The document discusses recruitment processes and techniques. It defines recruitment as finding and attracting capable applicants for jobs in an organization. The recruitment process includes identifying vacancies, preparing job descriptions, advertising positions, managing responses, shortlisting, interviewing, and making hiring decisions. Sources of recruitment can be internal like current employees or external like job boards, agencies, and colleges. The recruitment function is influenced by internal factors controlled by the organization and external factors outside its control like economic conditions. The objective of recruitment is to attract qualified candidates and hire the best ones to meet organizational needs.

















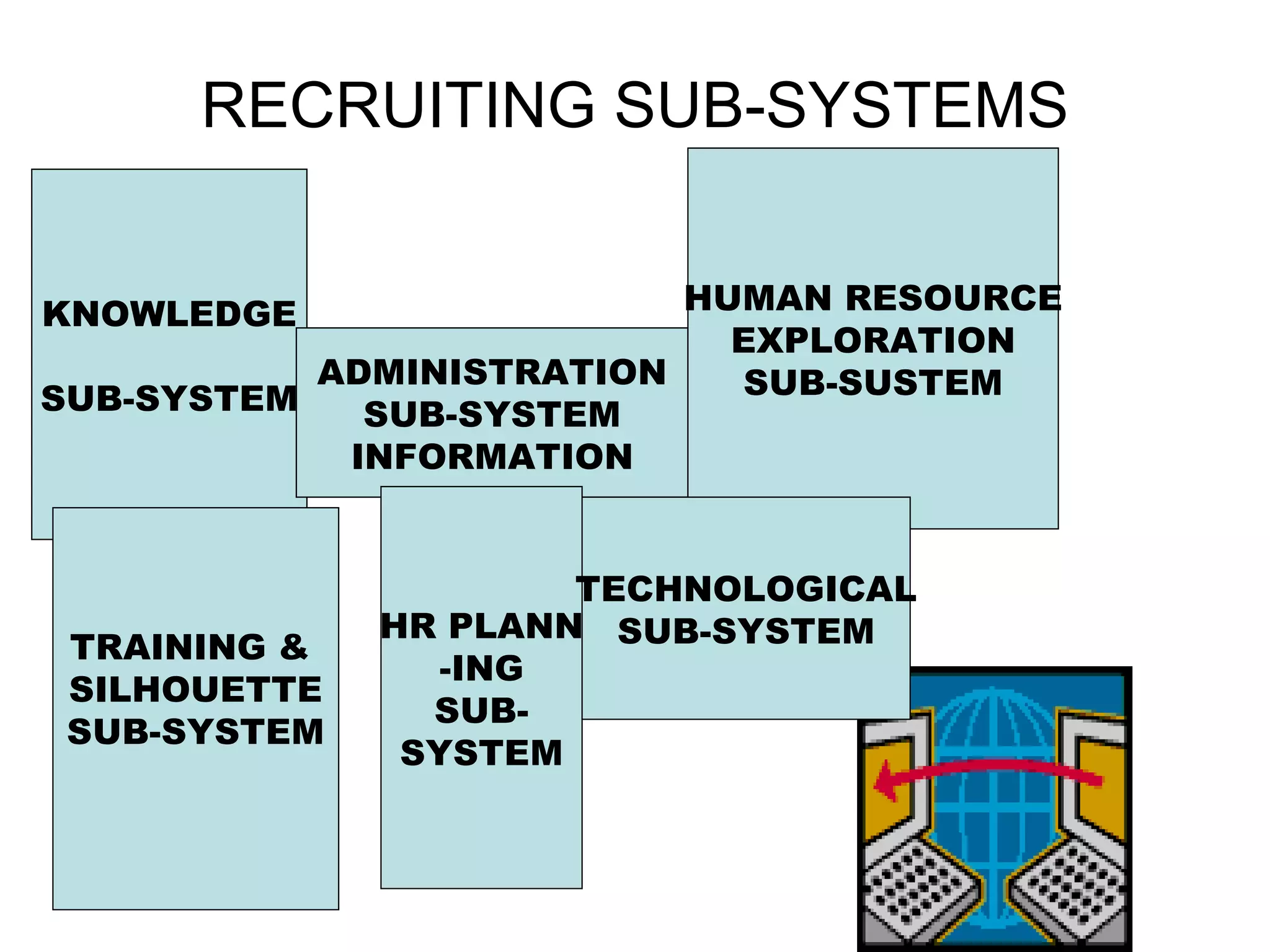

![KNOWLEDGE & ADM’N SUB-SYSTEM Knowledge Subsystem facilities reaching the right knowledge to the right person in right time. combination of culture, process and technology . Administration Subsystem internal/external advertisement module . applicant's profile, [curriculum vita/resume] appointment, types of appointment i.e. adhoc based, honorary, visiting/guest, temporary, apprentice etc.,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module3-recruitment-101222194622-phpapp02/75/Module-3-recruitment-20-2048.jpg)





