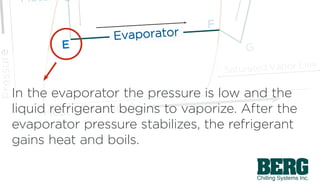
The refrigeration cycle is a process that removes unwanted heat from one location and discharges it elsewhere by utilizing a refrigerant that evaporates at low temperatures to rapidly extract heat. The cycle involves stages of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation, which are described through a pressure-enthalpy diagram that illustrates the relationships between heat, pressure, temperature, and cooling capacity. This document outlines the fundamental principles and phases of mechanical refrigeration and the role of refrigerants within the system.