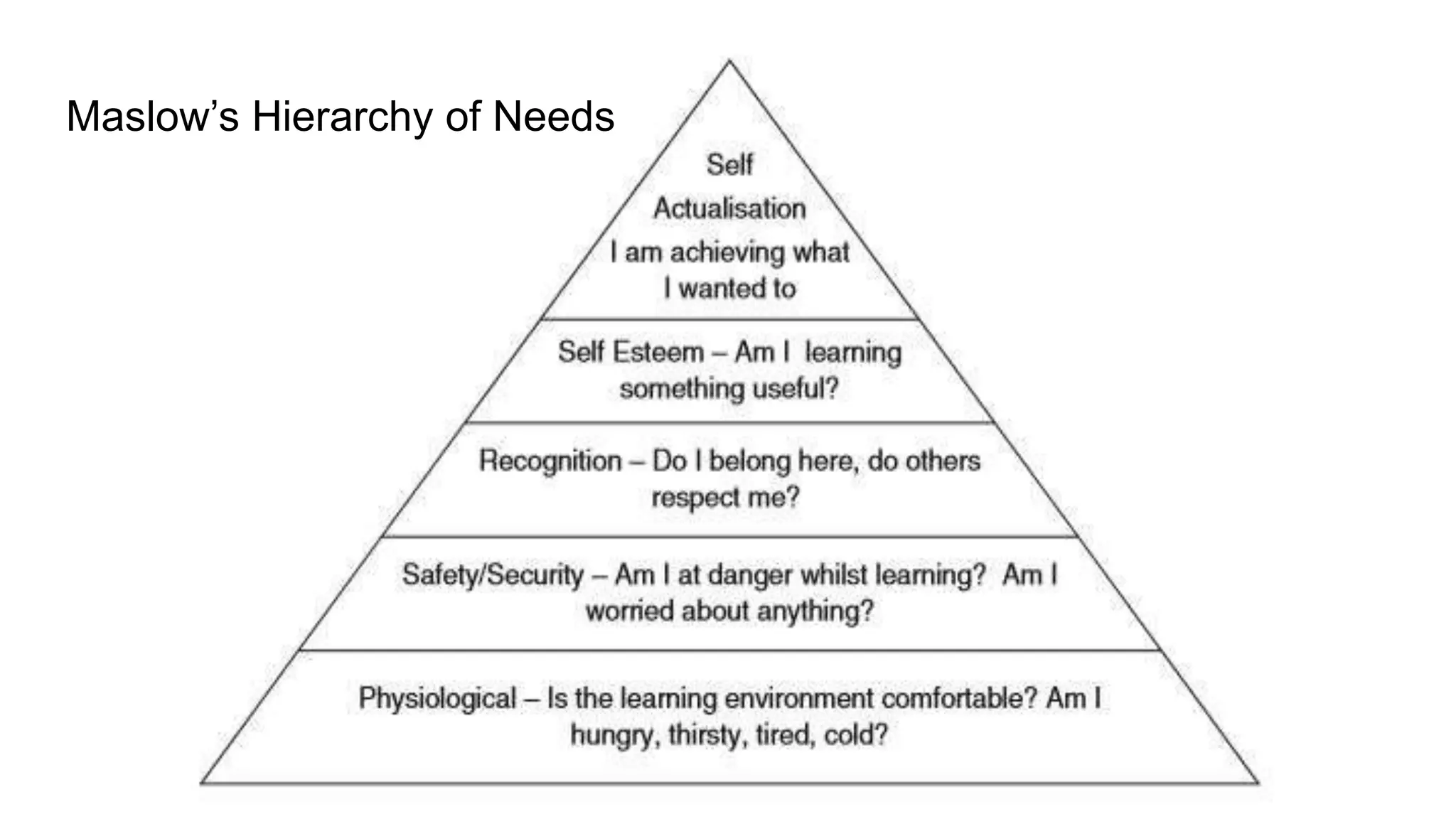
The document introduces reflective learning and its significance for effective training, emphasizing Maslow's hierarchy of needs and the importance of creating a safe, respectful, and inclusive learning environment. It discusses how reflection aids in personalizing learning experiences and the role of trainers in modeling appropriate behavior and setting boundaries. Key strategies for managing classroom dynamics and fostering a culture of respect are also outlined to enhance the learning experience.