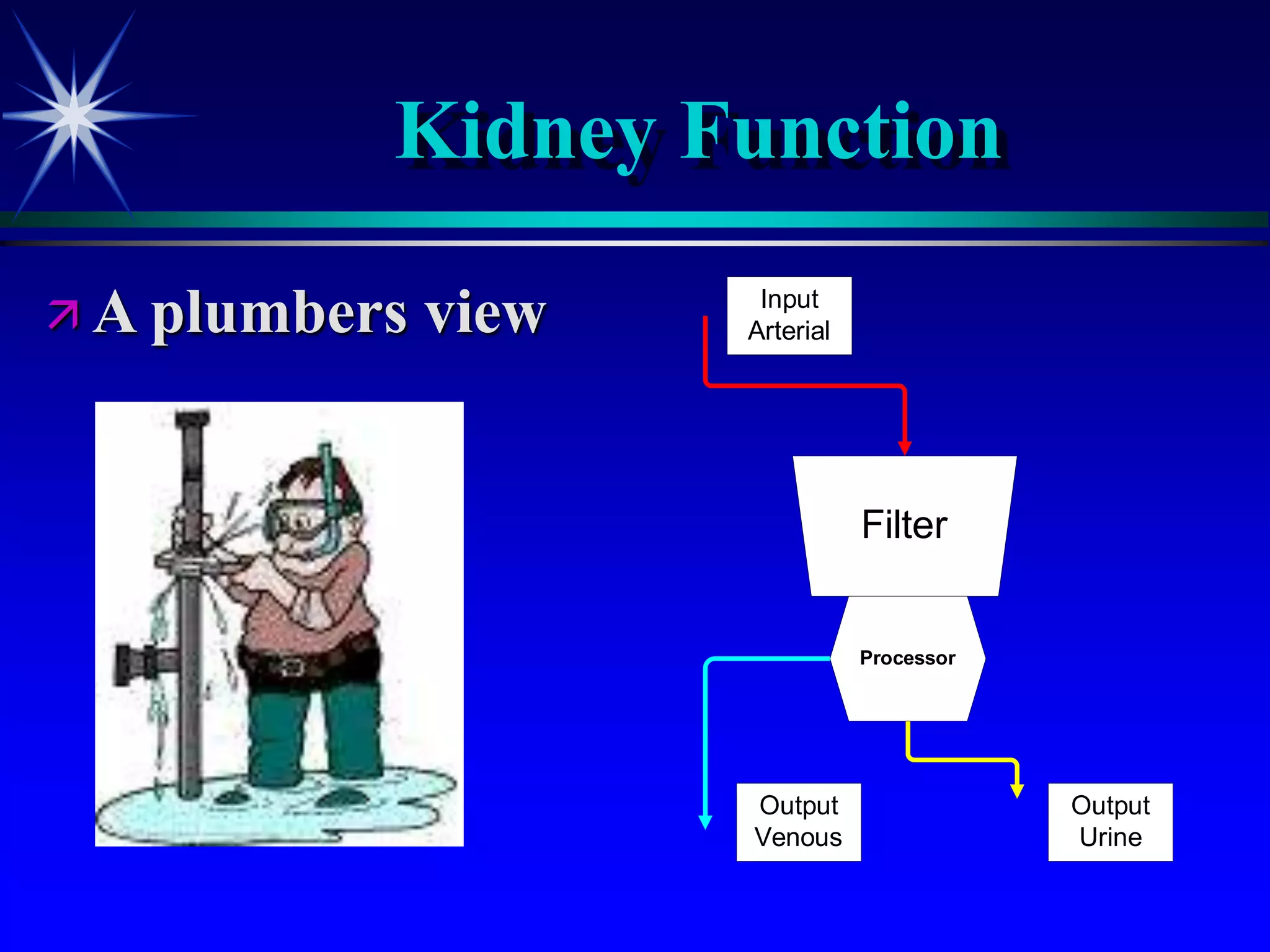
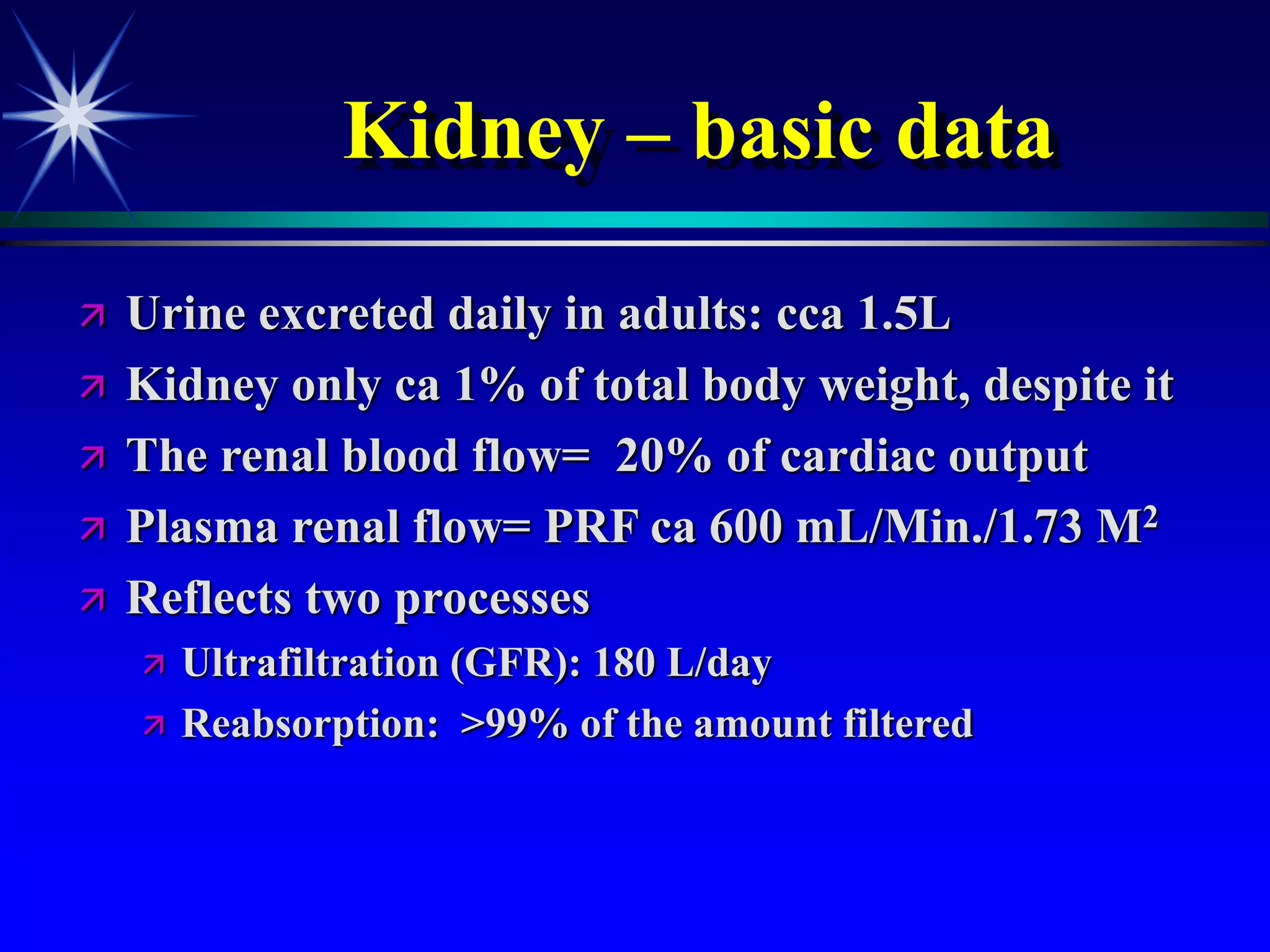
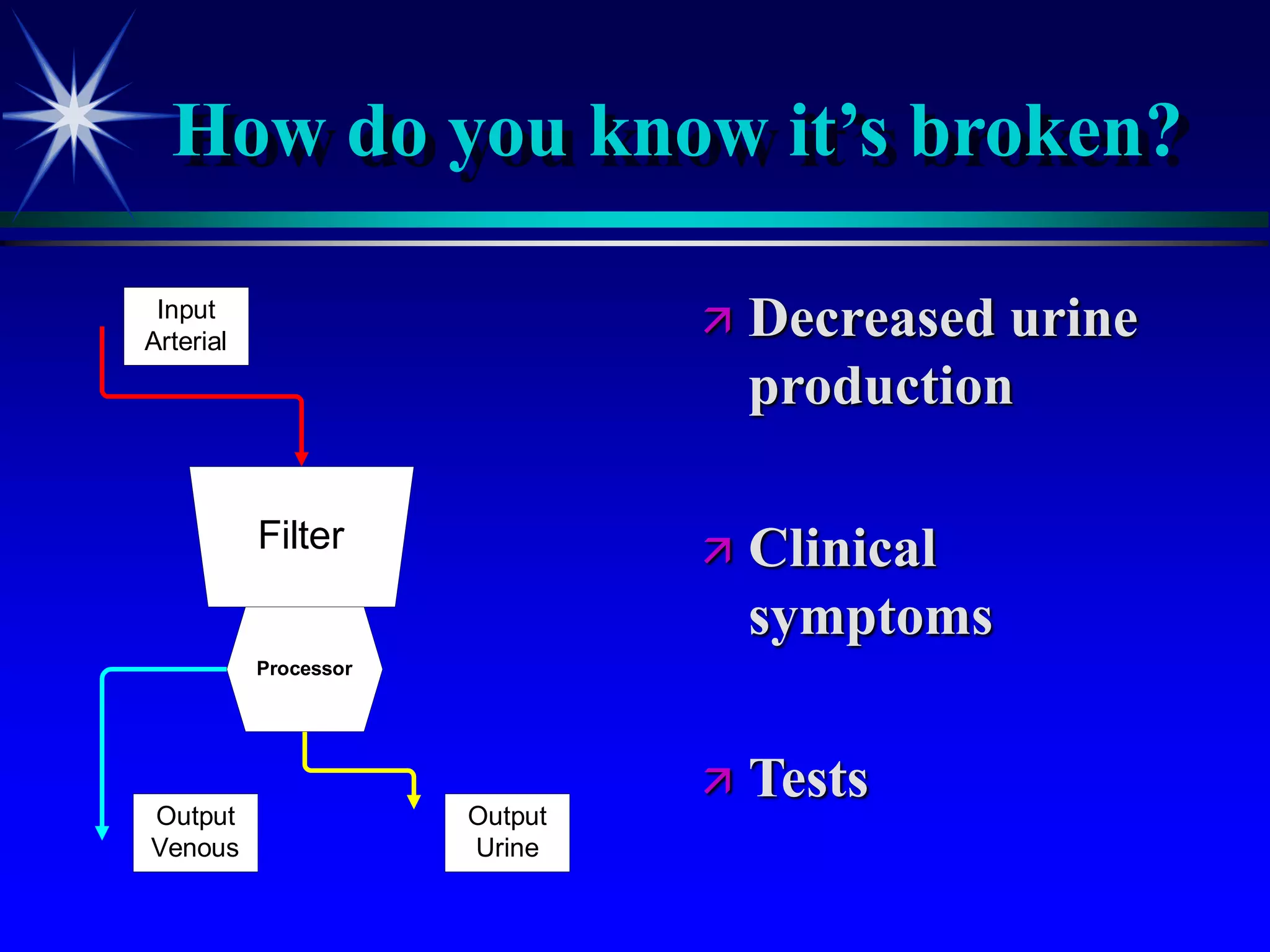
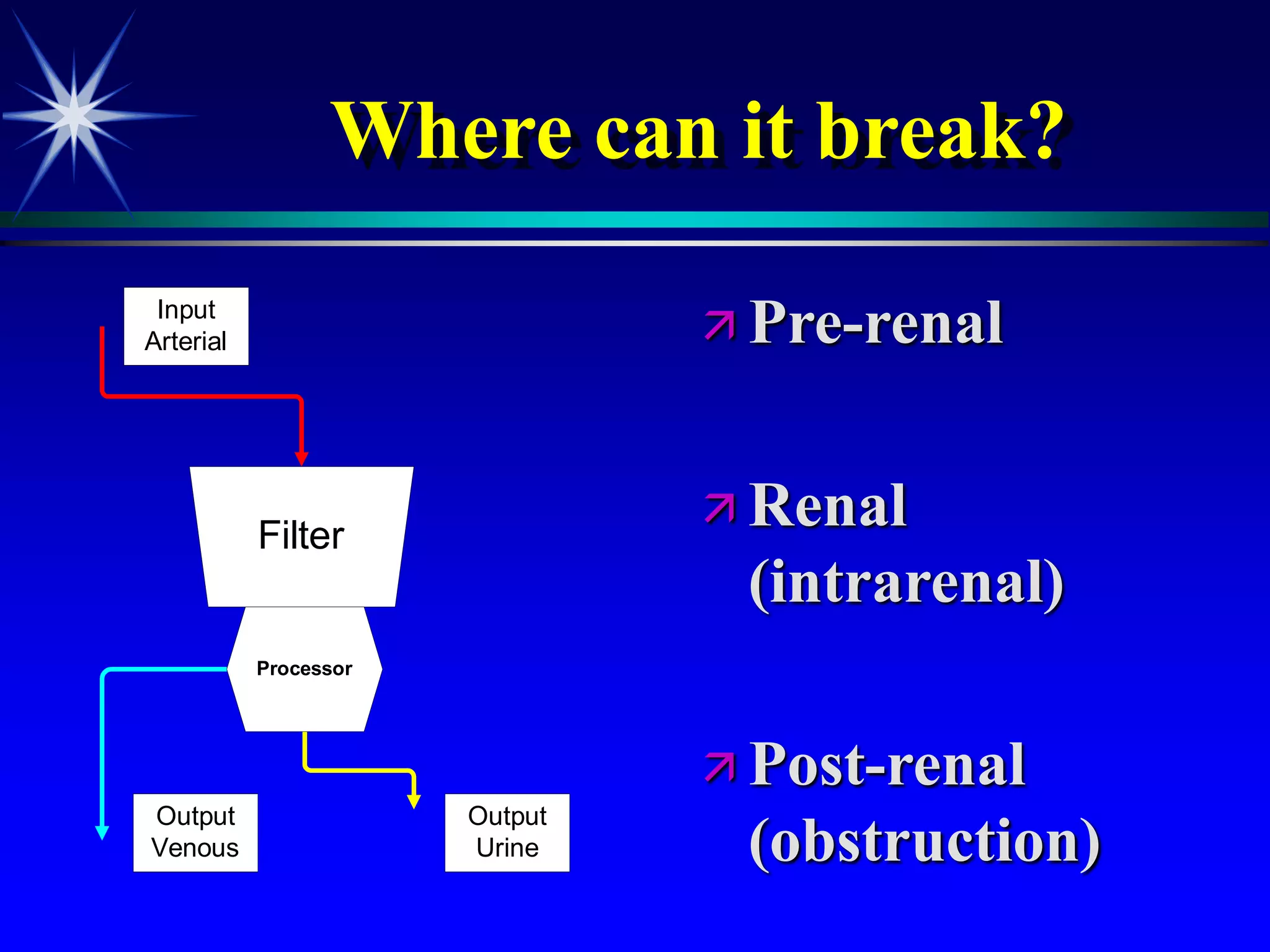
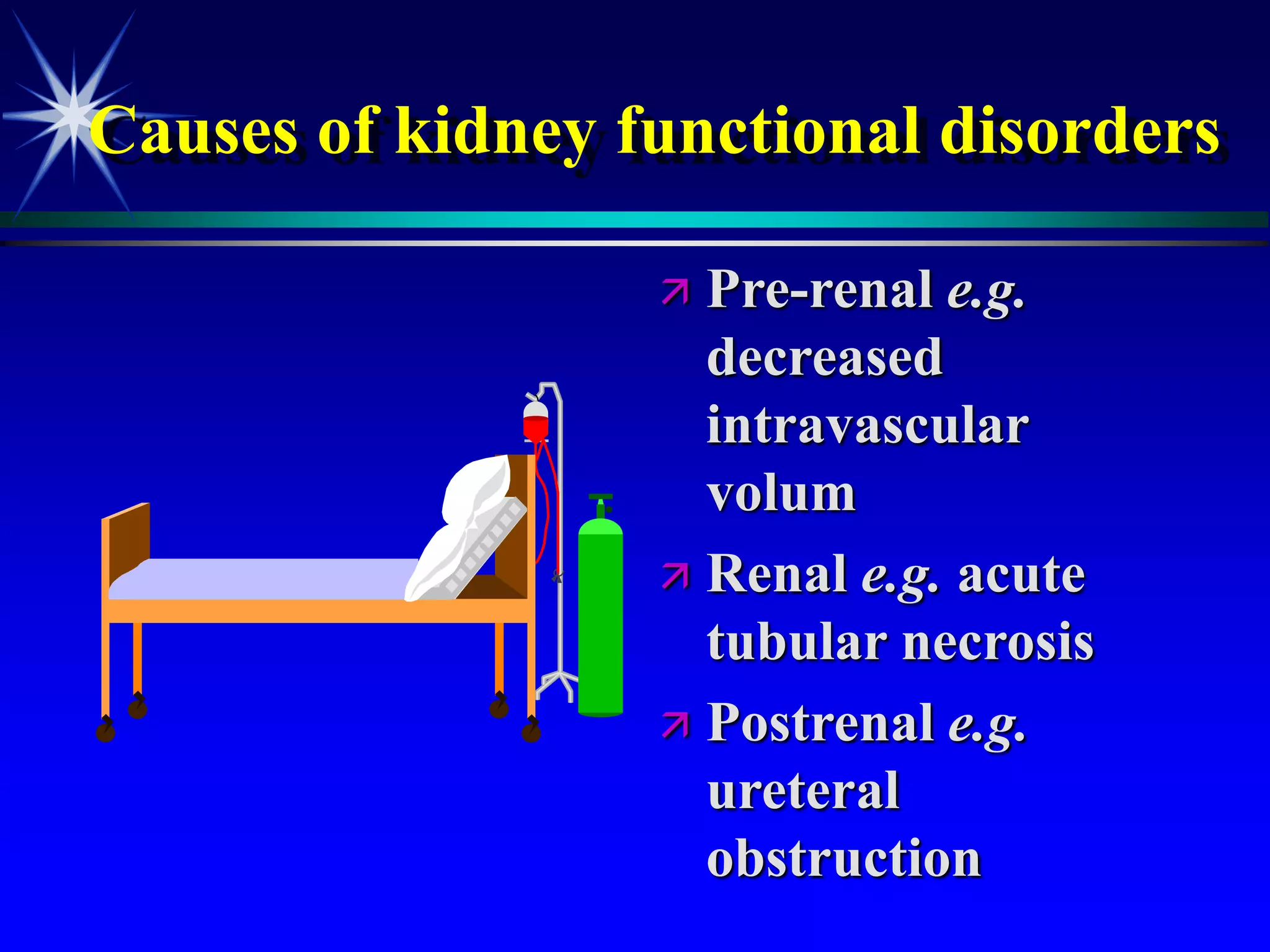
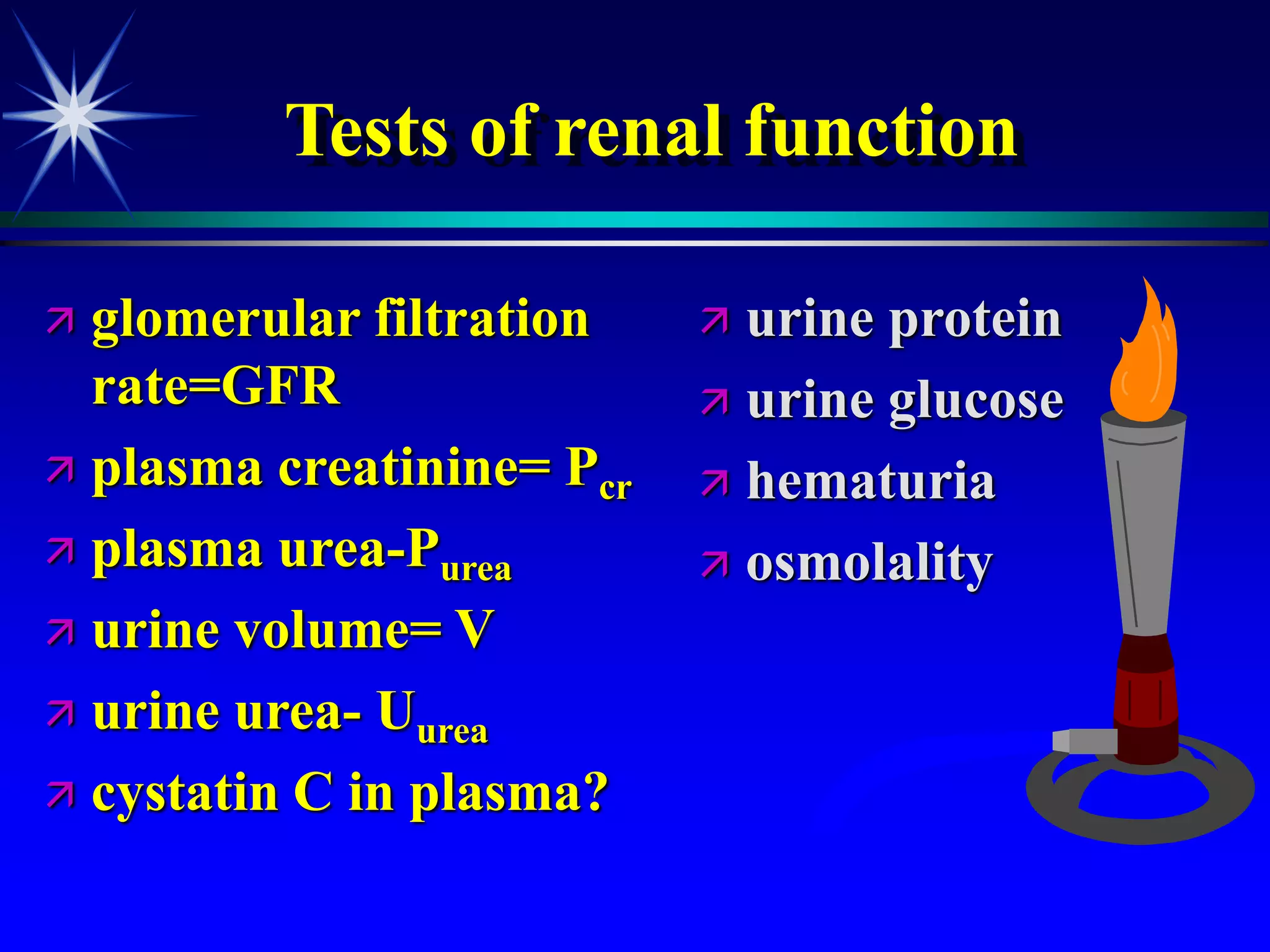
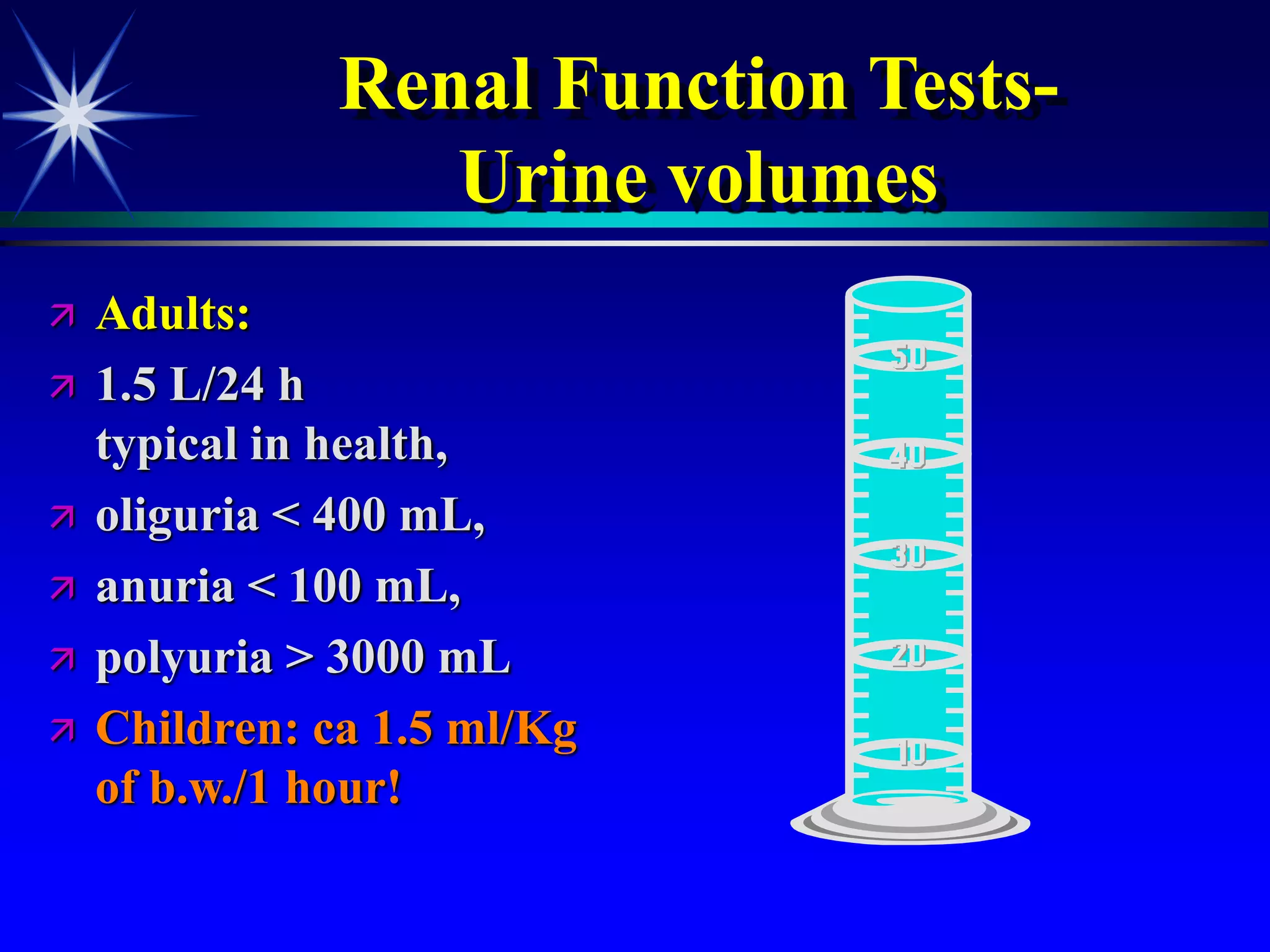
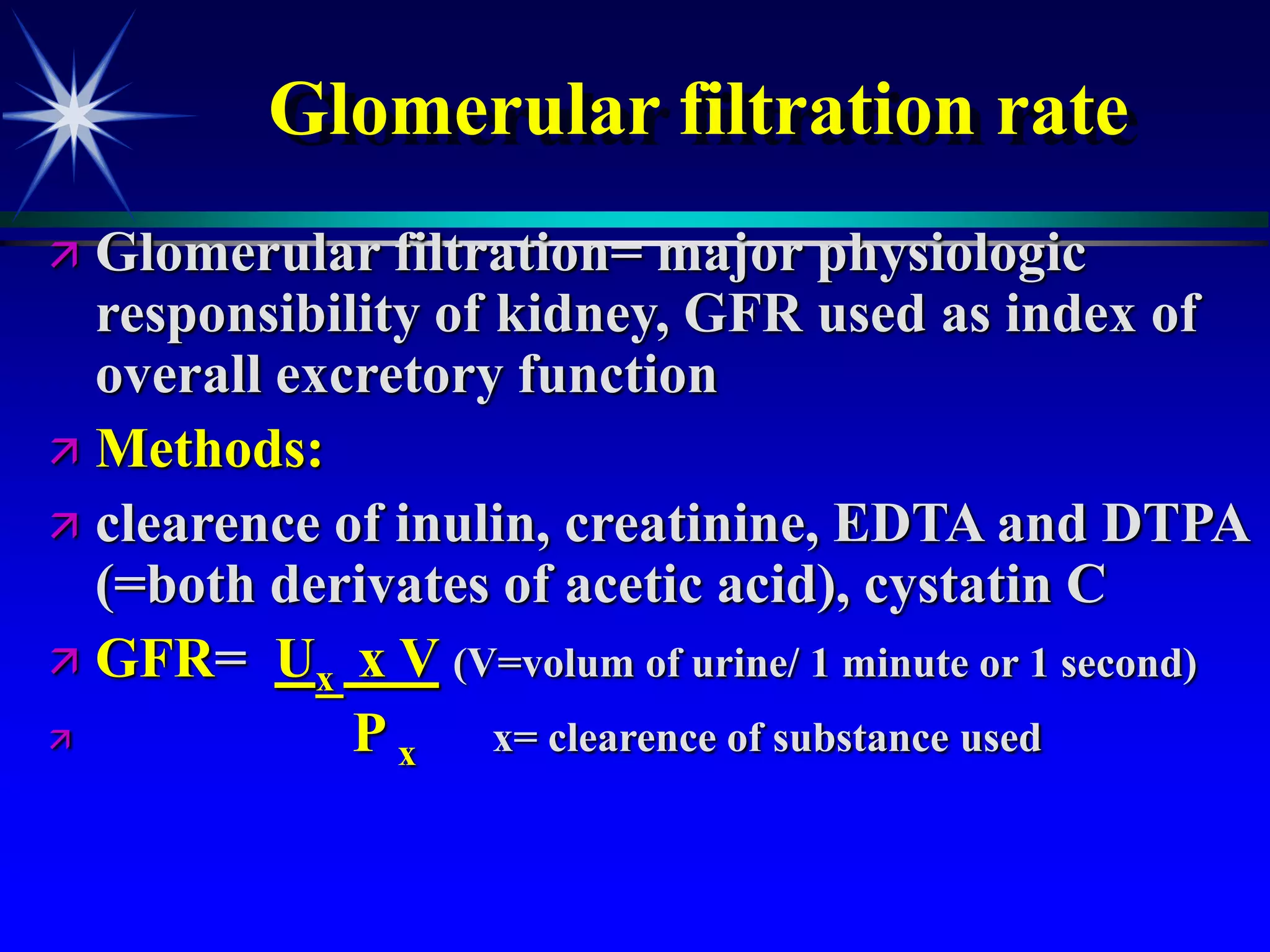
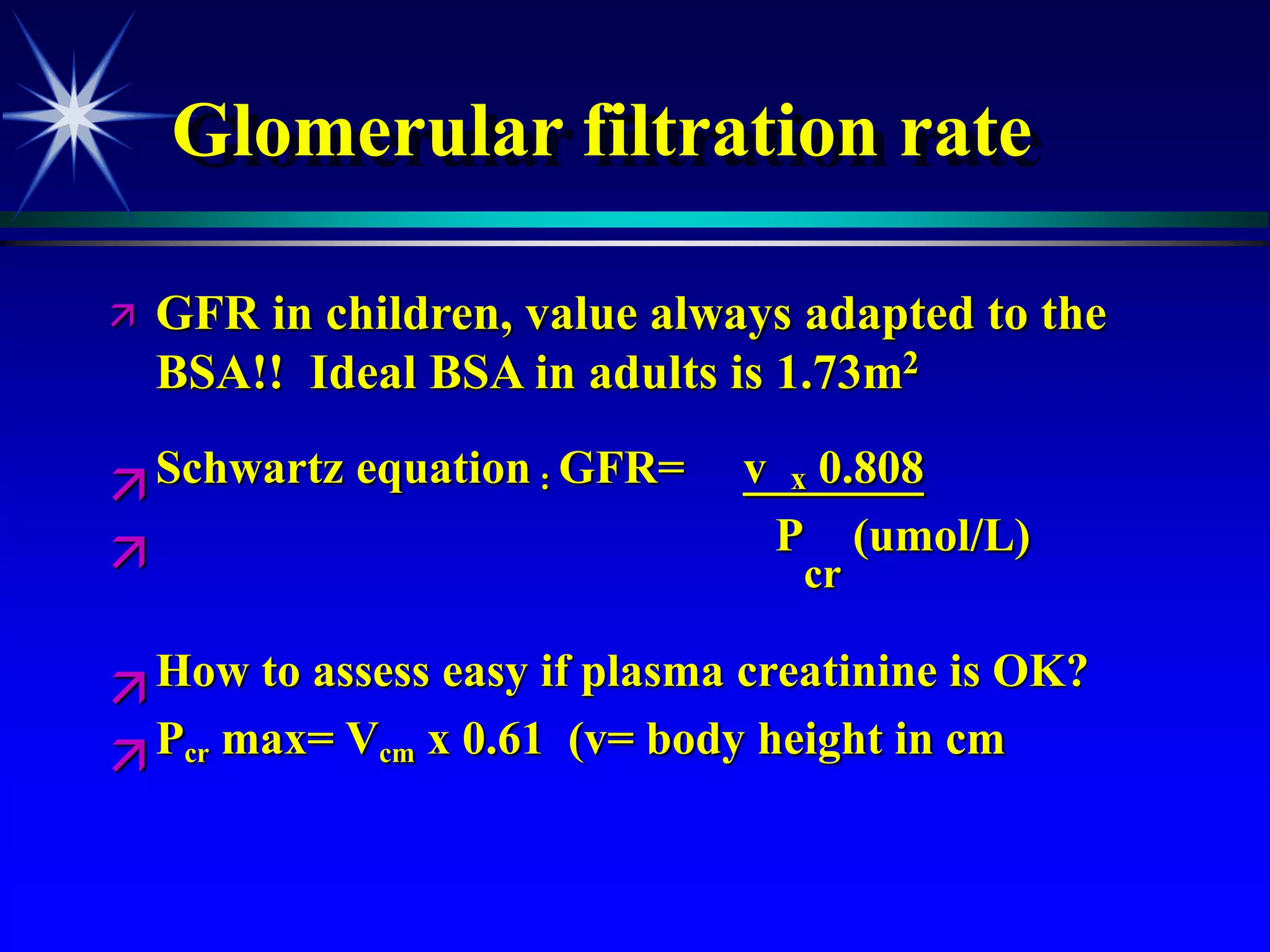
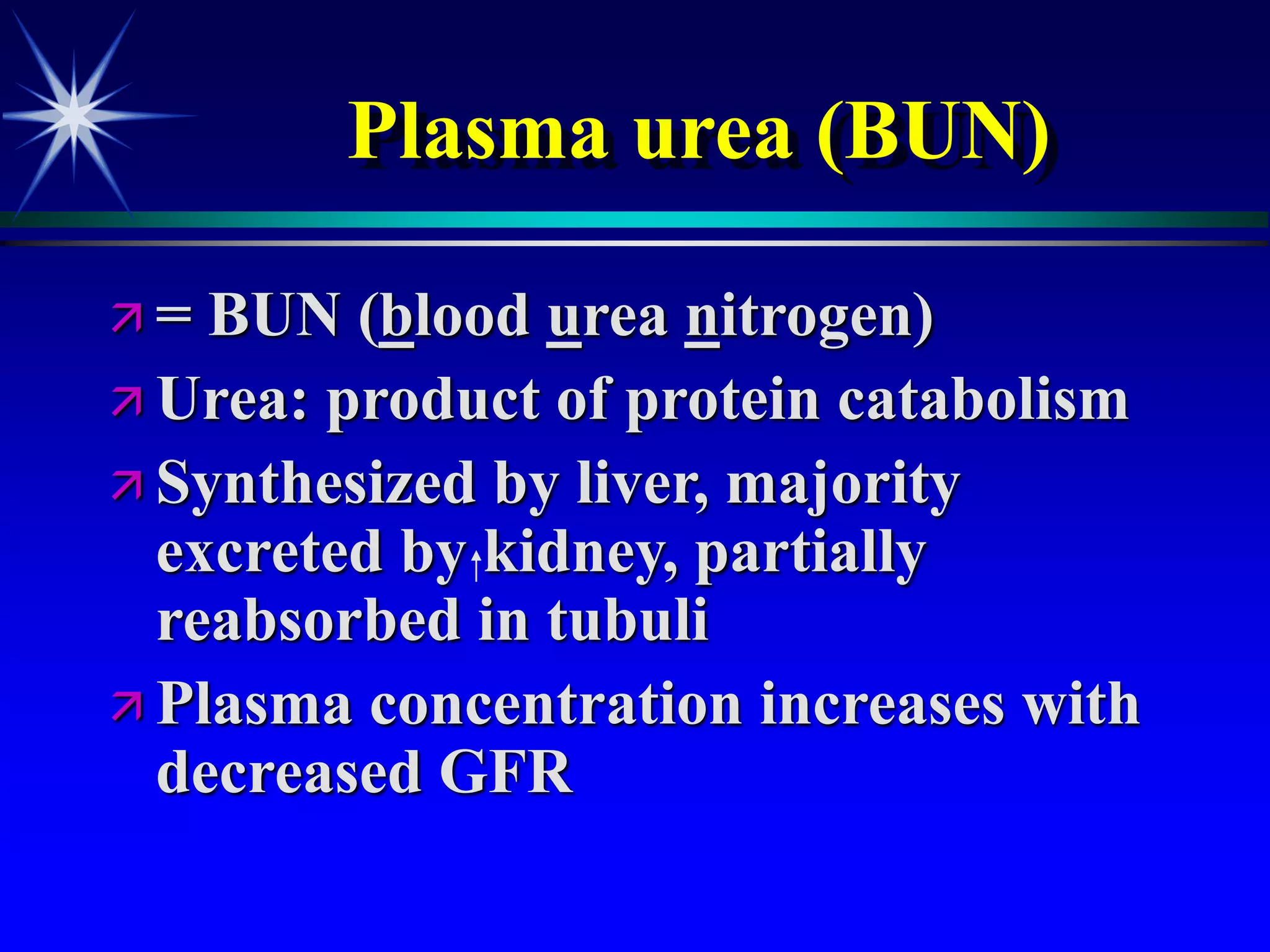
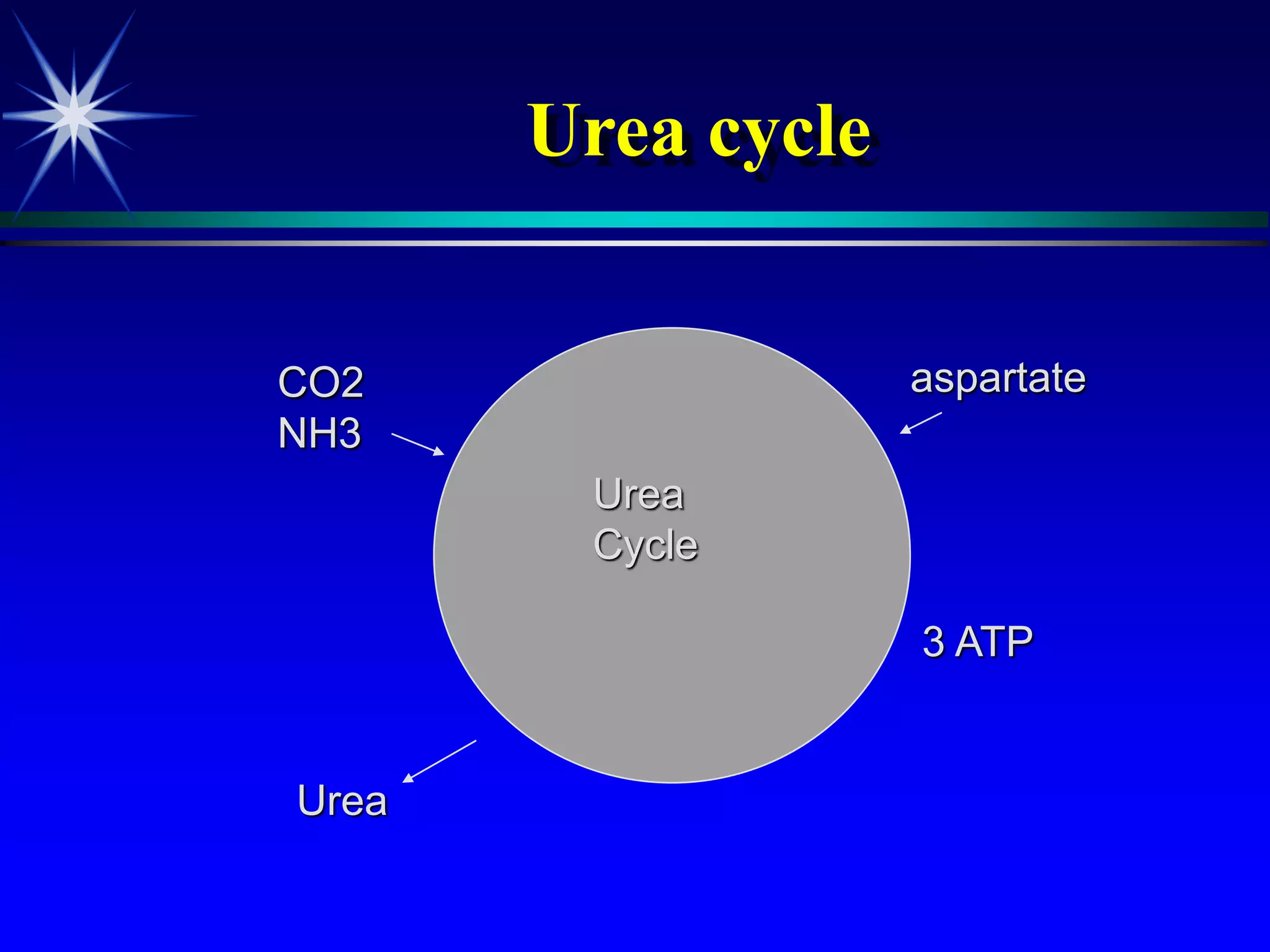
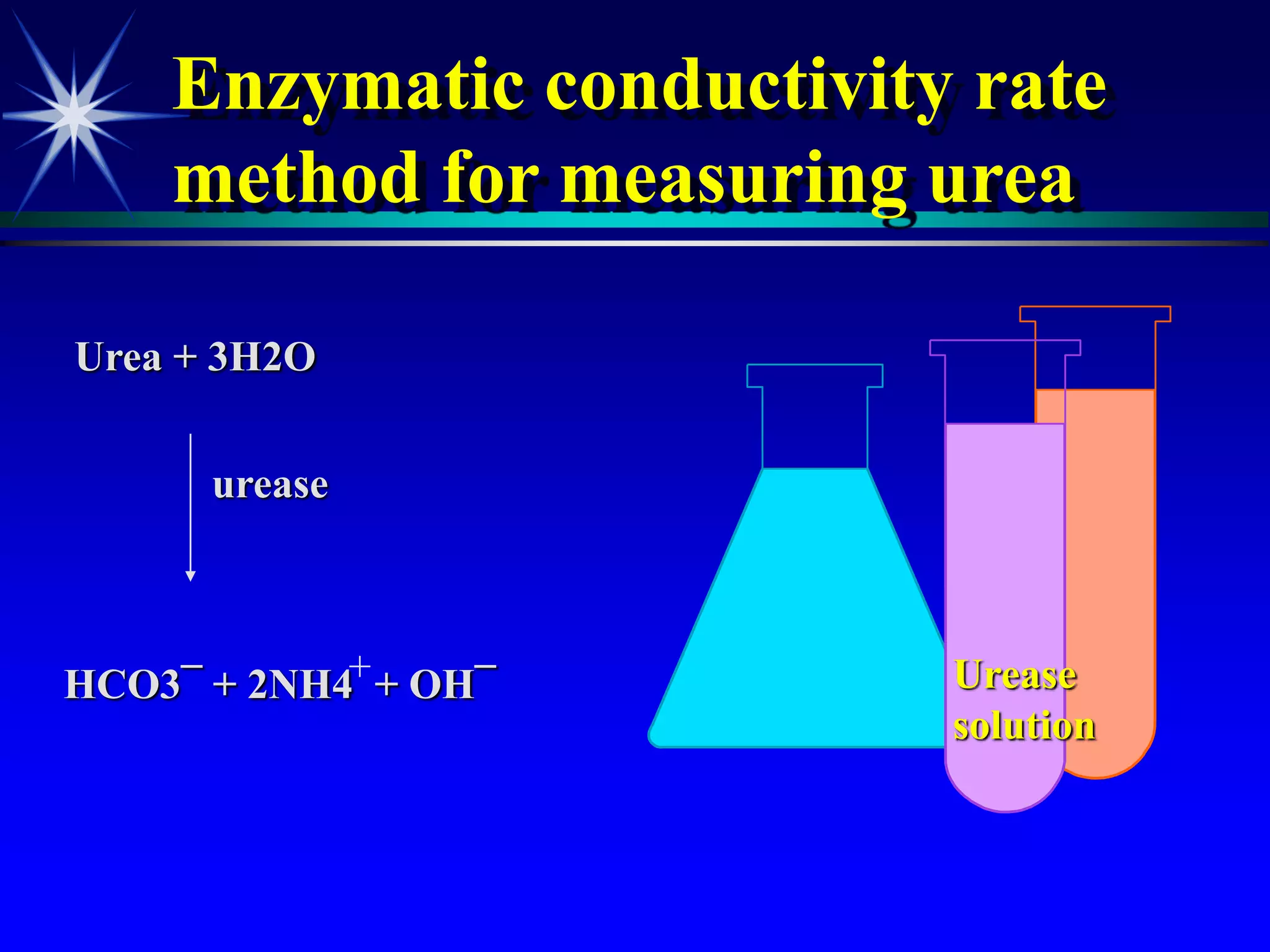
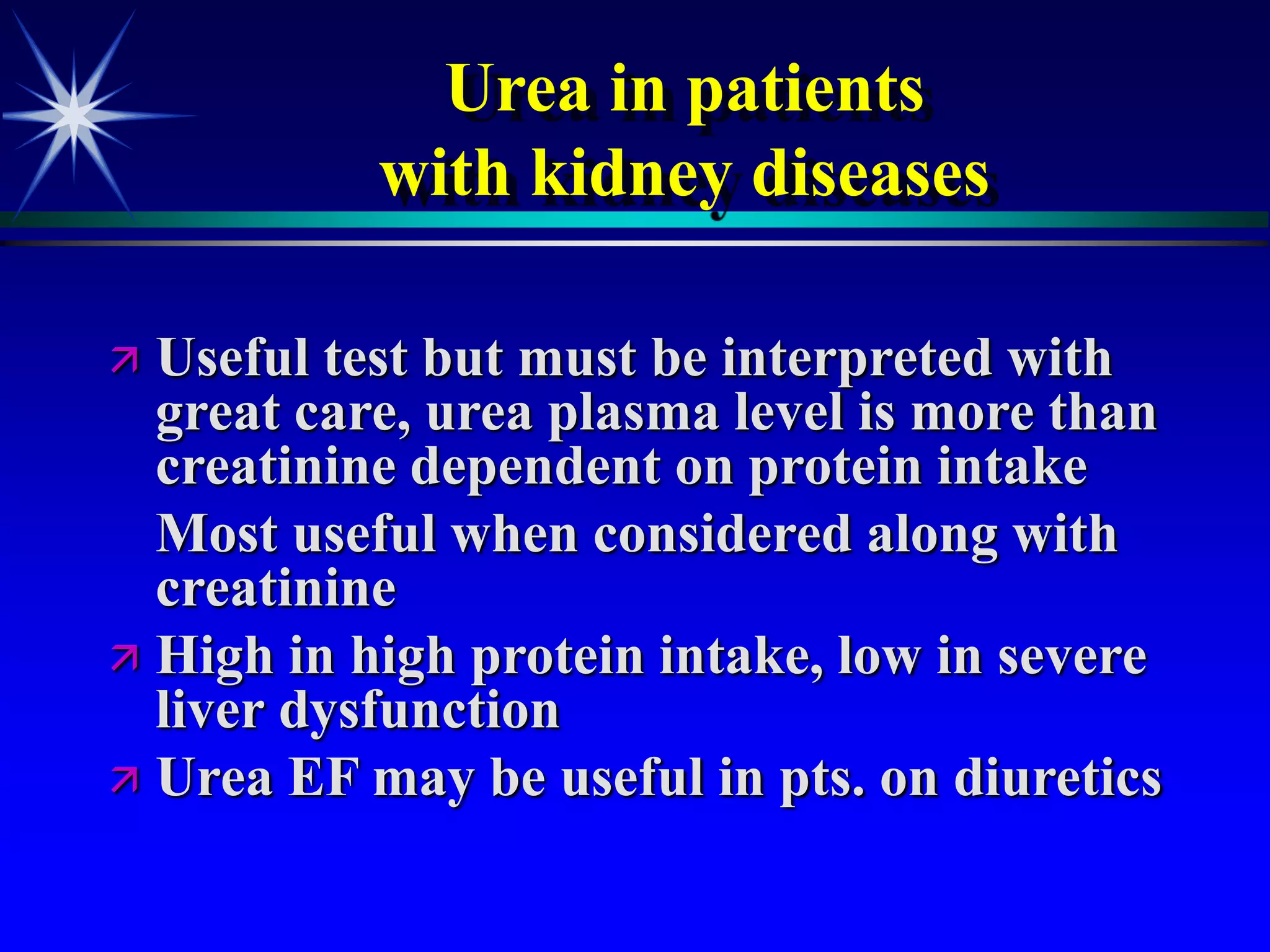
This document provides an overview of kidney function and renal function tests. It discusses the key functions of the kidney in regulating homeostasis, excreting waste, and endocrine functions. It then describes various laboratory tests used to evaluate renal function, including glomerular filtration rate (GFR), plasma creatinine, plasma urea, urine volume, urine protein, and osmolality. It explains how these tests can help detect and monitor kidney damage as well as determine the etiology of renal issues.



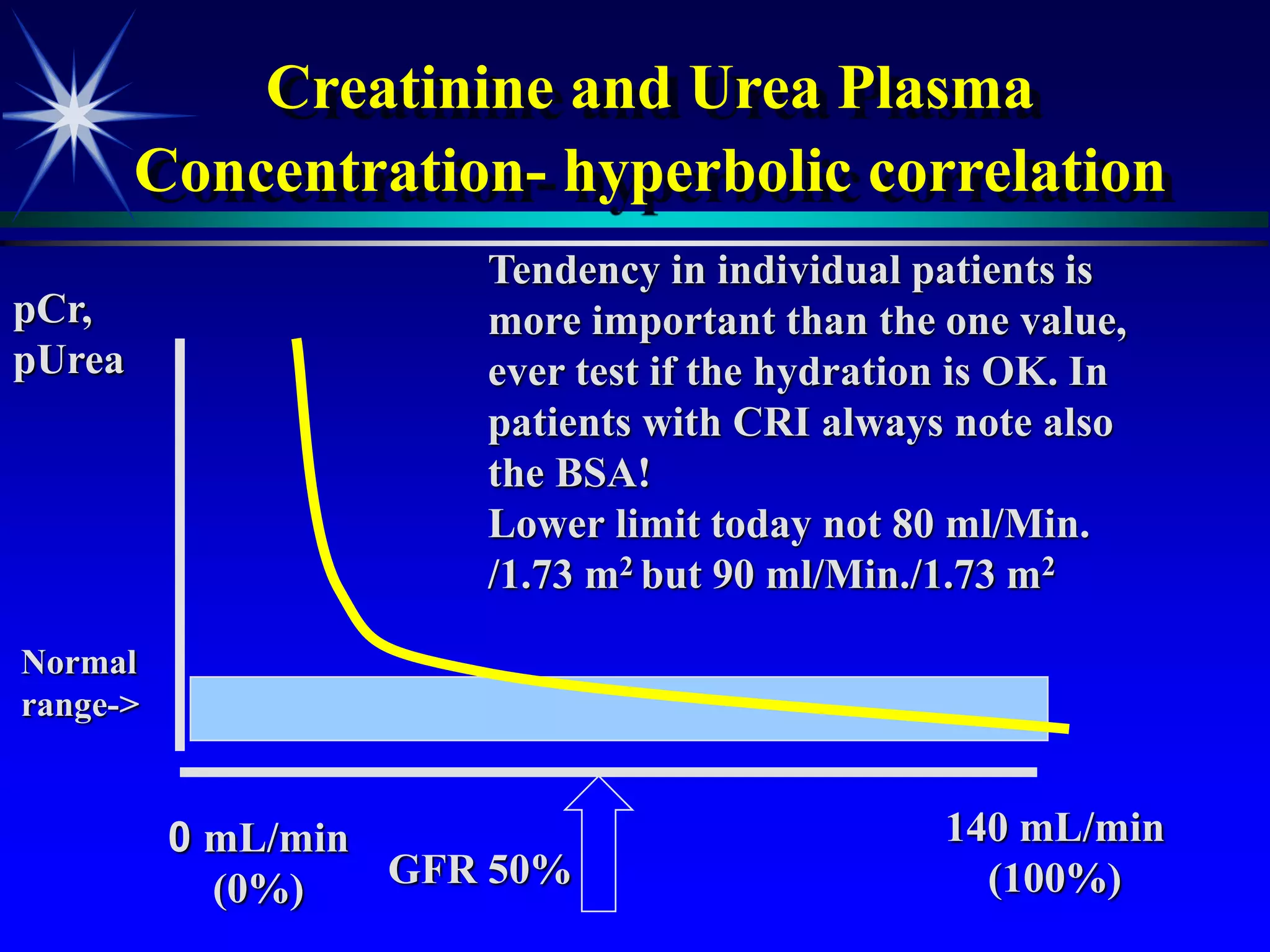
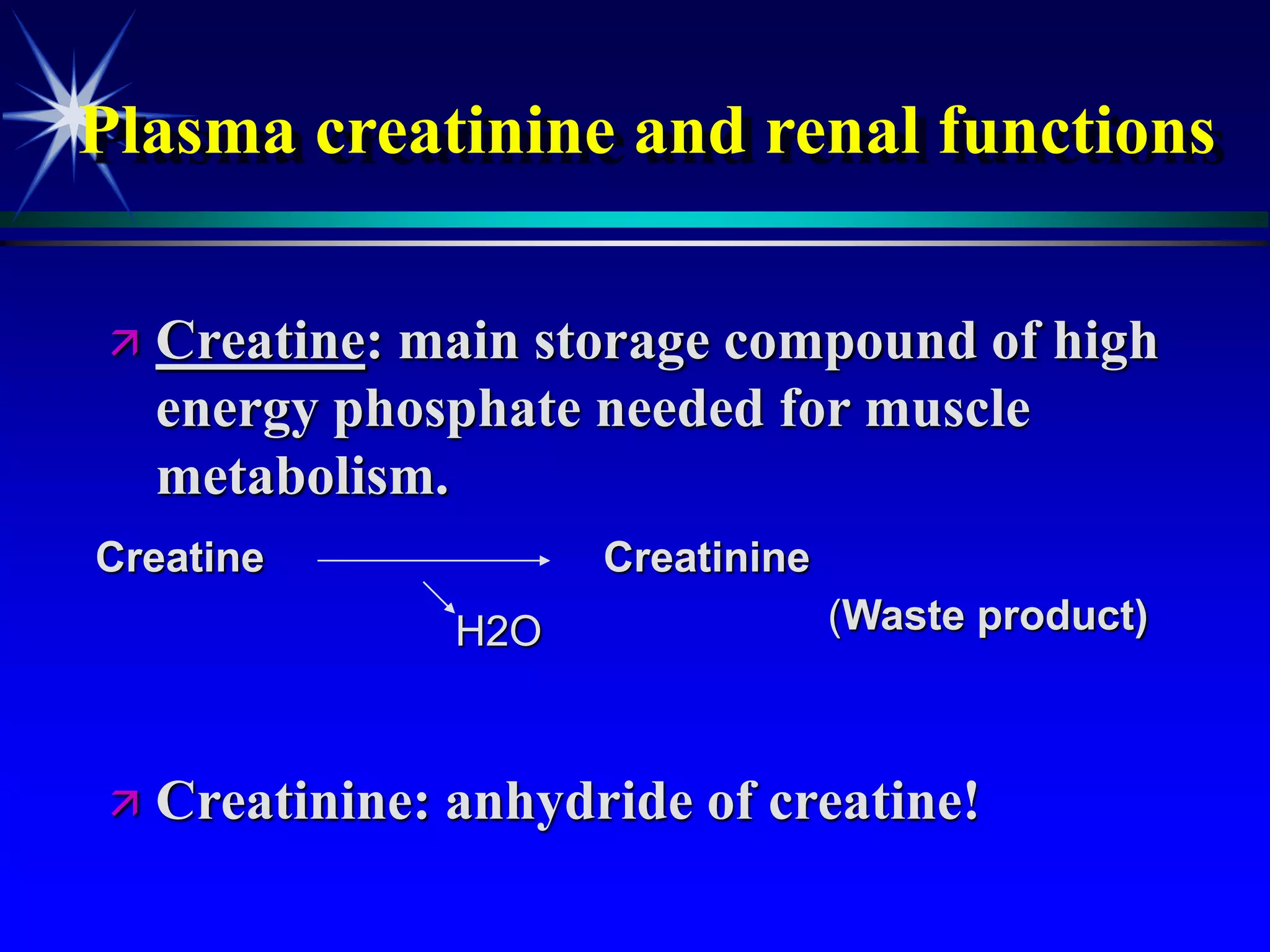
![Plasma creatinine vs. GFR
not linear, hyperbolic correlation!
GFR
[pCreat]
140 mL/min
(100%)
0 mL/min
(0%)
Change within an
individual patient is usually
more important than the
absolute value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renalfunctions-230828132717-1f572106/75/Renal-functions-ppt-22-2048.jpg)