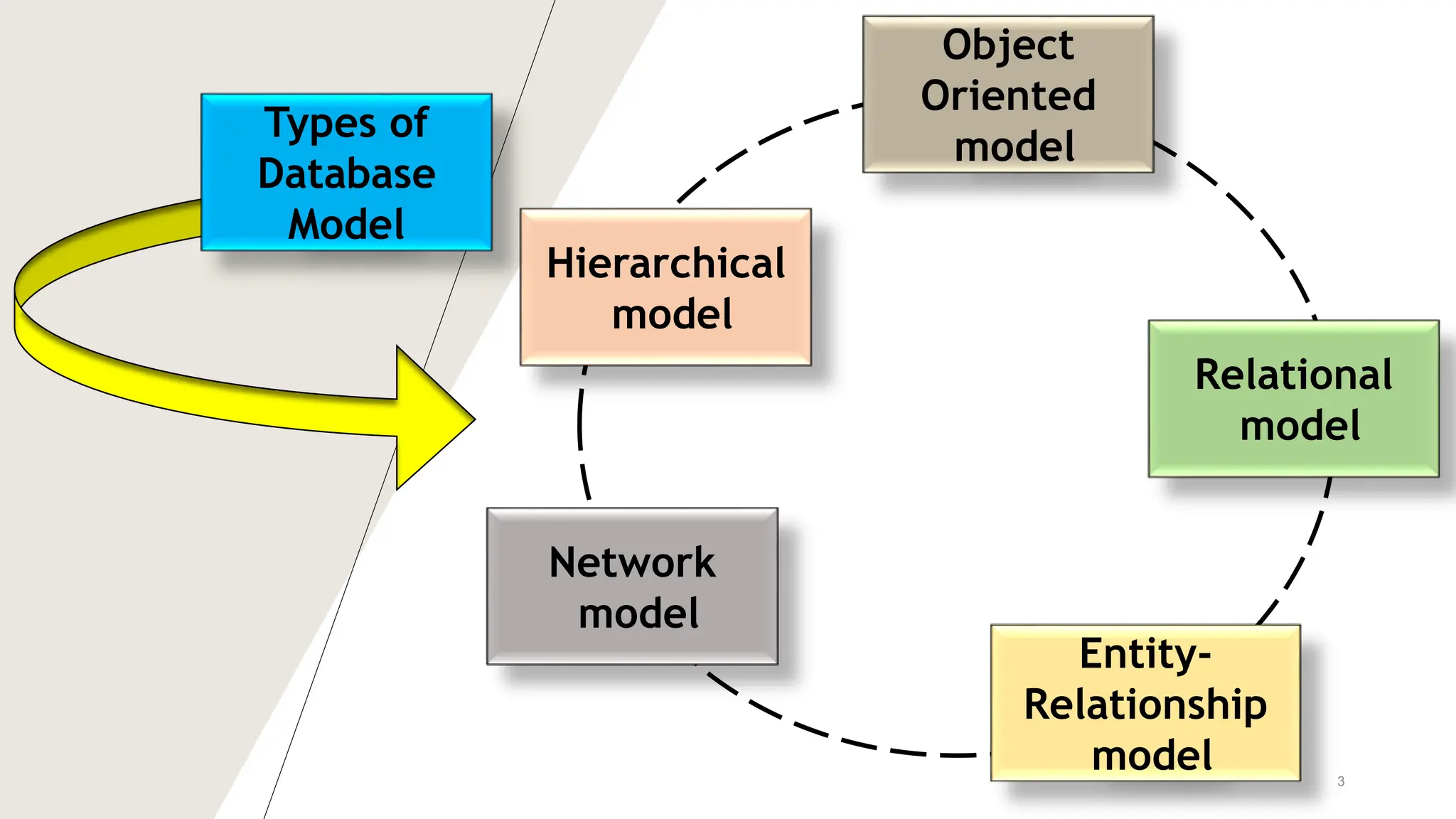
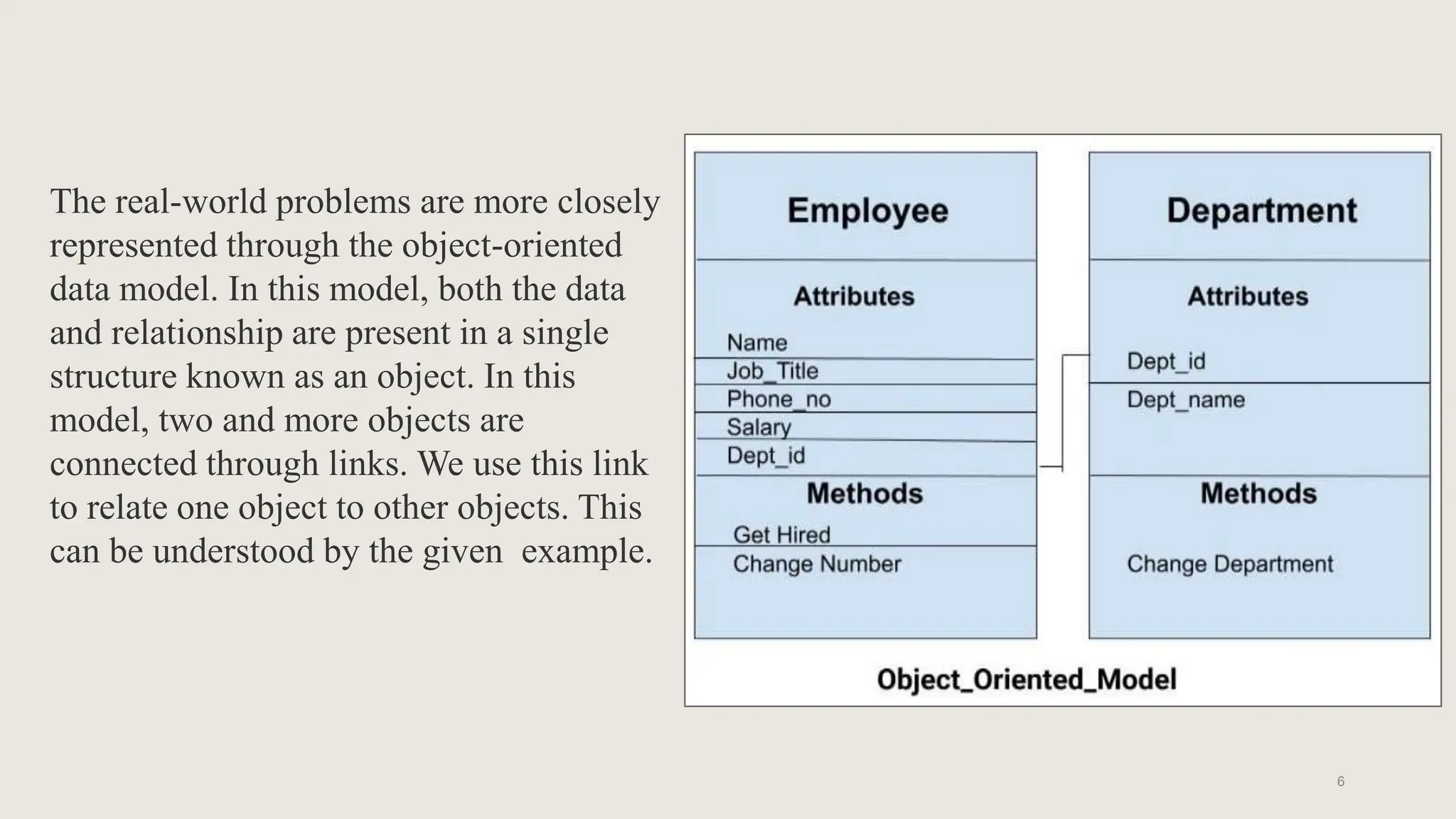
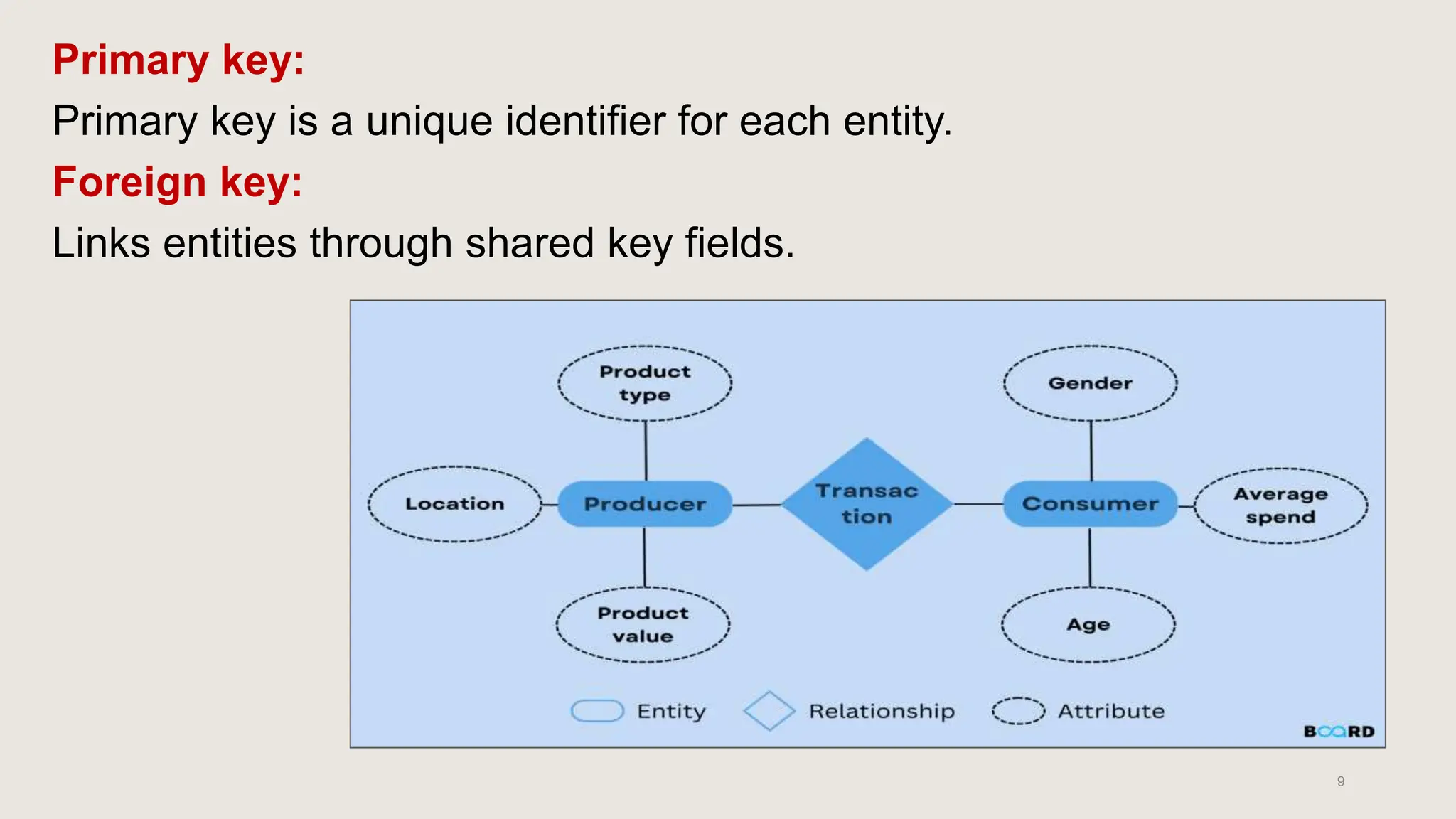
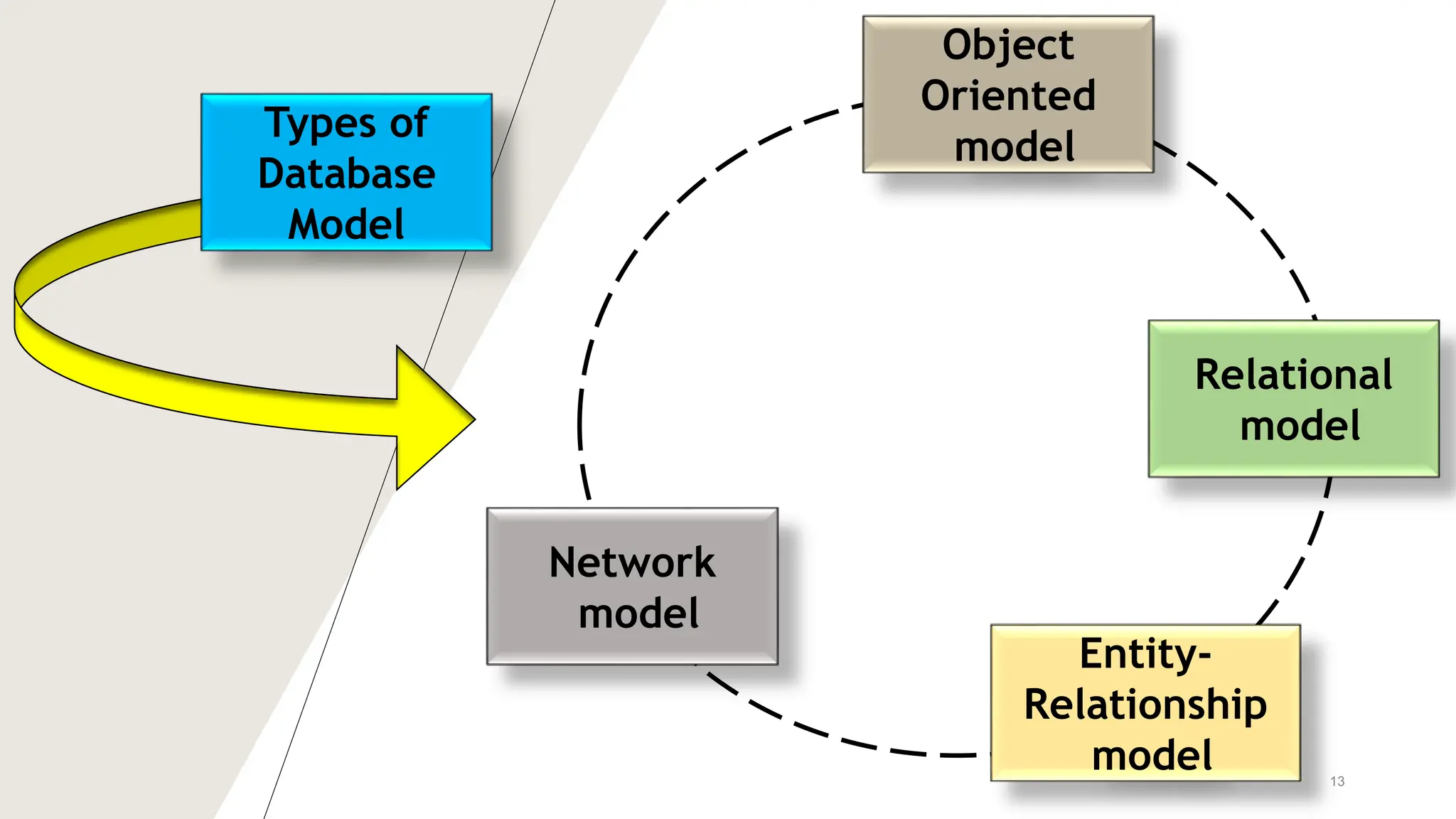
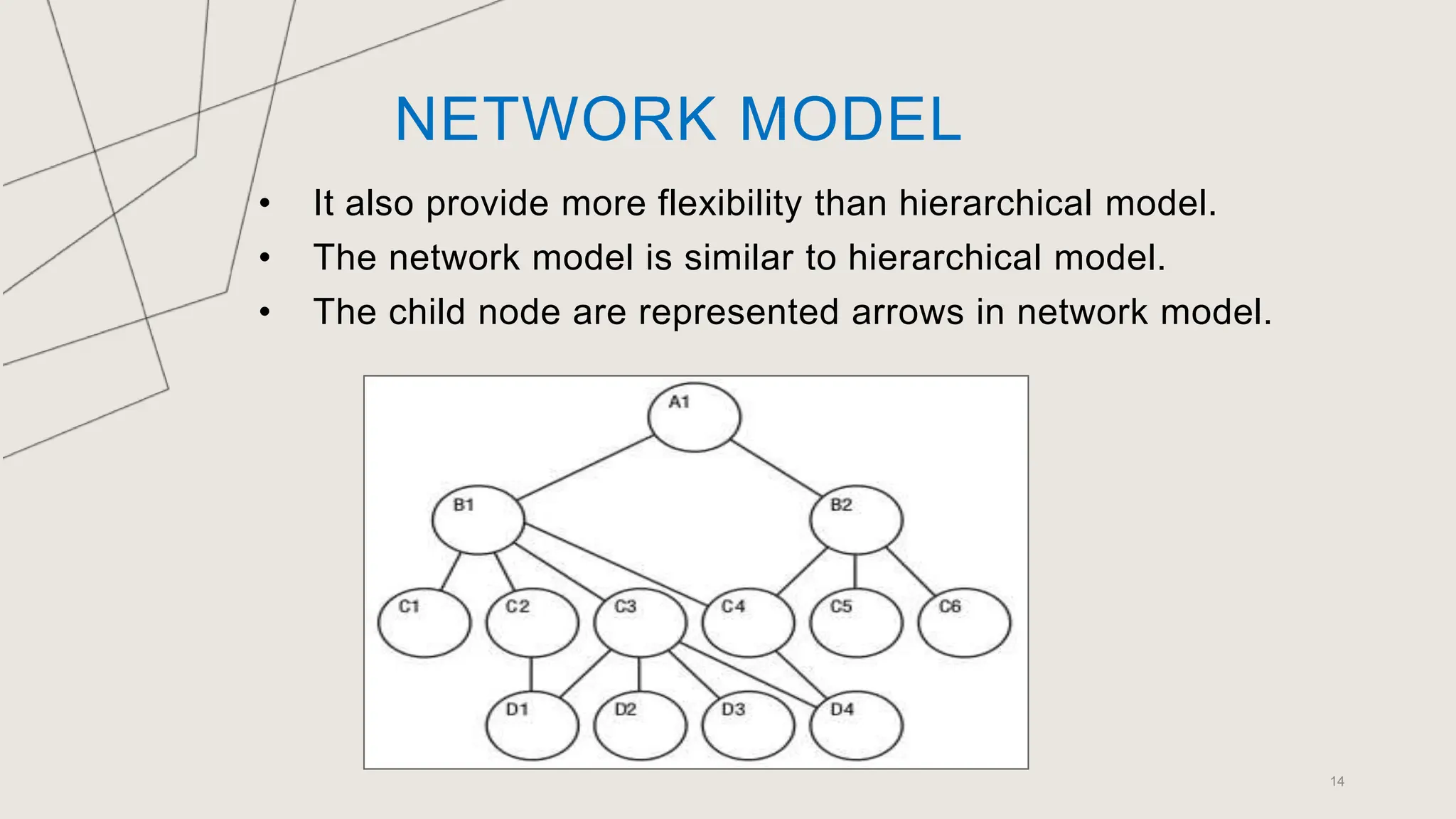
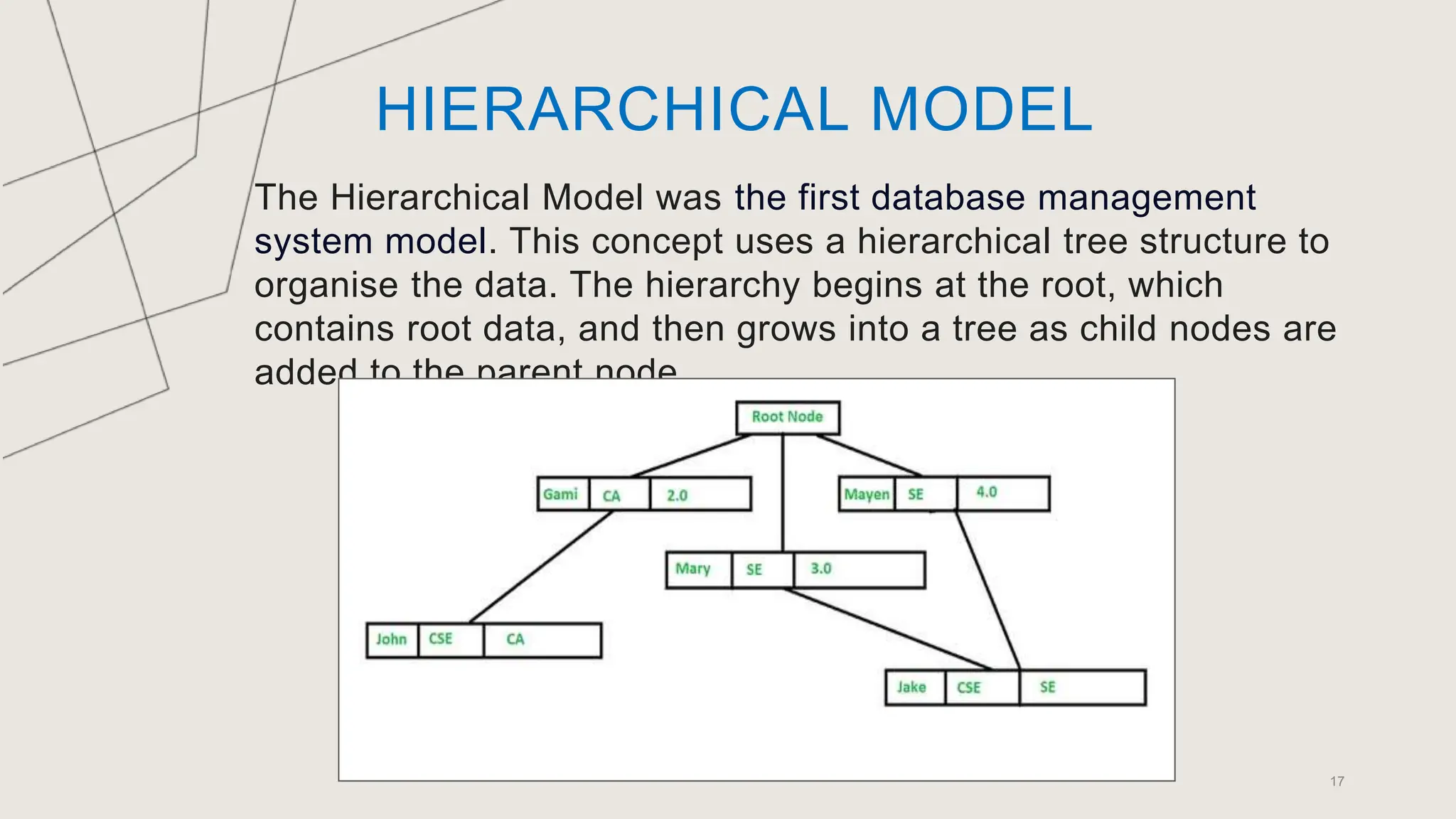
The document outlines various database models, defining a database model as a set of rules for organizing data and user views. It details object-oriented, entity-relationship, relational, and network models, each with specific structures and concepts for managing data. Key terms like entities, attributes, primary keys, and normalization are also explained in relation to these models.