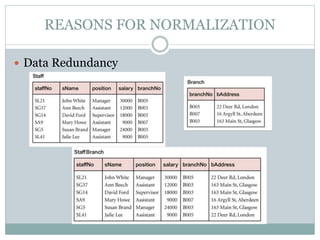
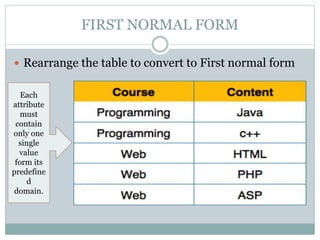
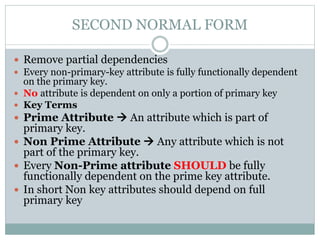
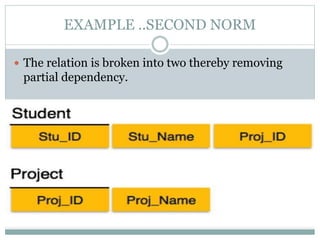
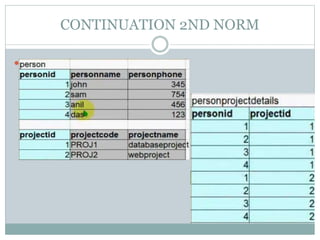
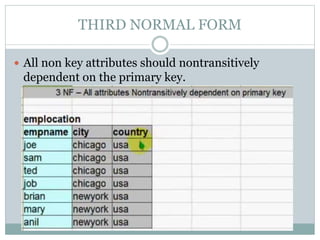
The document discusses database normalization. It defines normalization as a process of evaluating and correcting table structures to minimize data redundancies and anomalies. The normalization process involves converting tables to first, second, and third normal forms through removing partial and transitive dependencies. Higher normal forms like 3NF are better than 2NF and 1NF as they restrict relation formats and reduce vulnerabilities to update, delete, and insert anomalies.