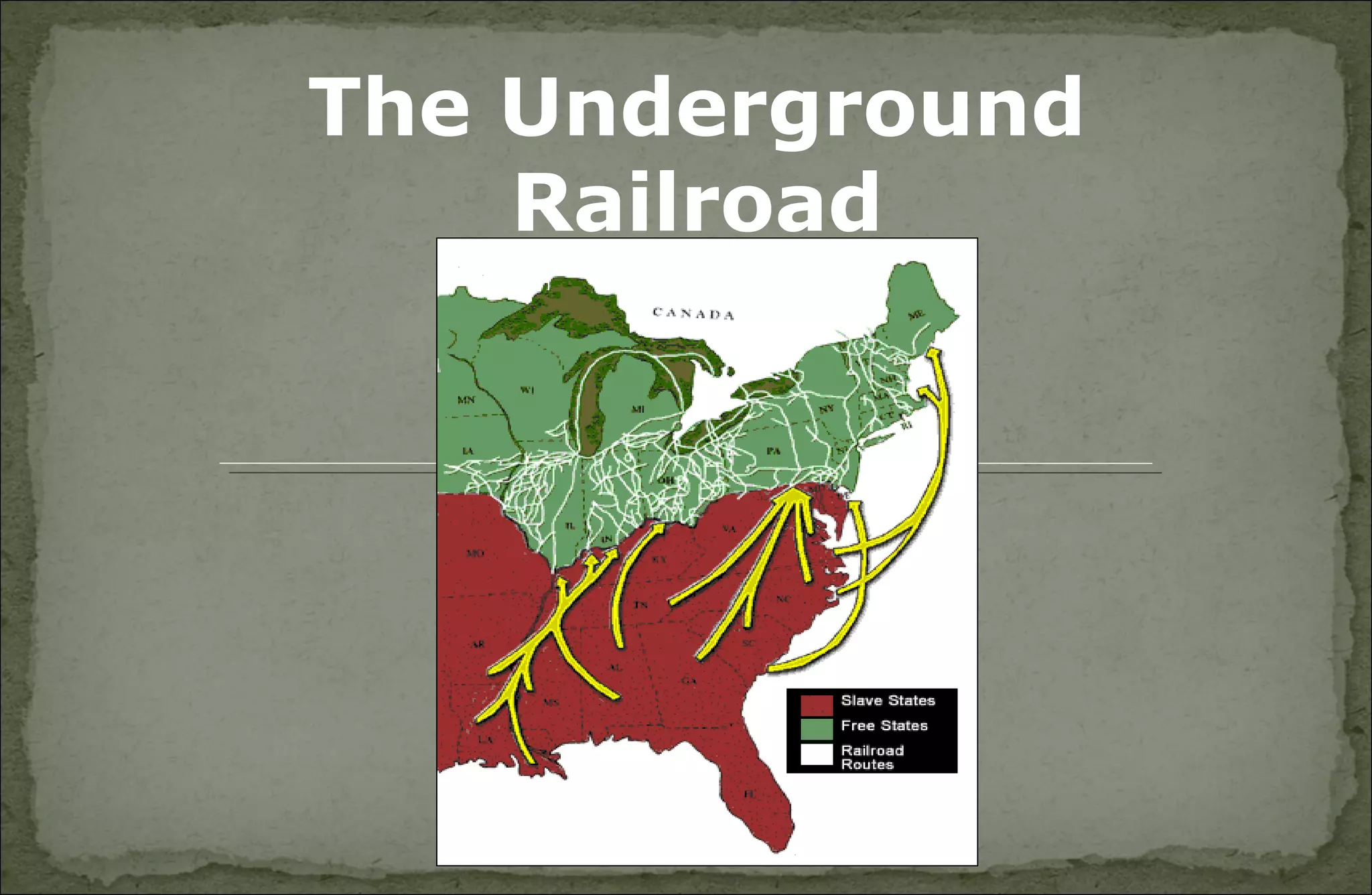
This document discusses several key events and figures in the abolitionist and women's rights movements in the early-to-mid 19th century United States. It mentions the American Colonization Society which sought to send freed slaves to Africa, influential abolitionist writings by David Walker, Frederick Douglass, and Sojourner Truth, and the Underground Railroad aided by Harriet Tubman. It also outlines the concept of "separate spheres" which restricted women's roles to the home and discusses some of the key figures and events in the movements for women's rights and suffrage as well as temperance and educational reform.