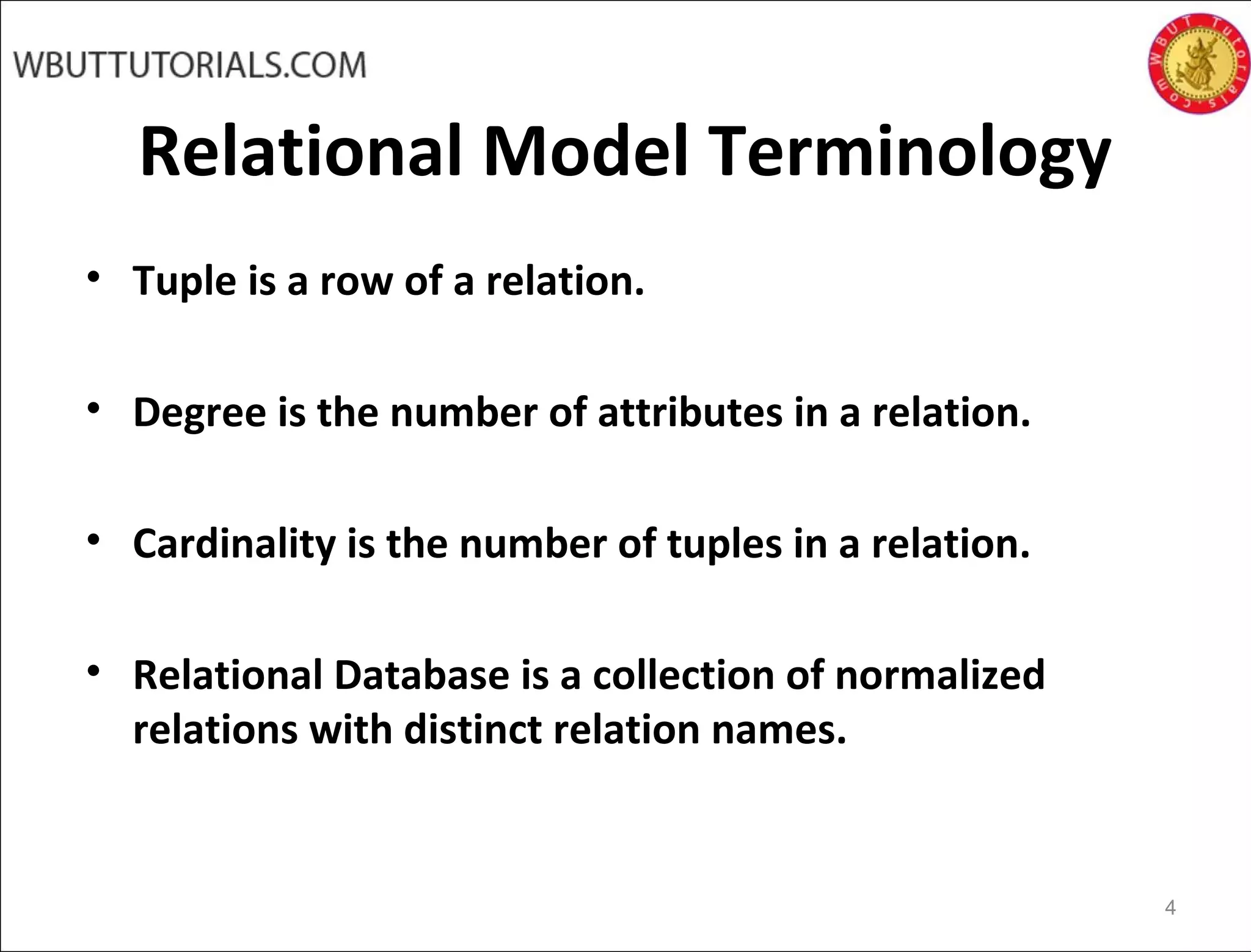
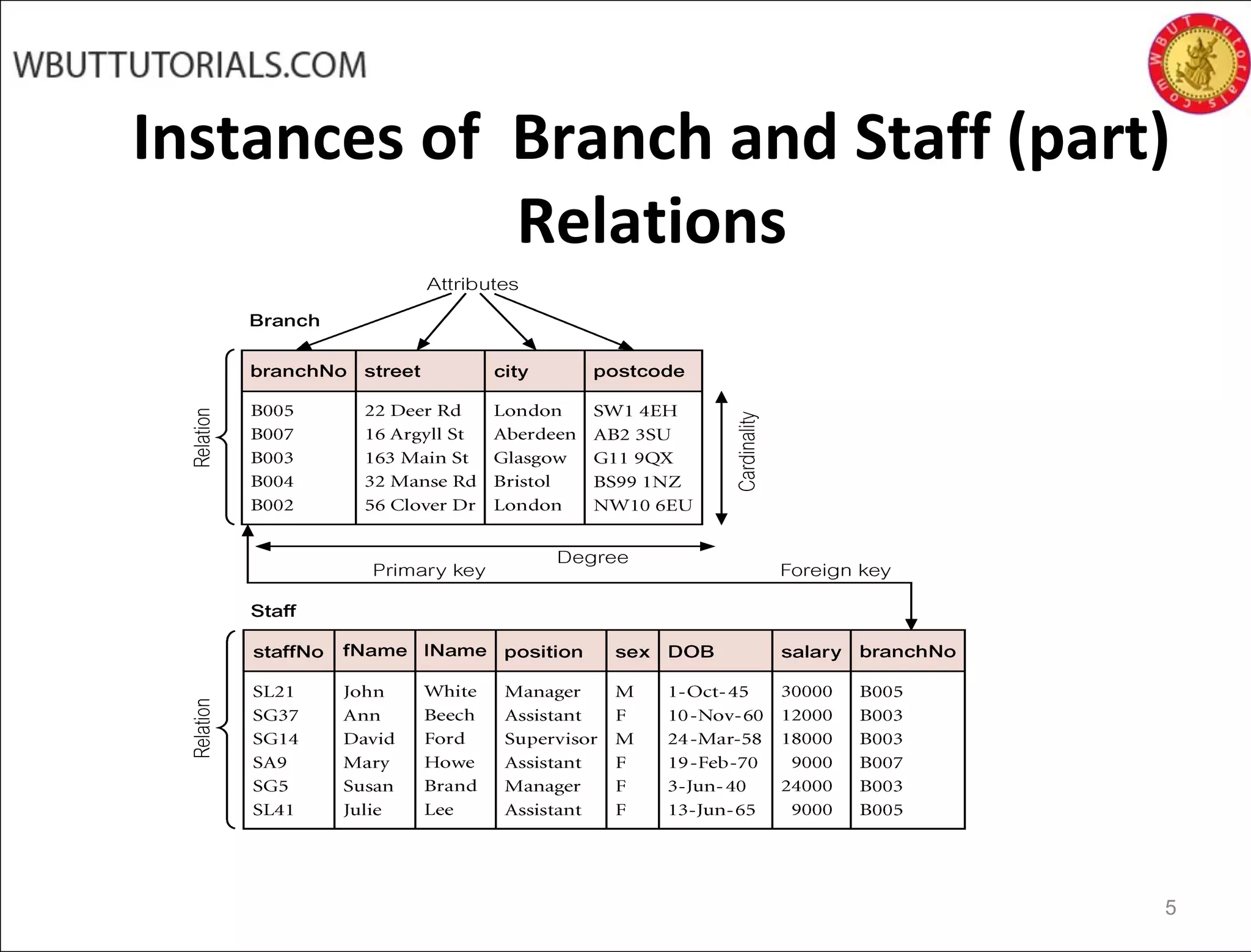
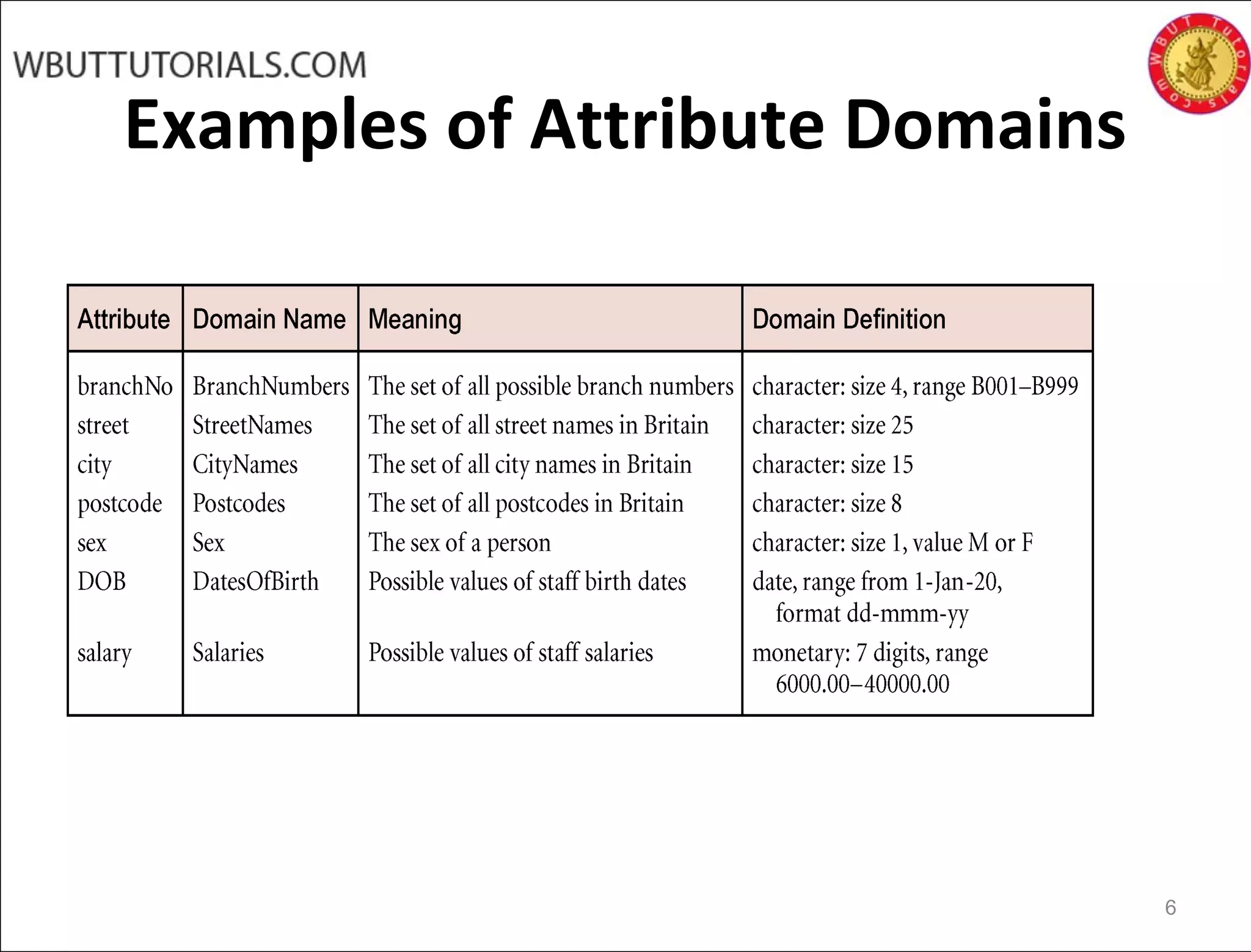
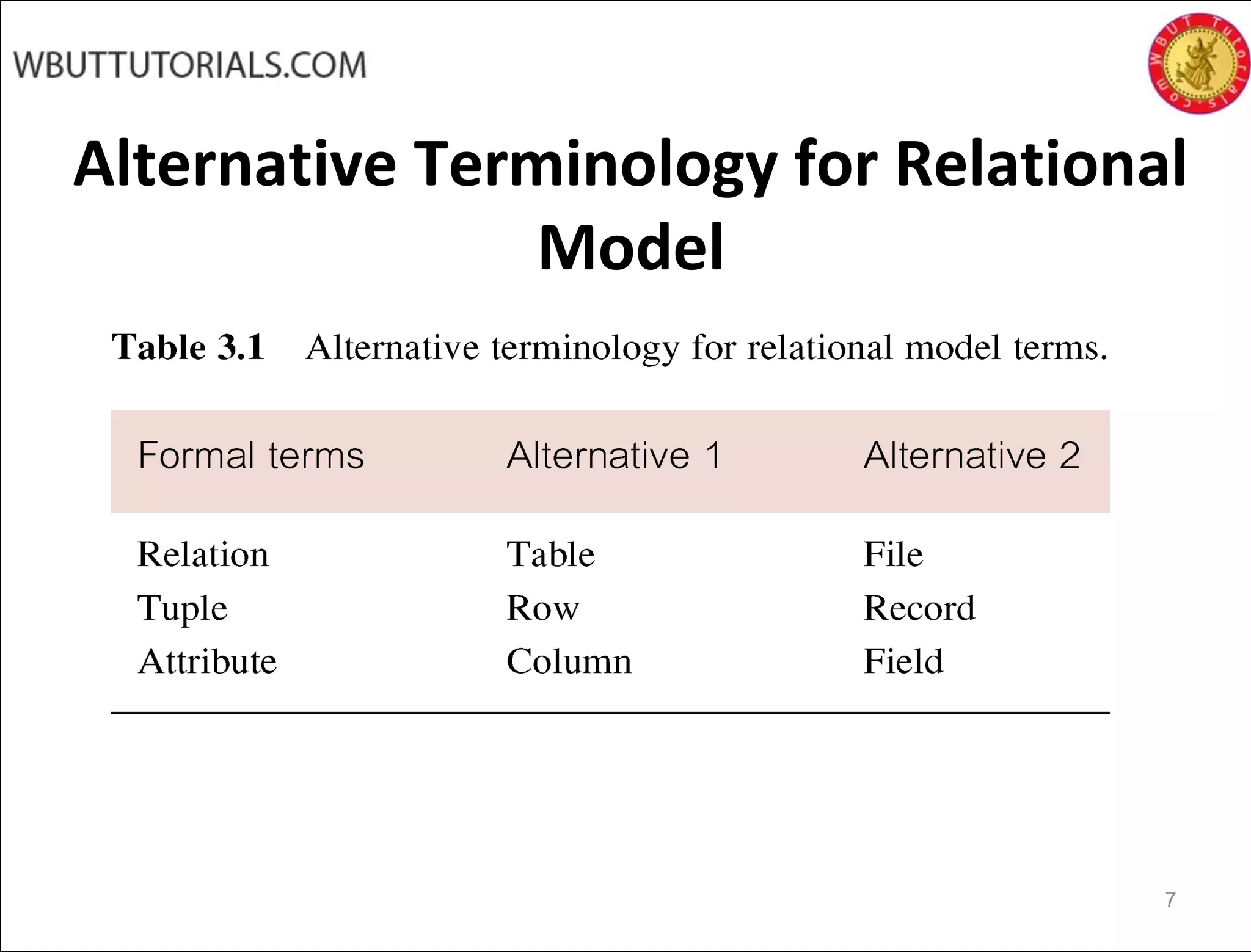
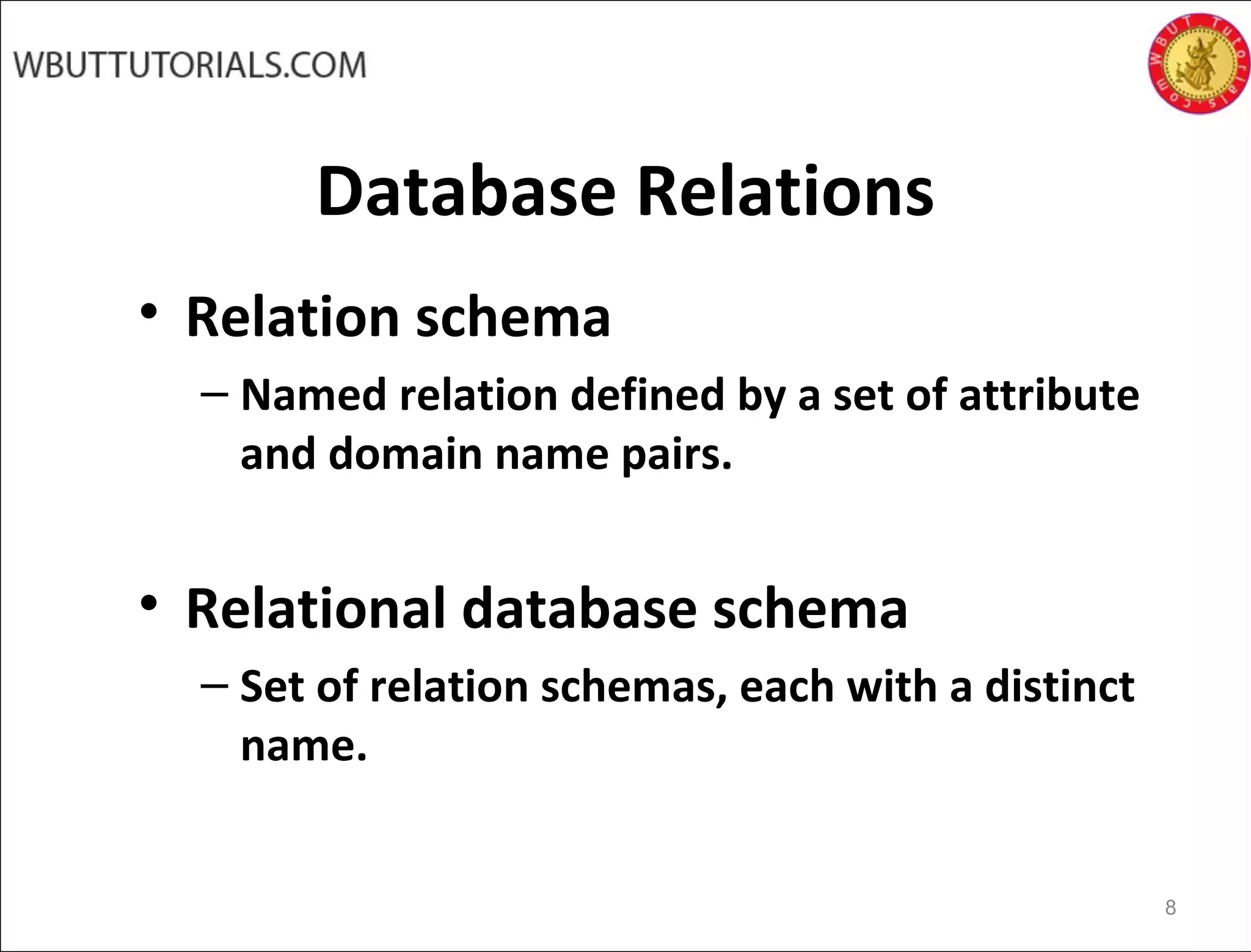
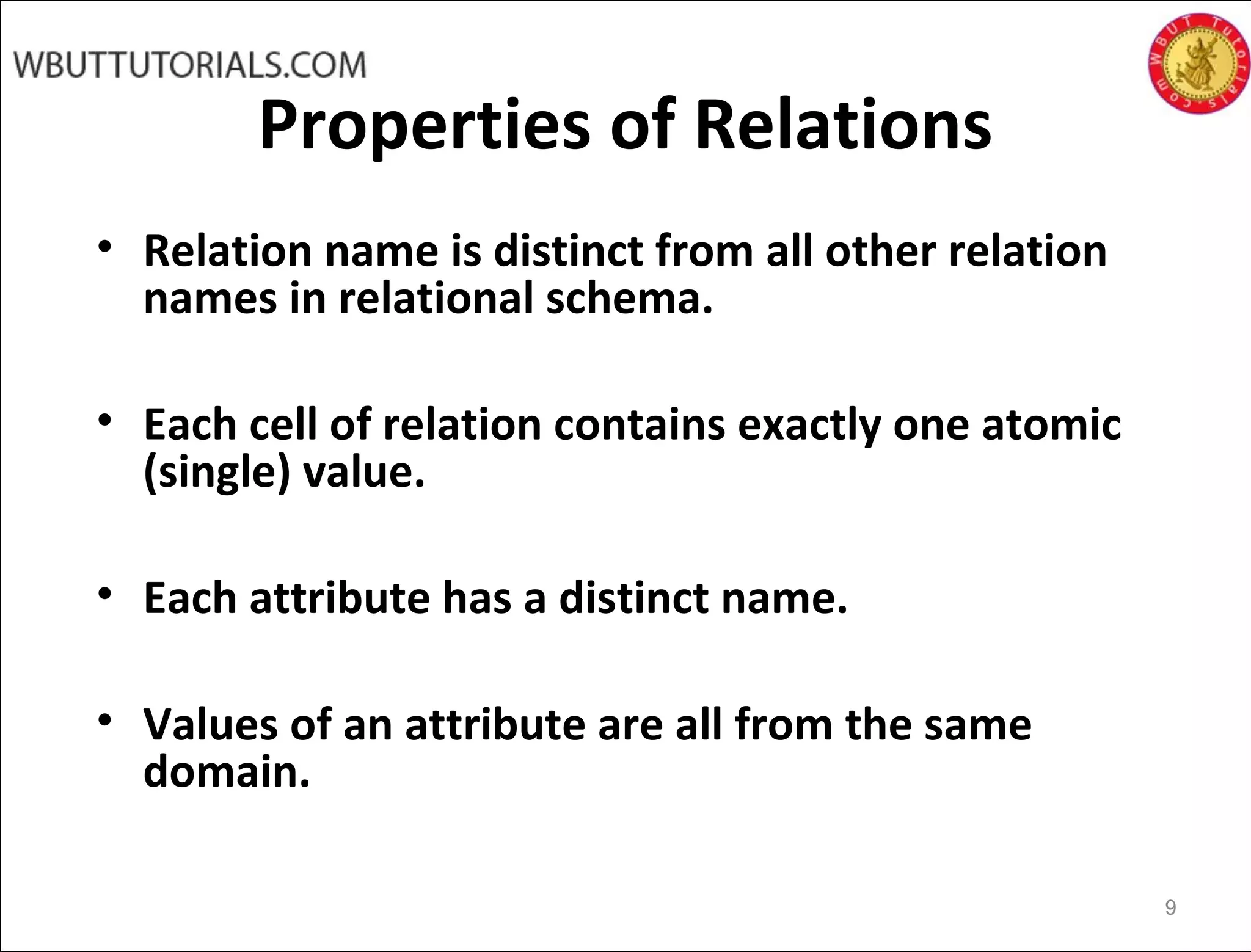
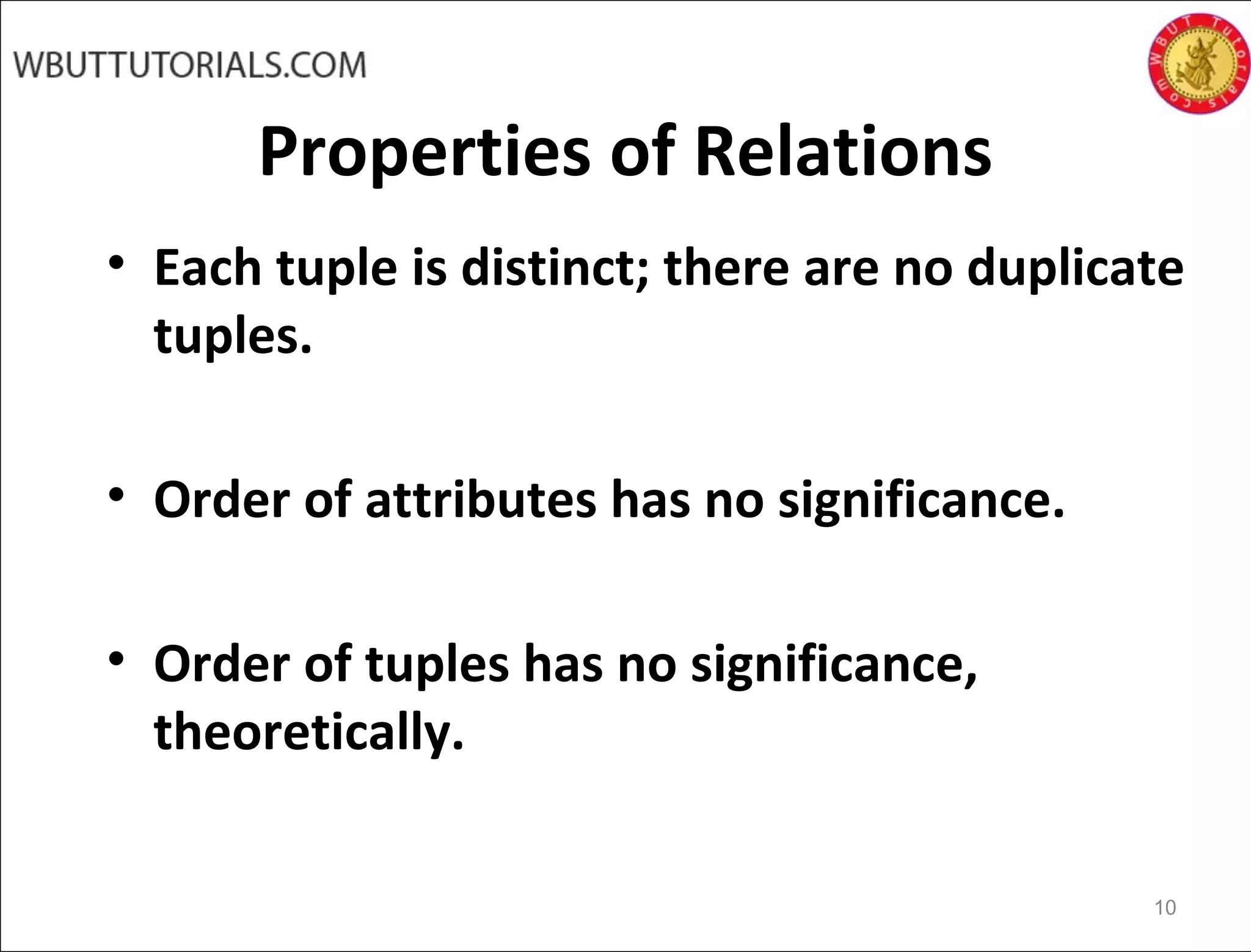
The document discusses key concepts of the relational database model including how tables represent data through relations, attributes, tuples, and domains. It defines primary keys, foreign keys, entity integrity and referential integrity. Views are described as virtual relations defined by queries on base relations that dynamically reflect changes to the underlying data. The purpose of views is to provide security, customization of data access, and simplification of complex queries. There are restrictions on updating data through views.