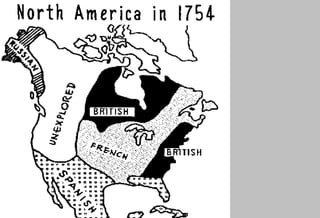
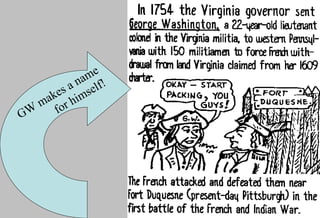
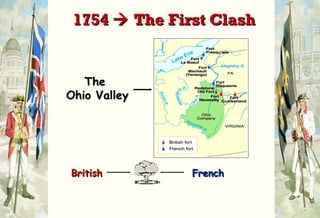
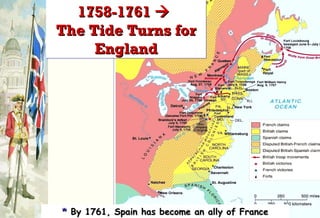
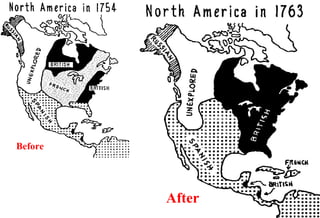
The document discusses the French and Indian War that took place between 1756-1763 between the British, American colonists, and French forces allied with Native American tribes. It led to several consequences, including increased unity among the colonies against a common enemy, bitterness towards the British from colonial forces over military organization and discipline, and a need for Britain to reorganize its American empire after taking on large war debts and expanding its colonial holdings.