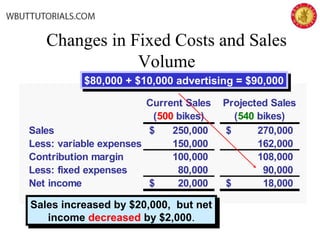
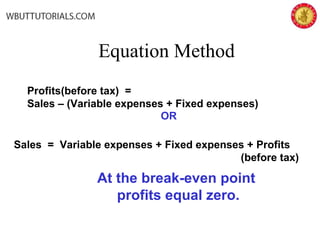
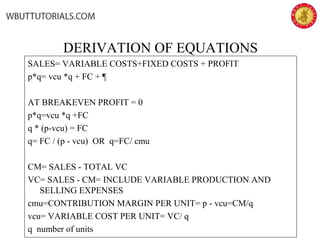
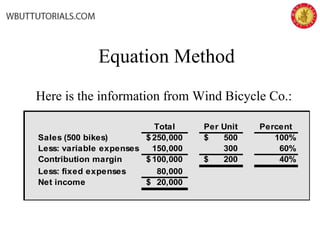
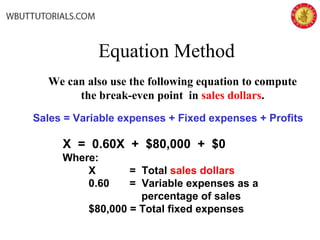
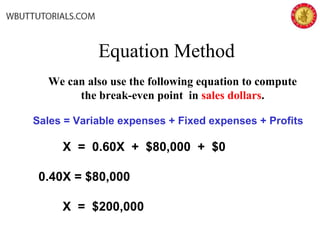
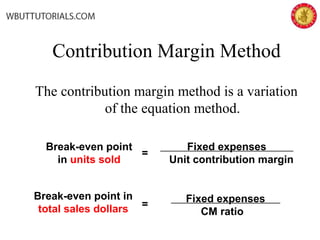
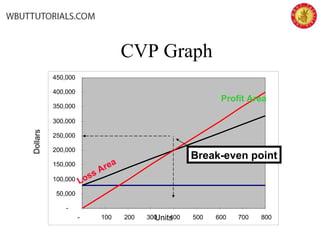
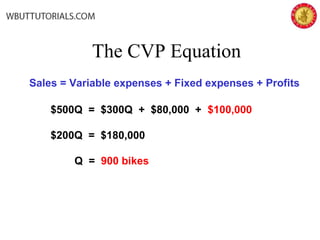
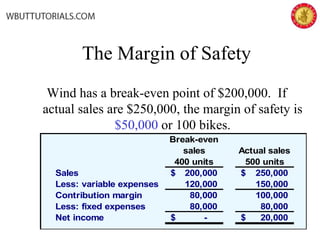
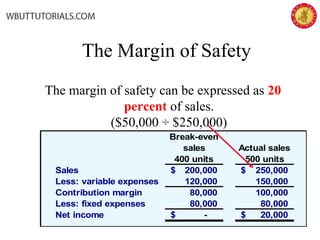
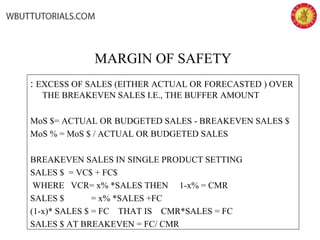
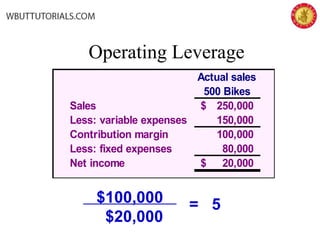
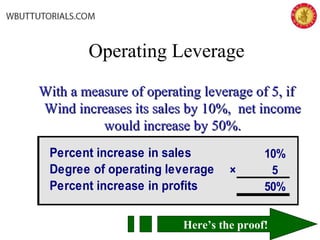
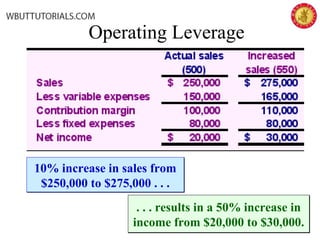
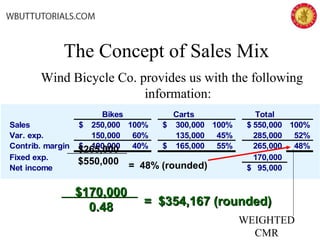
This document discusses cost-volume-profit analysis and break-even analysis. It defines key terms like contribution margin, variable costs, fixed costs, and sales mix. It provides examples of using the equation method and contribution margin method to calculate break-even points. It also discusses how to calculate target profit, margin of safety, operating leverage, and deals with break-even analysis for situations with multiple products or a sales mix.