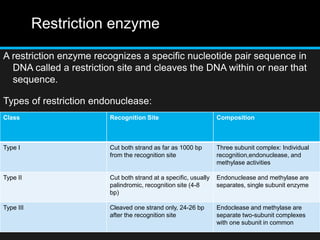
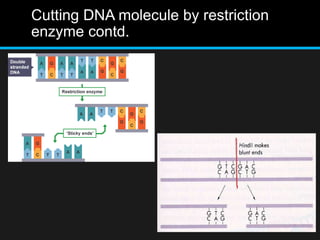
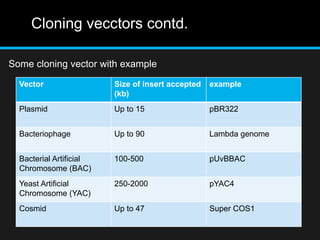
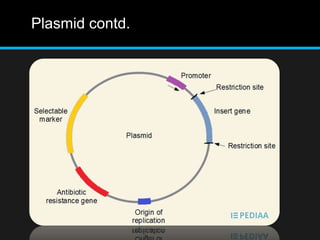
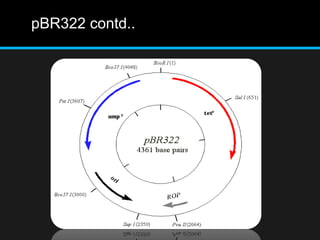
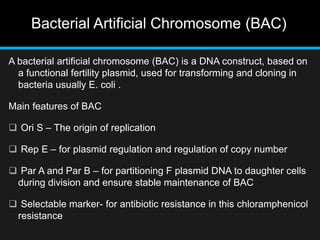
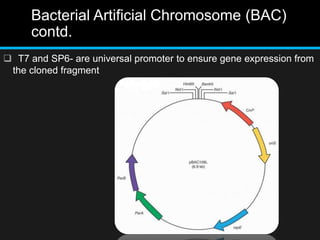
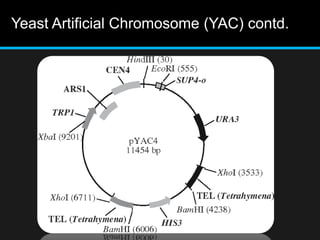
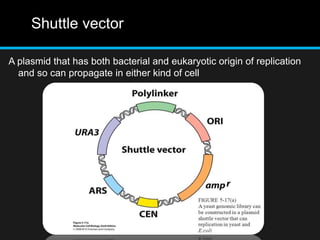
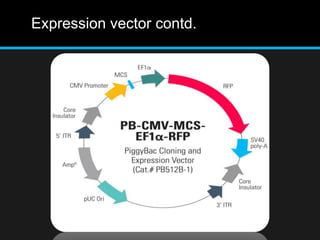
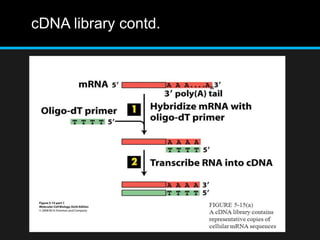
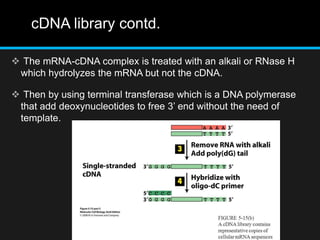
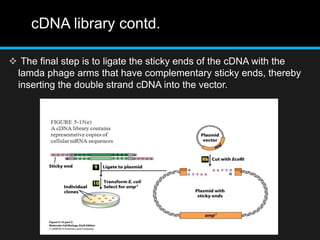
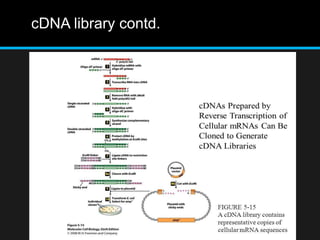
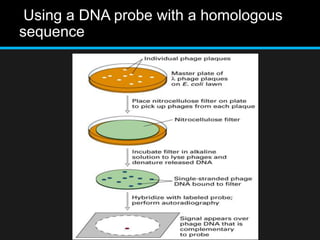
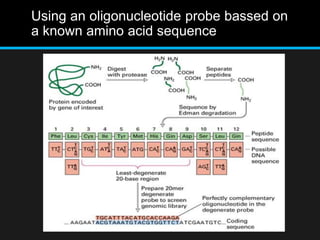
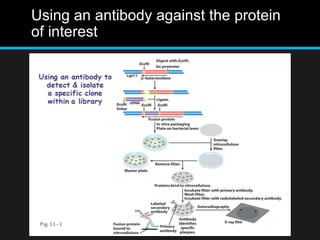
Recombinant DNA involves joining DNA segments from different sources using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase. The key steps are isolating and purifying DNA, cutting DNA with restriction enzymes to generate fragments, ligating fragments to a vector, introducing the recombinant DNA into host cells, replicating the DNA within the host, and isolating purified DNA fragments. Common vectors used include plasmids, bacteriophages, BACs, YACs, cosmids, and expression vectors. cDNA libraries allow screening for specific genes expressed in a cell type.