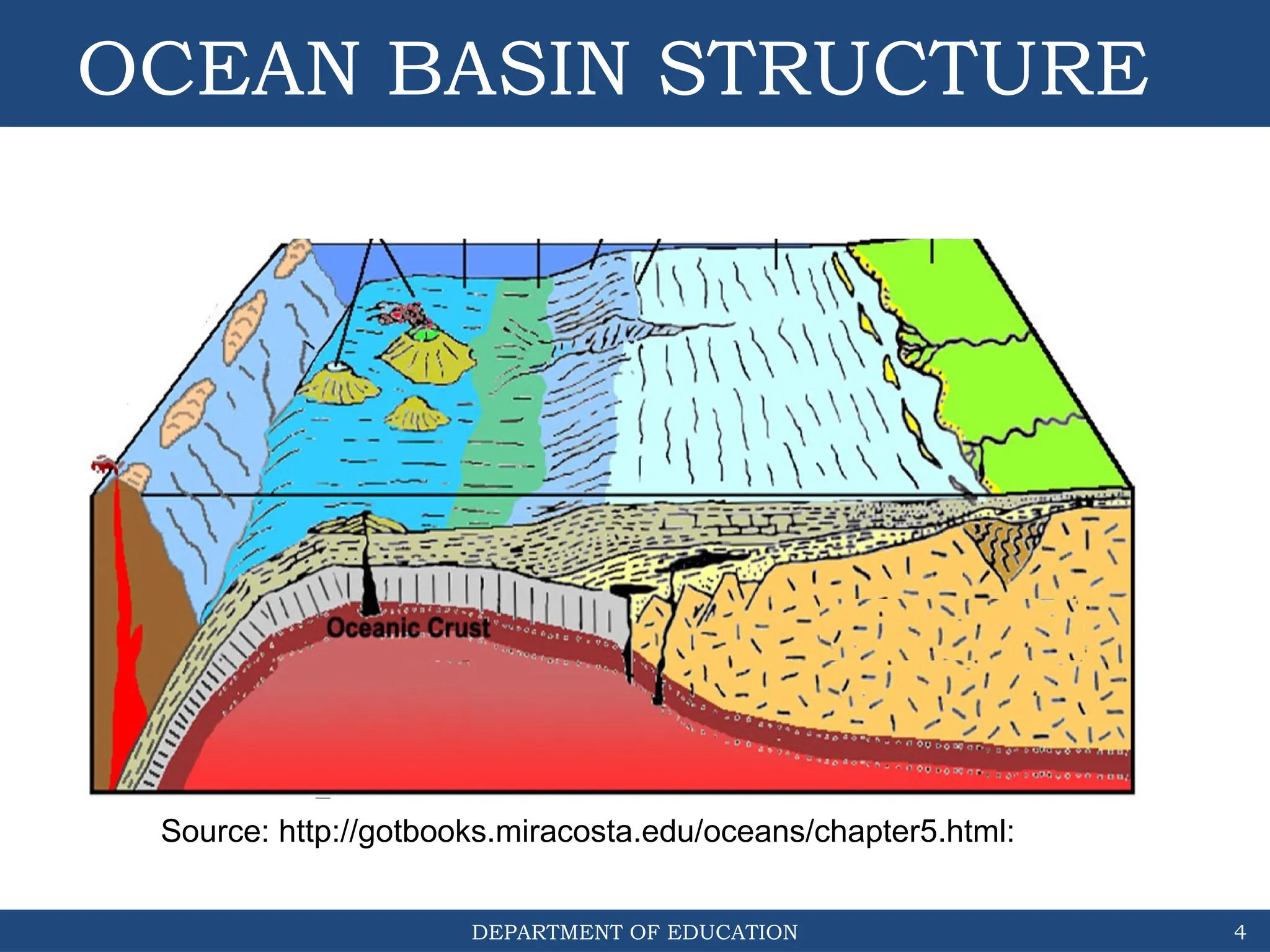
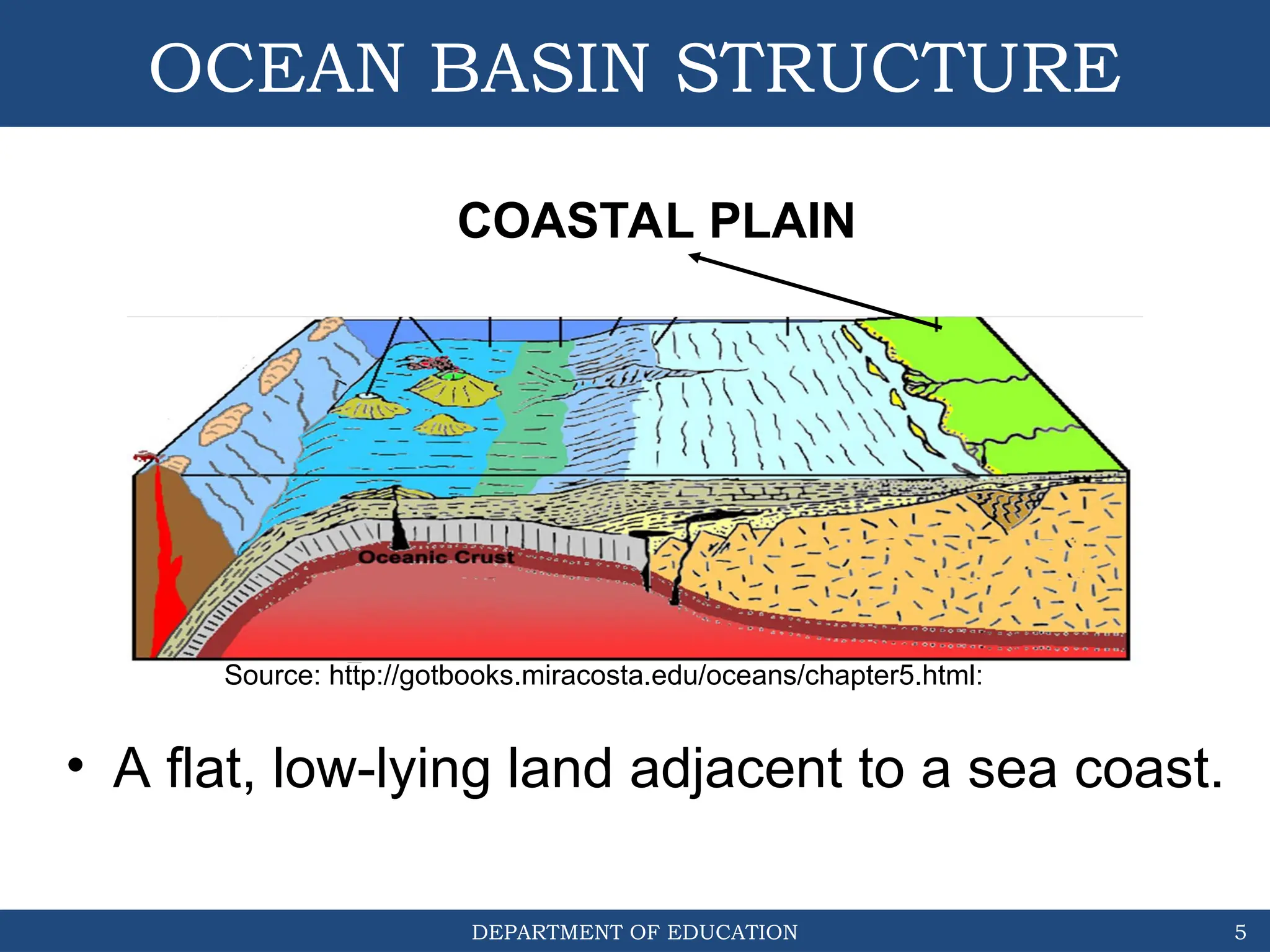
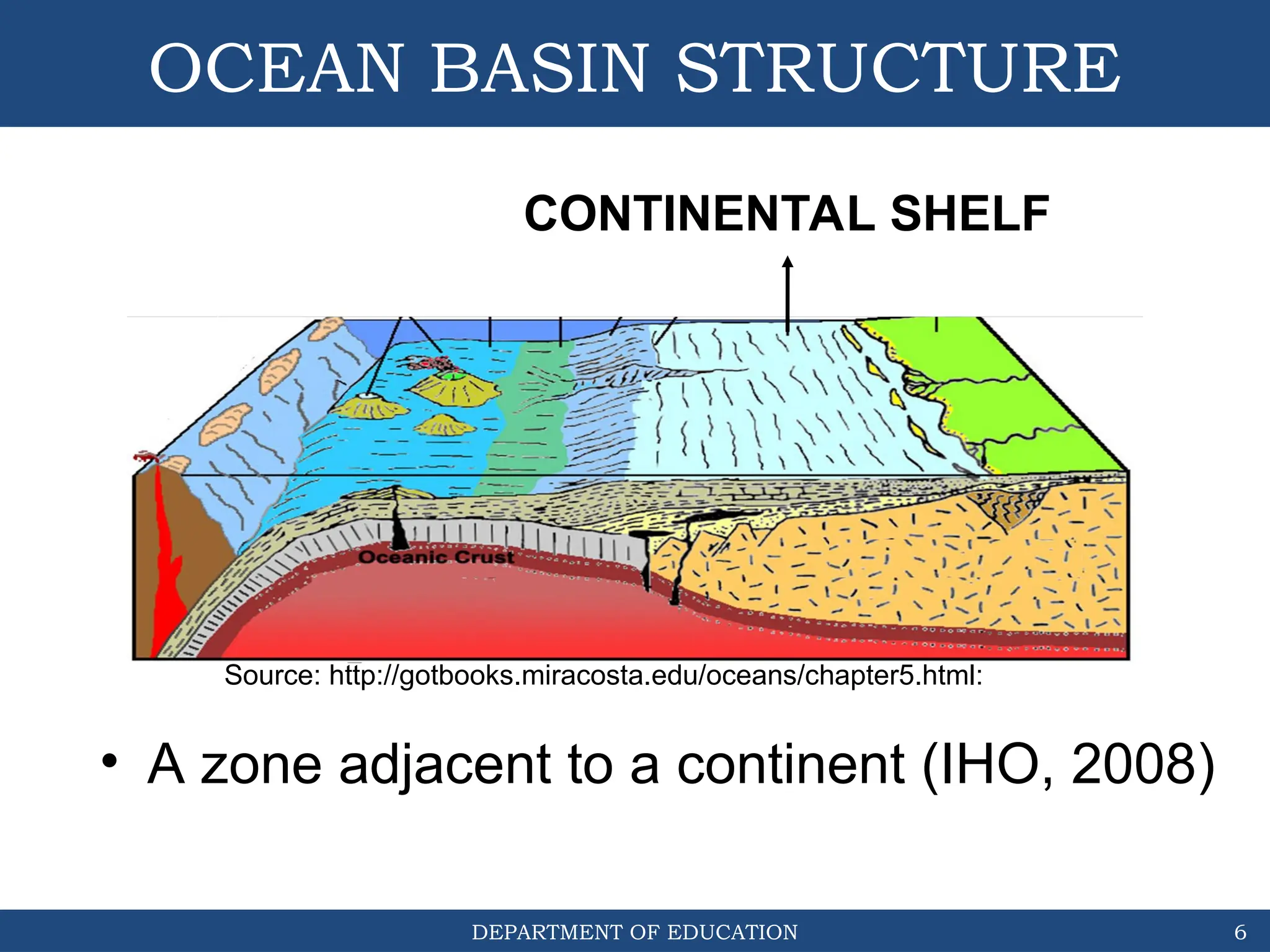
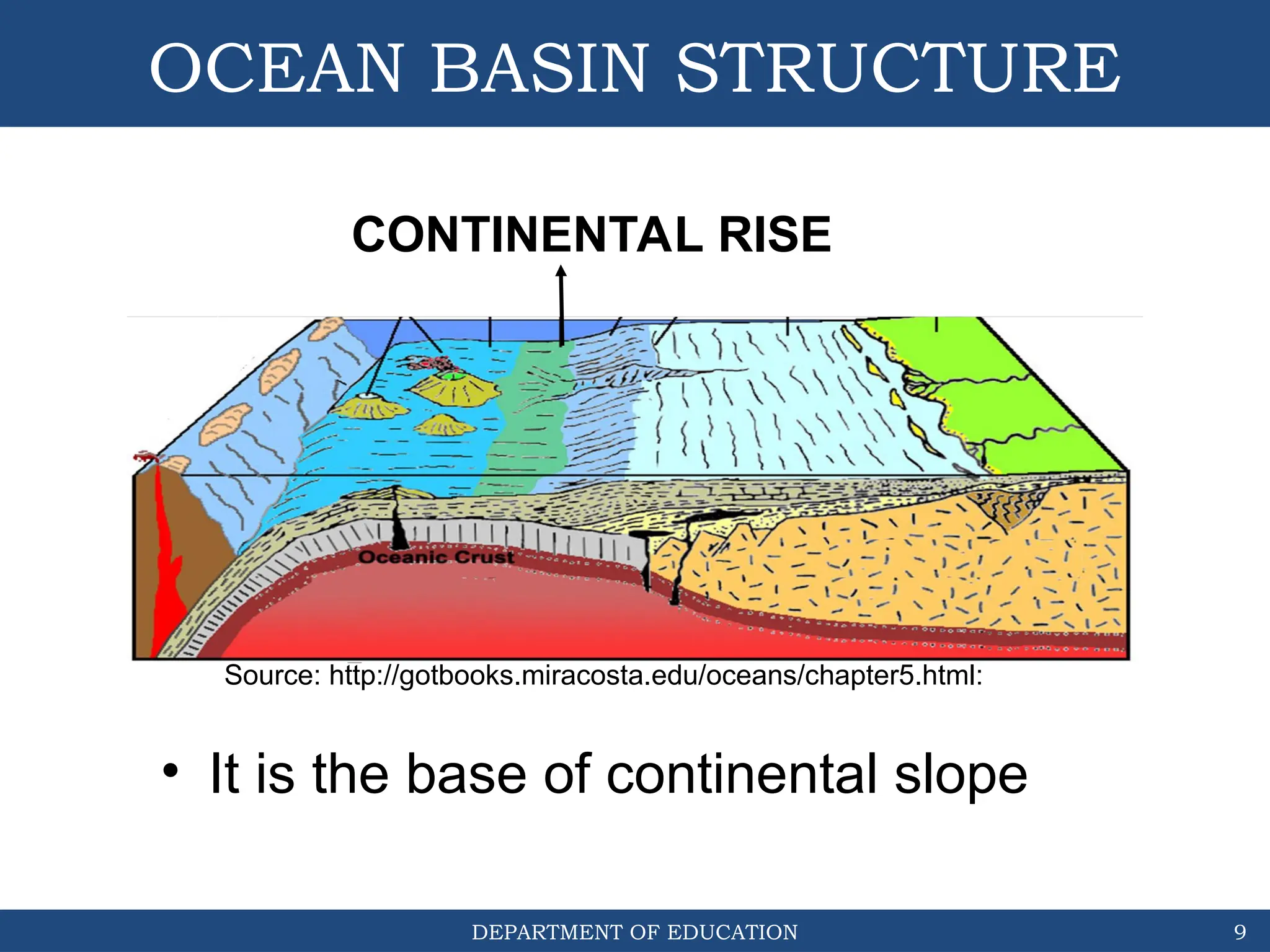
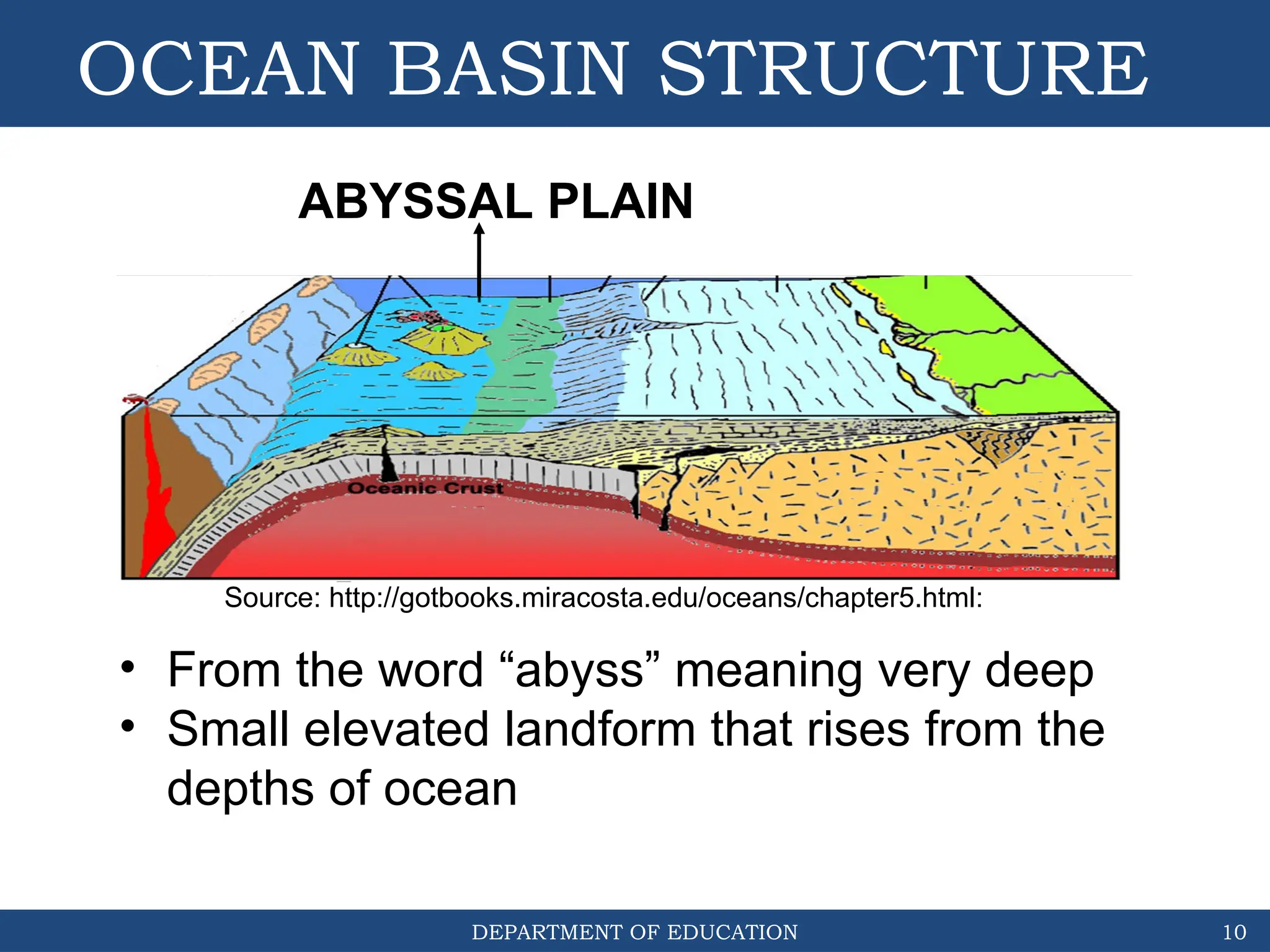
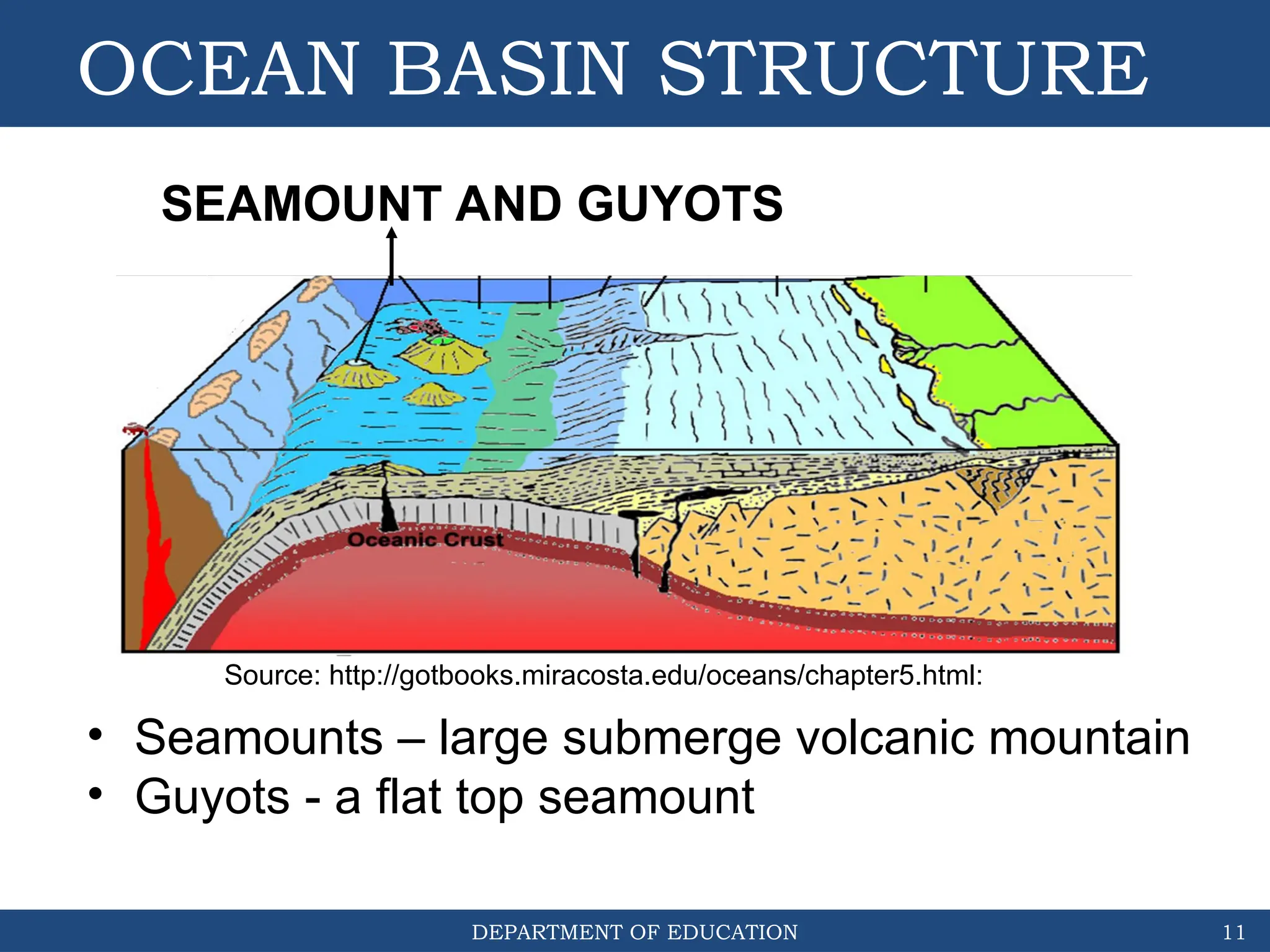
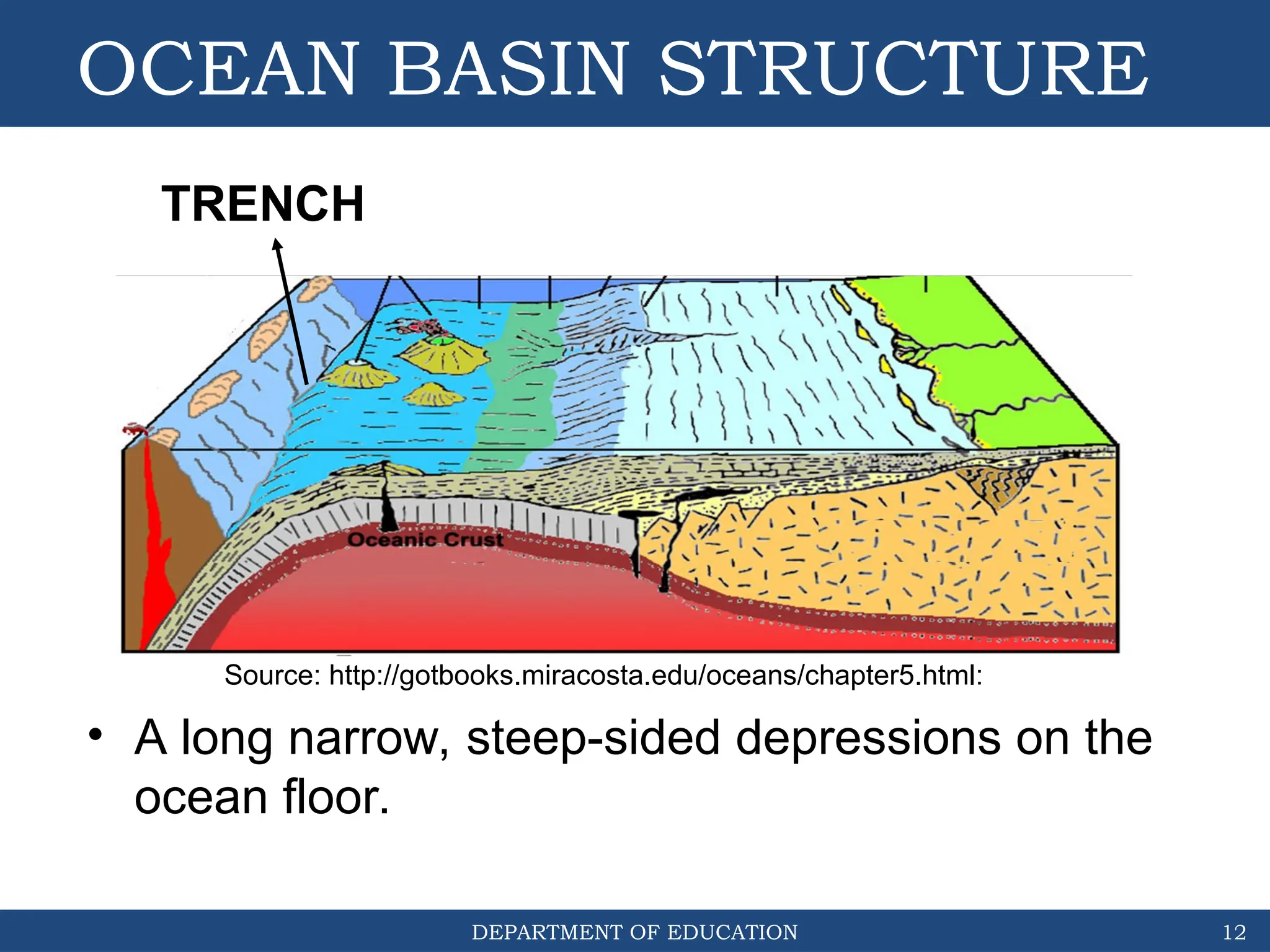
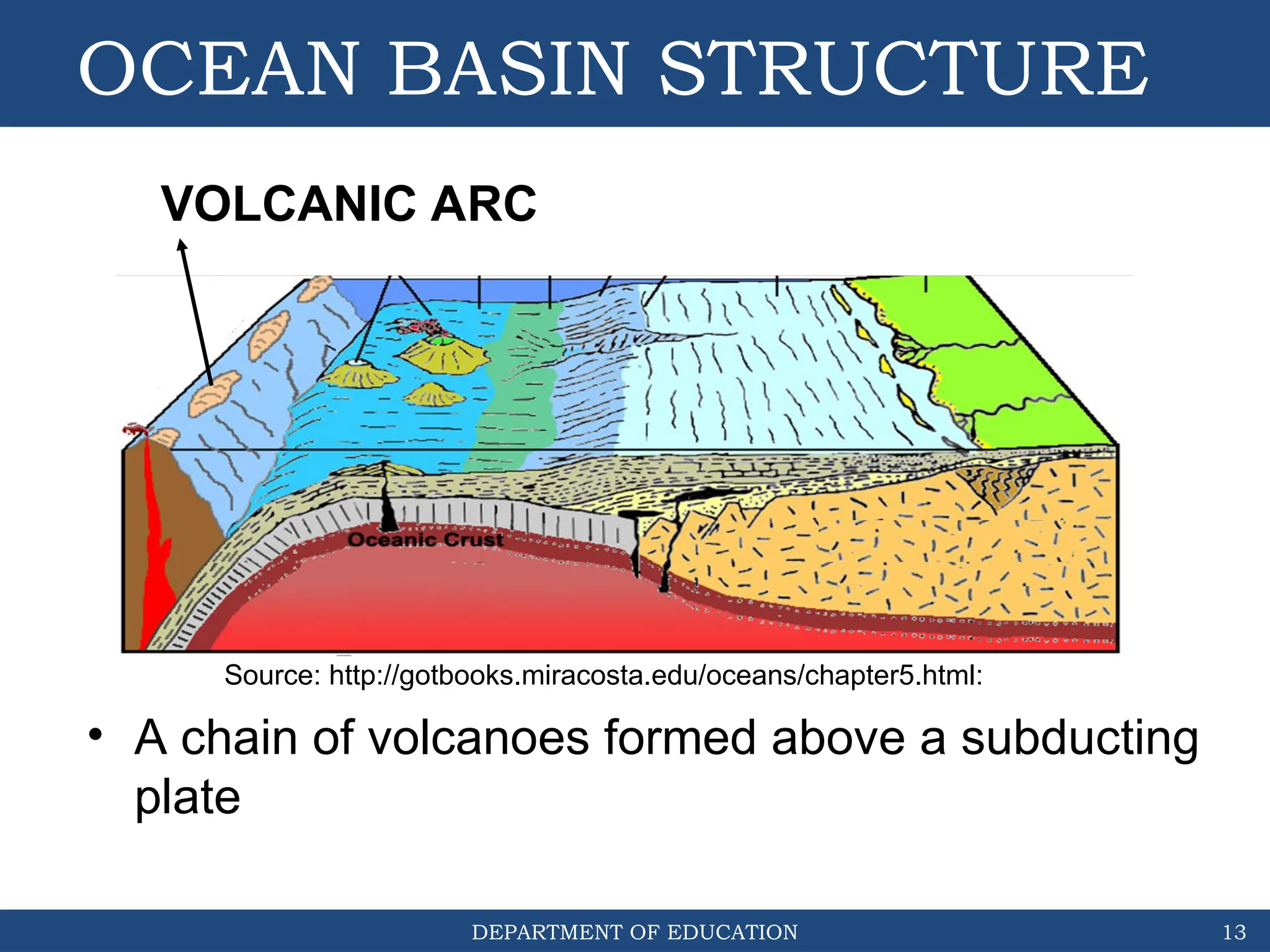
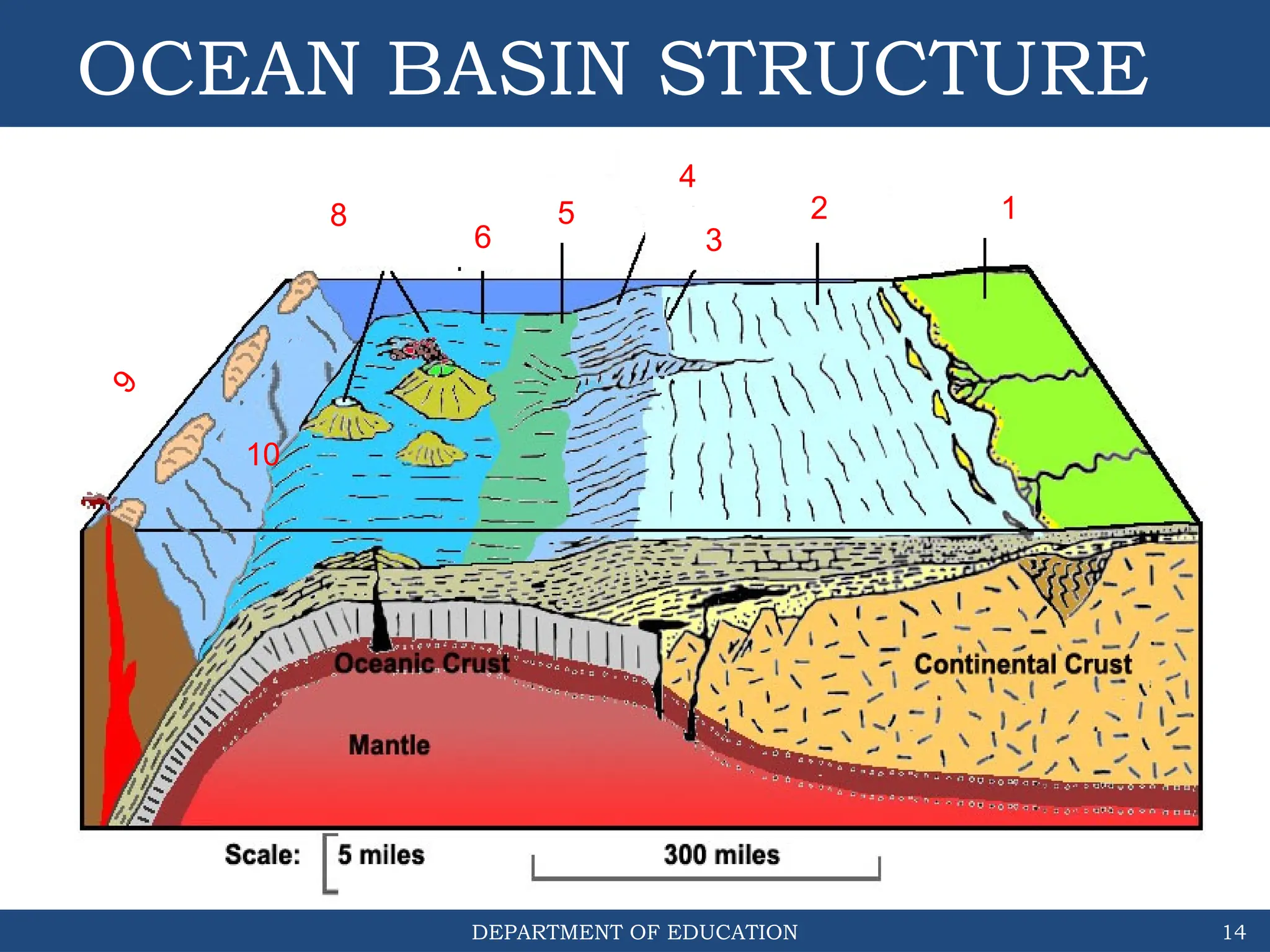
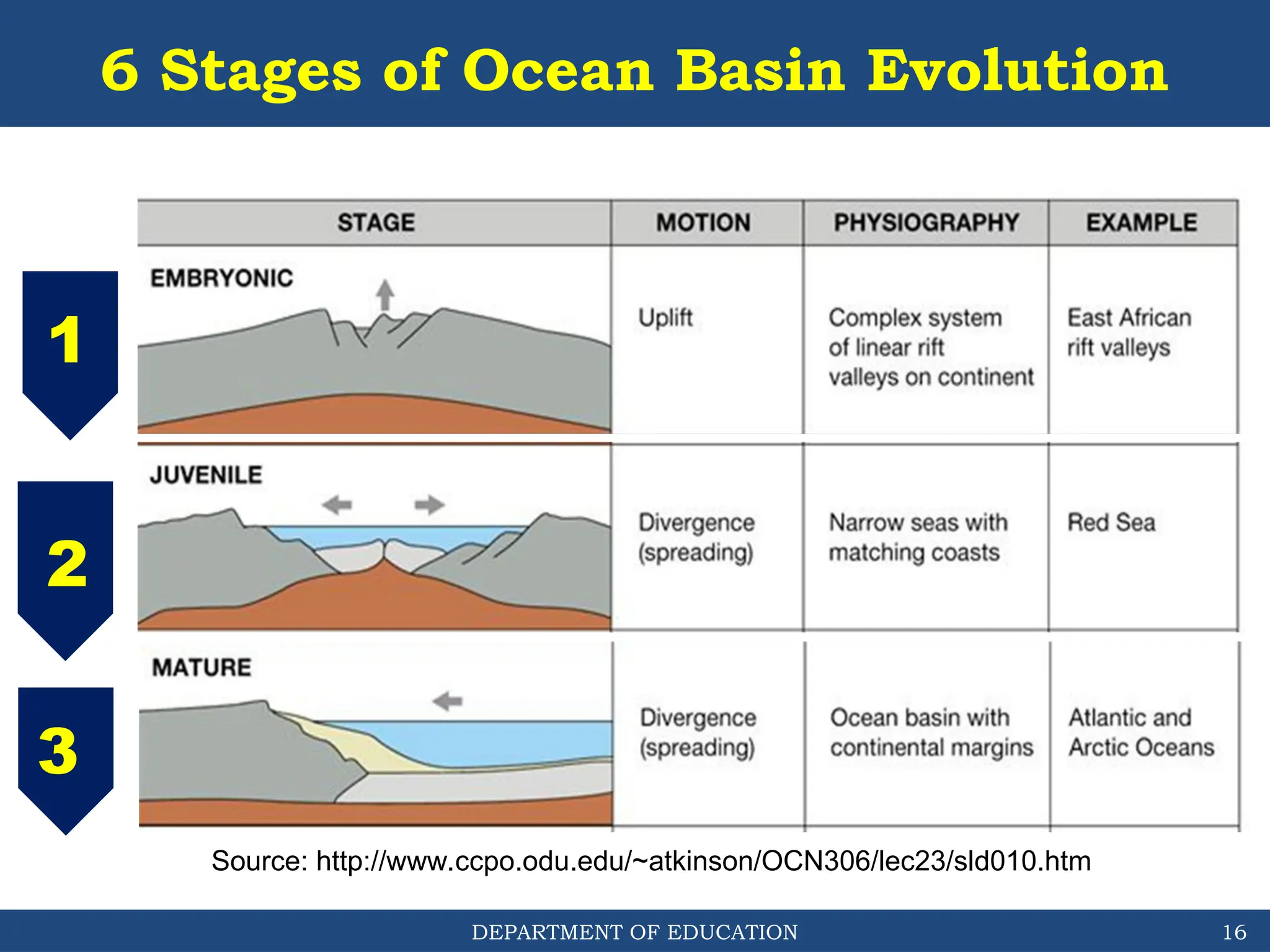
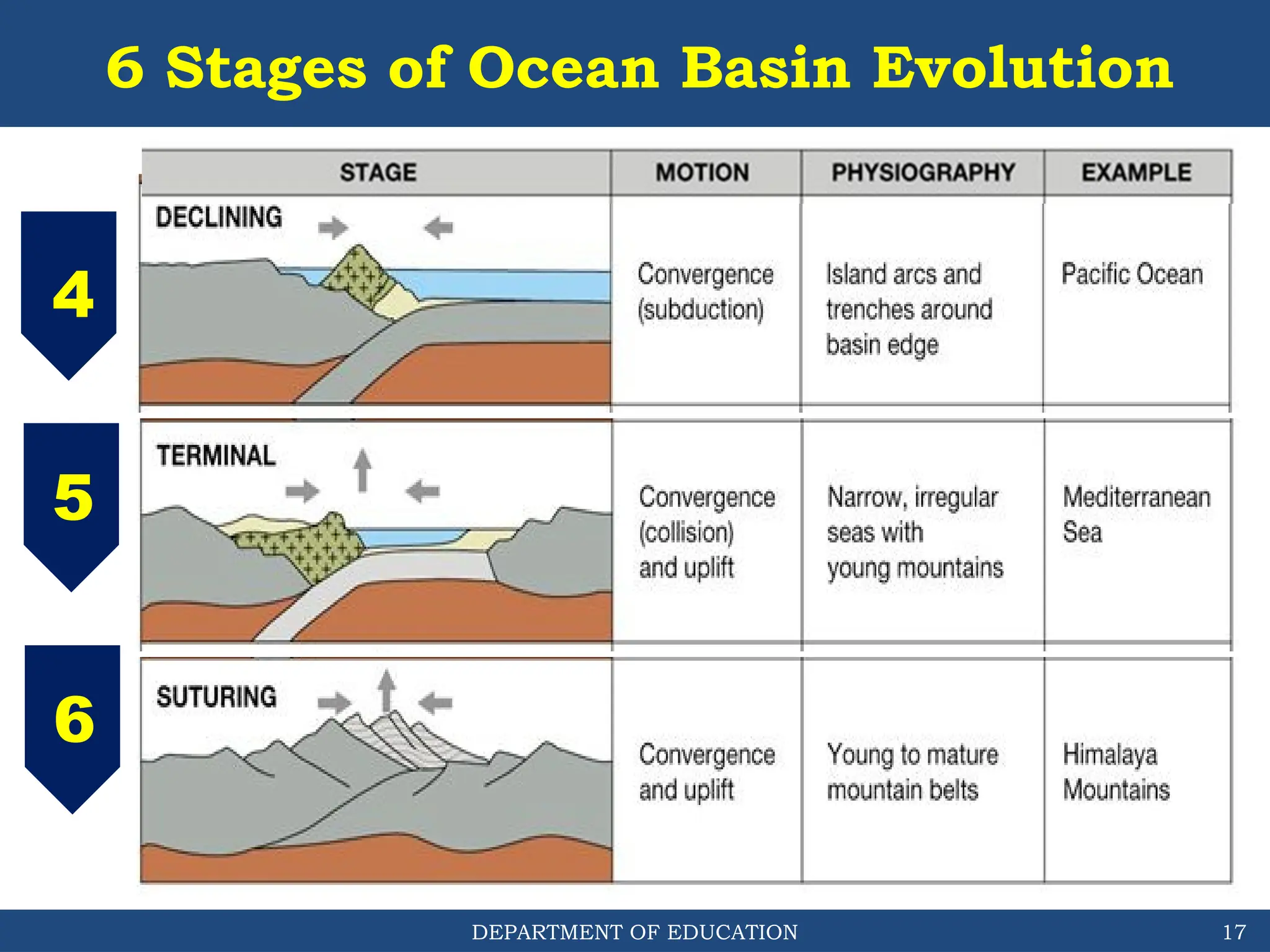
The document outlines the structure and evolution of ocean basins, detailing various features such as coastal plains, continental shelves, slopes, rises, abyssal plains, seamounts, and trenches. It highlights the six stages of ocean basin evolution known as the Wilson Cycle, emphasizing the importance of plate tectonics in this process. Additionally, the document encourages students to engage in activities that foster understanding and stewardship of ocean basins.