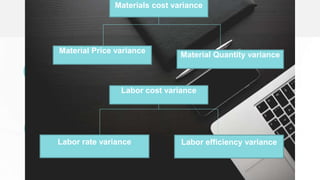
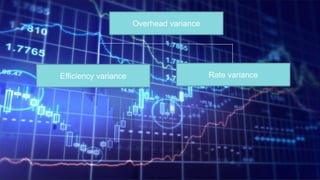
The document discusses standard costing and variance analysis. It provides objectives and explanations of key variances including: direct materials quantity and price variances, direct labor efficiency and rate variances, and variable manufacturing overhead efficiency and rate variances. Formulas are given for calculating each variance and interpreting whether it is favorable or unfavorable. An example calculation is also shown for several variances.