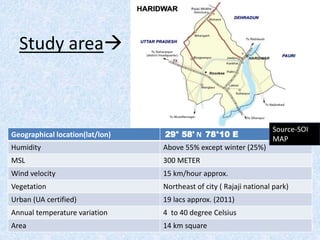
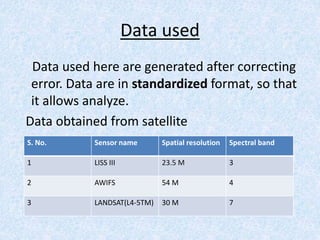
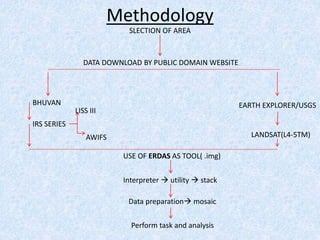
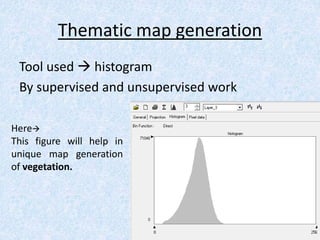
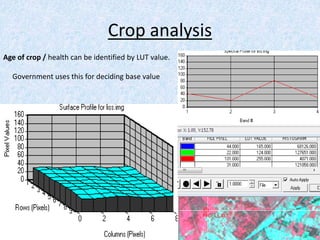
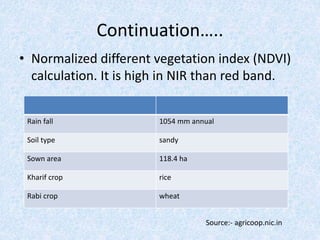
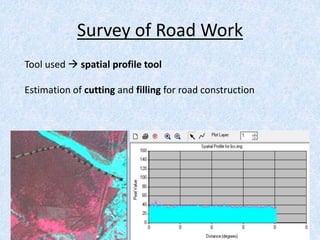
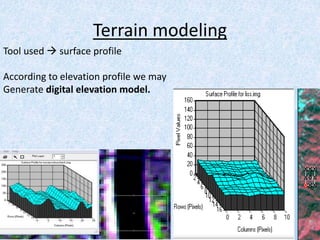
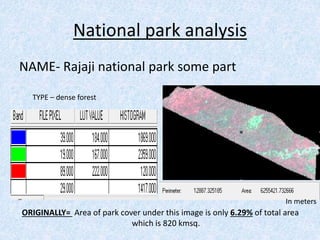
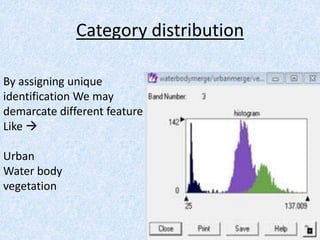
This report summarizes the analysis of satellite imagery for an area in India located at 29° 58' N 78°10 E. Three methods of remote sensing analysis were used: visual interpretation, digital analysis with Erdas Imagine, and classification of land features. Key findings include identification of urban areas, water bodies, vegetation/crops, and man-made structures. Crop analysis identified rice and wheat fields and estimated harvest amounts. River pollution analysis used reflectance values. Road construction needs were assessed using spatial and surface profiling tools. The study area and different land categories were delineated. Changes over time were observed using Landsat images from 1999 to 2003. Remote sensing allowed efficient land use planning and modeling of the terrain.