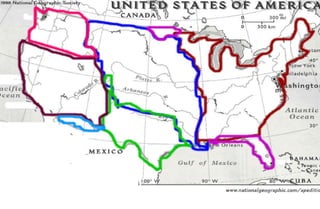
The document summarizes key events related to Manifest Destiny and the Mexican-American War, including:
1) John O'Sullivan's coining of the term "Manifest Destiny" to justify American expansionism.
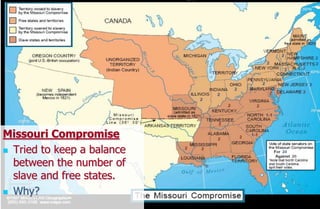
2) The Missouri Compromise which tried to balance slave and free states.
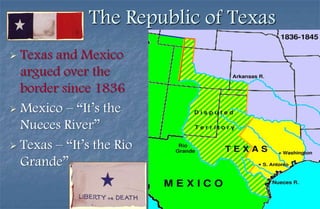
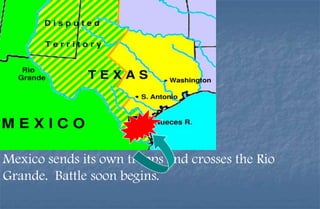
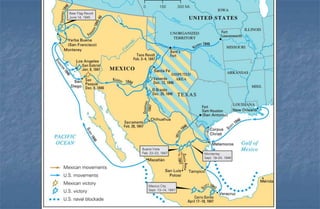
3) Polk sending troops to the Rio Grande and war beginning after clashes between American and Mexican troops.
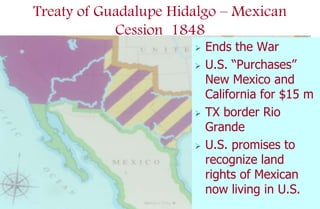
4) The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ending the war and the U.S. acquiring new territory including California and New Mexico.